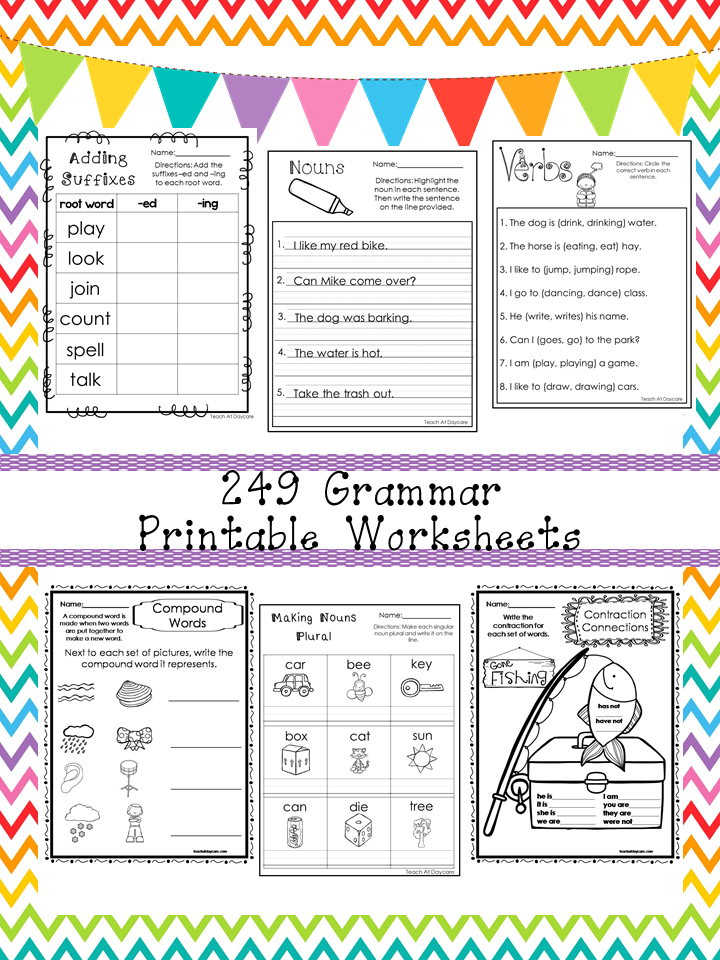
Contractions for 1st grade: How to Teach Contractions in First Grade
Posted onFirst Grade Language Arts Skills
Links verified on 10/27/2021
1. Contraction Action. Click Image to Enlarge
Join the fiesta in «Arcade» mode by tapping/clicking on the correct contraction spelling and using the slingshot to make the piñata burst open or play «Practice» mode to test your knowledge on contractions and hone your slingshot skills. SEE MORE
2. Contractions in Sentences. Click Image to Enlarge
Complete the sentence with the best contraction. SEE MORE
3. Contractions PowerPoint Game. Click Image to Enlarge
Give your students practice with forming and using contractions. This tool themed interactive PowerPoint game is designed to be a free literacy center for your classroom. (You can download this free PowerPoint Game by clicking on the bold, bright link at the bottom of the post.) SEE MORE
4. Contractions Song. Click Image to Enlarge
Videos and songs to help First Grade kids learn how to use contractions to shorten words. An apostrophe is used to take the place of the missing letters. SEE MORE
5. Contractions. Click Image to Enlarge
Type the contraction beside the two words.
 SEE MORE
6. Contractions. Click Image to Enlarge
Quia Quiz, Match contractions. 
 SEE MORE
7. Fly By Contraction Practice. Click Image to Enlarge
Find the correct airplane to match with the contraction. Click Go each time to get a new question.
 SEE MORE
8. Form Contractions With «Not». Click Image to Enlarge
Fill in the contraction that matches the words. SEE MORE
9. Form Pronoun-Verb Contractions. Click Image to Enlarge
Fill in the contraction that matches the words. SEE MORE
10. Match the Contractions. Click Image to Enlarge
Match the contractions to the words by dragging the contractions to the correct group of words. (Audio available) SEE MORE
11. Spelling City — Contractions. Click Image to Enlarge
Select your target contraction and then play the games!  SEE MORE
12. Treasure Trove. Click Image to Enlarge
Read the words on the treasure chest. Click on the key that shows the contraction for the two words on the chest. (10 questions)
 SEE MORE
Contractions with not — Miss. Papa’s Student Teaching Experience & Online Portfolio
TEACHER’S NAME:Alicia Papa GRADE:
First Grade
SUBJECT(S): Grammar LESSON
TOPIC: Contractions with not
TIME FRAME: 20 minutes (February 5th)
NJCCCS INDICATOR(S):
- CCSS.
ELA-Literacy.L.2.2.c
Use an apostrophe to form contractions and frequently occurring possessives.
ENDURING UNDERSTANDING: My students will be able to identify
and read contractions with not
ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S):
- What is a contraction?
- How many words make up a contraction?
- What does n’t stand for?
PERFORMANCE OUTCOME:
- Students will be able to orally explain what a
contraction is - Students will be able to orally explain how many words
are in a contraction - Students will be able to orally explain what n’t
stands for in a word
TEACHER RESOURCES:
- Treasures Teacher Edition Textbook
- smartboard
Bear, D. R., &
Macmillan/McGraw-Hill School Publishing Company. (2009).
reading /language arts program. New York: Macmillan McGraw-Hill.
LIST OF STUDENT MATERIALS:
- Band aids
- Name tags
- Surgical gloves (17)
- Masks (17)
- Contraction word cards
- Scissors (17)
- Contraction recording sheet
LEARNING EXPERIENCE
STEP-BY-STEP PROCEDURE: List in
sequence the steps of this lesson, from beginning to end. Lessons should be
divided into two parts: (1) describe how the content will be taught and (2) how
the students will practice applying the content.
The teaching of content includes 3 parts:
- Guided
Practice – For the guided practice students will be put into pairs.
Each pair will receive cut out words, gloves, masks, and band aids. I will
explain that they will be doing contraction surgery. They will have to cut the word
and nt out and use a band aid to connect the contraction together.I will explain that the band aid will be like
our apostrophe. Students will record contractions on the contraction recording
worksheet.
- Independent
Practice – For the independent practice students will complete the
workbook page GR75 in pairs.- We do not
have any students with special needs in our classroom at this time but for
students who are struggling with the concept will receive assistance.
- We do not
- Closure – For
closure to the activity I will go over workbook page GR75 on the smartboard.
Stages of childbirth. From the first contraction to the birth of the baby
Experienced women in labor joke: “Don’t worry, you won’t miss the birth and you won’t make a mistake!” But the young mother is still worried: what awaits her when the baby decides to be born?
First period: Labor
This is the longest period of labour. Usually at the birth of the first baby, it lasts from 7 to 12 hours.
How do you feel?
The birth process starts in different ways. Most women experience aching sensations in the lower abdomen, which gradually turn into distinct uterine contractions. The frequency and strength of these contractions is increasing. The very first contractions take place at intervals of 10-15 minutes for 15-30 seconds and they are weakly felt, immediately before birth they last 60-90 seconds with an interval of 1-3 minutes. The main sign of the onset of childbirth, in contrast to the preparatory contractions, is the intensification of sensations during the contraction. In some women, the birth process begins with the fact that amniotic fluid is poured out, and only then contractions begin.
What’s going on?
Preparing for childbirth, the cervix becomes softer. During contractions, it gradually opens up so that the baby can be born. The hormone oxytocin and prostaglandins, which are produced in response to the “Start the birth process” command, help her in this.
What is the baby doing?
Baby feels unusual discomfort. He is sensitive to the state of his mother and experiences similar feelings: if his mother is alarmed, he receives his dose of her stress hormones. If the mother is calm, then he is easier to endure childbirth.
How to behave?
The ideal birth takes place in a state of complete rest. In order for oxytocin to do its job, a woman needs to relax and turn off her head. That is why in traditional obstetrics it is customary to exclude bright light, loud sound, extraneous interference in the course of childbirth — everything that makes a woman experience stress and emerge from her cozy little world. nine0003
Usually, at the very beginning of labor, the mother wants to lie down and fall asleep — this is a normal reaction. In the future, she may want to move or take the most unexpected position: some want to stand on all fours, others hang on the back of a chair, on a horizontal bar, or with the support of a person who helps in childbirth.
How about various labor control techniques such as counting breaths? Purely individual. If you want to breathe according to the scheme, well, perhaps this is how it is easier for you to relax (by performing monotonous mental operations). But don’t force yourself. The same applies to massage, which is taught in courses for pregnant women. Point out to your assistant in childbirth the area on the sacrum, the massage of which brings relief, tell him with what strength and intensity you need a massage. If you don’t want to be touched, that’s fine too. nine0003
Who will help?
An experienced midwife can provide peace and security to a woman, who will act as a buffer between the mother and the outside world, as well as calm her, instilling a sense of confidence. There are also many natural painkillers: acupressure, aromatherapy, etc. At the same time, a warm bath is an ideal and favorite method for women.
Second period. Attempts
During contractions, a woman feels detached from reality, but not so much as to “fall out of this world” completely. The closer the birth, the more detached she becomes. The duration of the push is very individual.
How do you feel?
Before that, you were lying, standing, walking, etc., but here you want to bend your legs in a fight and at the same time grab onto someone or something. A woman may want to squat down, she has a feeling that the chair is moving away. Many begin to make a rather loud, deep sound, similar to throat singing. A woman, seemingly weakened by long contractions, has a surge of strength. nine0003
What’s going on?
The cervix has opened and the baby begins to move through the birth canal. At this stage, the bones of the mother’s pelvis and the baby’s head adjust to each other.
What is the baby doing?
The baby is not easy. Its head «squeezes» through a rather narrow passage. The skull of the baby is not hard, so it can change its shape for easier passage through the birth canal.
How to behave?
Listen to your body. Any painful sensation is a signal that the baby will be comfortable if you, obeying the command of the body, change position. It happens that contractions during this period fade for a while — this is not scary, so your body is preparing for the final chord.
Michel Auden writes in her book «Birth Reborn»: «Many women give birth in a mechanically effective supported squatting position, as it maximizes the baby’s downward pressure along the birth canal, minimizing the necessary muscle tension and oxygen consumption, provides maximum relaxation of the muscles of the perineum … A woman can choose another position: facing him, spreading her legs wide. This position, in which the woman’s legs are off the ground from time to time, is also very useful.
Who will help?
Childbirth assistant in this period supports the woman not only morally, but also physically. Even if a woman gives birth in an ordinary maternity hospital on a chair, she has a desire to try to lift the body, as if to fold in half. An assistant can support her under her back. Forcibly, on command, it is necessary to push the child out only if it is necessary to speed up the birth and the child needs help. The task of the midwife is not to demand “push!” like in a comedy series, but to give a woman an attitude like «let your child go out.» nine0003
Third period: Birth
The baby is born — this is the most joyful period of childbirth.
How do you feel?
You have absolutely no control over the process. The expulsion of the fetus is a powerful reflex that is triggered as soon as the baby is ready.
What’s going on?
A powerful surge of adrenaline makes the uterus literally push the baby out.
What is the baby doing?
He feels fear and discomfort. He expects the new world to meet him with love and tenderness. nine0003
How to behave?
Everything happens by itself. The main thing is not to start forcibly actively pushing the baby ahead of time. Let his head be ready to “emerge” and come out gradually. When the baby arrives, you will be overcome by a strong feeling of love. Let them put a baby on your stomach: admire it, hug it. This is how the strongest feeling of affection between mother and baby is formed.
Who will help?
The midwife will take the baby into her good hands. Agree in advance that you and the baby will not be separated if there are no fears for the health of the crumbs. Agree that the umbilical cord should not be cut immediately after the baby appears, but when it stops pulsing.
The midwife will also remove the placenta — it will come off at the next special contraction. This is just a general description of how natural childbirth works. Yours may be a little different. Listen to your body and it will tell you the ideal plan for your birth.
Class XV. Pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period (O00-O99)
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 6
2012 No. 581n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care at
spontaneous labor in breech presentation»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 6, 2013 No. 27524)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: planned, urgent, emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 5
ICD code X
Nosological units
O80.
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 6,
2012 No. 582n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care at
uterine rupture»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 22, 2013, No. 27848)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: emergency, emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 10
ICD code X
Nosological units
O71.0 Uterine rupture prior to labor
O71.1 Uterine rupture during labor
O71.9 Obstetric injury, unspecified
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 6,
2012 No.
delivery by caesarean section»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 5, 2013, No. 27475)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: planned, emergency, emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 6
ICD code X
Nosological units
O82.1 Urgent caesarean section
O82.2 Perform caesarean section with hysterectomy
O82.8 Other singleton births by caesarean section
O82.9 Delivery by caesarean section, unspecified
O84.2 Multiple births, wholly by caesarean section
O84.8 Other delivery in multiple births
O84.9Multiple births, unspecified
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 6,
2012 No.
spontaneous labor in occiput presentation»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 5, 2013, No. 27471)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complications: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: planned, urgent, emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 4
ICD code X
Nosological units
O80.0 Spontaneous delivery in occipital presentation
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7,
2012 No. 588n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care at
fetal hypoxia, insufficient fetal growth, other placental
violations»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on January 31, 2013, No.
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: emergency, urgent, planned
Average treatment time (number of days): 10
ICD code X
Nosological units
O36.3 Signs of intrauterine fetal hypoxia requiring medical attention
mother’s help
O36.4 Fetal death requiring medical attention
mothers
O36.5 Inadequate fetal growth requiring maternal medical attention
O36.6 Fetal overgrowth requiring maternal medical attention
O36.8 Other specified fetal abnormalities requiring
maternal care
O36.9 Fetal abnormalities requiring medical attention
mothers, unspecified
O43.0 Placental transfusion syndromes
O43.1 Anomaly of placenta
O43.8 Other placental disorders
O43.9Placental disorder, unspecified
O68.
O68.1 Labor complicated by the passage of meconium into the amniotic fluid
O68.2 Labor complicated by changes in fetal heart rate with
output
meconium into amniotic fluid
O68.3 Labor complicated by biochemical signs of fetal stress
O68.8 Labor complicated by other signs of fetal stress
O68.9 Labor complicated by fetal stress, unspecified
P02 Fetus and newborn affected by complications
placenta, umbilical cord and membranes
P05 Fetal growth retardation and malnutrition
P20.0 Intrauterine hypoxia, first noted before the onset of labor
P20.9 Intrauterine hypoxia, unspecified
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7,
2012 No. 589n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care at
ectopic pregnancy»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 15, 2013, No.
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: no complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical assistance: emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 7
ICD code X
Nosological units
O00.1 Tubal pregnancy
O00.2 Ovarian pregnancy
O00.8 Other forms of ectopic pregnancy
O00.9 Ectopic pregnancy, unspecified
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7,
2012 No. 590n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care at
spontaneous termination of pregnancy»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on May 15, 2013, No. 28409)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: no complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical assistance: emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 3
ICD code X
Nosological units
O03 Spontaneous abortion
O03.
O03.9 Complete or unspecified abortion without complications
O05 Other types of abortion
O05.4 Uncomplicated incomplete abortion
O05.9 Complete or unspecified abortion without complications
O06 Abortion, unspecified
O06.4 Uncomplicated incomplete abortion
O06.9 Complete or unspecified abortion without complications
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7,
2012 No. 591n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care at
violations of labor activity»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on February 20, 2013, No. 27217)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical assistance: emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 6
ICD code X
Nosological units
O47.
O47.1 False contractions from 37 completed weeks of pregnancy
O47.9 False contractions, unspecified
O61.0 Unsuccessful attempt to induce labor with medication
O61.1 Unsuccessful attempt to induce labor by instrumental methods
O61.8 Other failed induction attempts
O61.9 Unsuccessful attempt to induce labor, unspecified
O62.0 Primary weakness of labor activity
O62.1 Secondary weakness of labor
O62.2 Other weaknesses in labor
O62.3 Rapid labor
O62.4 Hypertonic, uncoordinated and prolonged uterine contractions
O62.8 Other disorders of labor
O62.9 Violation of labor activity, unspecified
O63.0 Protracted first stage of labor
O63.1 Prolonged second stage of labor
O63.2 Delayed second birth of twins, triplets, etc. nine0119
O63.9 Prolonged labor, unspecified
O75.5 Delayed labor after artificial rupture of membranes
O75.
shells
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 7, 2012 No. 597n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care for bleeding due to placenta previa requiring medical care for the mother»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 25, 2013 No. 27857)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complications: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: emergency, emergency
Average treatment time (number of days): 10
ICD code X*(1)
Nosological units
O44.1 Placenta previa with haemorrhage
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2012 No.
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on May 22, 2013 No. 28461)
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: emergency, urgent
Average treatment time (number of days): 14
ICD code X*(1)
Nosological units
O21.1 Excessive or severe vomiting of pregnant women with metabolic disorders
O21.2 Late pregnancy vomiting
O21.8 Other forms of vomiting complicating pregnancy
O21.9 Vomiting of pregnancy, unspecified
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2012 No. 596n «On approval of the standard for specialized medical care for edema, proteinuria and hypertensive disorders during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period»
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on February 26, 2013 No.
Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: planned, emergency, urgent
Average treatment time (number of days): 21
ICD code X*(1)
Nosological units
O11 Pre-existing hypertension with associated proteinuria
O12.1 Pregnancy-induced proteinuria
O12.2 Pregnancy-induced edema with proteinuria
O13 Pregnancy-induced hypertension without significant proteinuria
O14.0 Moderate pre-eclampsia [nephropathy]
O14.1 Severe preeclampsia
O14.9 Pre-eclampsia [nephropathy], unspecified
O15.0 Eclampsia during pregnancy
O15.1 Eclampsia in childbirth
O15.2 Eclampsia in the puerperium
O15.9 Eclampsia, unspecified
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2012 No.
(Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 5, 2013 No. 27501)
nine0002 Age category: adults and minors
Gender: female
Phase: any
Stage: any
Complication: regardless of complications
Type of medical care: specialized medical care
Condition of rendering: stationary
Form of medical care: emergency, urgent
Average treatment time (number of days): 10
ICD code X*(1)
Nosological units
O72.0 Bleeding in the third stage of labor
O72.1 Other bleeding in the early postpartum period
O72.2 Late or secondary postpartum haemorrhage
O72.3 Postpartum coagulation defect, afibrinogenemia, fibrinolysis
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2012 No.


 (Audio available) SEE MORE
(Audio available) SEE MORE ELA-Literacy.L.2.2.c
ELA-Literacy.L.2.2.c I will explain that the band aid will be like
I will explain that the band aid will be like