Examples of a prepositional phrase: 600+ Easy Examples of Prepositional Phrases in English • 7ESL
Posted on60+ Top Examples Of Prepositional Phrases
Are you confused by prepositions? Study these examples of prepositional phrases to get them down pat.
A prepositional phrase is a helpful tool in the English language. It connects nouns to other parts of the sentence, giving information that adds clarity to the sentence.
For some English learners, prepositional phrases get confusing because they look like they may contain a subject. Understanding how these groups of words work in the sentence and studying examples of prepositional phrases will help you use them more effectively and identify them when studying English grammar.
Contents
- Examples of Prepositional Phrases: How to Spot Them
- Types of Prepositional Phrases
- More Examples of Prepositional Phrases
- Special Case: Gerunds as Objects
- A Final Word on Examples of Prepositional Phrases
- FAQs About Examples of Prepositional Phrases
- Author
Examples of Prepositional Phrases: How to Spot Them
To become skilled at using prepositions and their phrases, you must be able to spot them. This starts with knowing some common prepositions. This list of prepositions shows some of the common ones in English.
- According
- Across
- After
- Amid
- Around
- Before
- Between
- By
- Like
- Near
- Of
- Off
- Out
- Through
- Throughout
- To
Many of these prepositions show direction or position, such as near or through.
Prepositional phrases combine these prepositions with an object of the preposition, which is a noun or pronoun. They also include the adjectives that serve as modifiers of the object, which are the adjectives that describe those nouns and pronouns. Here is an example of a prepositional phrase:
- We went to the store.
“To” is the proposition and “store” is the object, while “the” is a modifier.
Types of Prepositional Phrases
Prepositional phrases can show different parts of speech in the sentence. Much like transition words for essays, knowing how prepositional phrases function is key to identifying them.
Adjective Phrases
Many prepositional phrases serve as adjectives in the sentence. These adjectival phrases modify nouns and pronouns. Here are a couple of examples:
- The book with the dog-eared pages was well-loved.
- The largest present under the tree is yours
In the first sentence, the prepositional phrase is “with the dog-eared pages,” and it describes the noun “book.” In the second sentence, the phrase “under the tree” modifies “present.”
The following examples show more prepositional phrases that modify a noun or pronoun:
- The boy with my sister is her new boyfriend. (“With my sister” modifies “boy”)
- All of the passengers on the plane gasped when it hit turbulence. (“On the plane” modifies “passengers” and “of the passengers” describes “all”)
- The car on the shoulder had a flat tire. (“On the shoulder” modifies “car”)
- The red jacket on the hook is mine. (“On the hook modifies “jacket”)
- Tell me the story about the princess.
(“About the princess” modifies “story.”)
- The rooms on the second floor are luxury suites. (“On the second floor” describes “rooms.”)
Adverb Phrases
Some sentences have more than one prepositional phrase that describes the same verb
Some prepositional phrases will serve as adverbs in the sentence. They modify verbs, adjectives and other adverbs. They answer the questions where, when, how, why or to what extent.
Here is an example:
- The boy ran toward the finish line.
In this sentence, “toward the finish line” modifies the verb “ran,” showing which direction (where) the boy ran.
Here are some more example sentences:
- I will climb up the stairs each night. (“Up the stairs” modifies the verb “climb”)
- We won against the reigning champions. (“Against the reigning champions” modifies the verb “won.”)
- I love to take my Jeep off the beaten path. (“Off the beaten path” modifies the verb “take.”)
- I don’t like to get up early in the morning.
(“In the morning” modifies the adverb “early.”)
- You look tired from all the hard work. (“From all the hard work” modifies the adjective “tired.”)
Some sentences have more than one prepositional phrase that describes the same verb. For example:
- We always go to Disney World on vacation. (Both “to Disney World” and “on vacation” describe the verb “go.”)
- She sat on the bench near her friend. (Both “on the bench” and “near her friend” modify the verb “sat,” telling where she sat.)
More Examples of Prepositional Phrases
Here are more examples of prepositional phrases using common prepositions. They include both adjective and adverb phrases.
- Aboard: Climb aboard the ship before we set sail.
- About: She was crazy about her new boyfriend.
- Above: Above ground, the groundhog blinked at the bright sun.
- Across: The neighbor across the street waved.
- After: After the wedding, the couple left for their honeymoon.
- Against: The team played against their biggest rivals.
- Along: Give him the gift card along with the greeting card.
- Amid: Even amid turmoil, you can find joy.
- Among: Among his friends, Charles felt very comfortable.
- Around: The busy squirrels were scattering walnuts around the yard.
- At: Please give him the raise at the appropriate time.
- Before: The dog must be fed before you leave.
- Behind: The ball fell behind the bleachers.
- Below: The dog dug below the mulch.
- Beneath: She was the wind beneath his wings.
- Beside: She laid the book beside her bed.
- Between: The teacher placed the quiet child between the two talkers.
- Beyond: The boy threw the ball beyond the boundary.
- But: Everyone but Samantha ate the spicy dip.
- By: The car by the railroad tracks was red.
- Concerning: The memo concerning PTO went out yesterday.
- Considering: The old man had a good pace in the marathon considering his age.
- Despite: Despite the cold, we enjoyed the festival.
- Down: She paddled down the river.
- During: During halftime, go get more popcorn.
- Except: The boys, except Caleb, went to the game.
- Following: The students answered the questions following the chapter.
- For: The book is for the teacher.
- From: The book is from her class.
- In: My foot was stuck in the mud.
- Inside: The signature is inside the book’s cover.
- Into: Do not run into the street.
- Like: I look like a burnt lobster.
- Minus: The girls, minus Rosanne, went shopping.
- Near: They moved to be near their grandparents.
- Of: All of them went to the mall.
- Off: The locomotive blew off steam before chugging out of the station.
- On: Set the keys on the bookshelf.
- Onto: They drove onto the dirt road.
- Opposite: She lived in the house opposite the convenience store.
- Out: Call out the ice cream flavor you want.
- Outside: It is raining outside of town.
- Over: Nathaniel lives over the next hill.
- Past: Drive past the red house and ours is the yellow one.
- Plus: The vacation included a week at the beach plus a few days in the city.
- Regarding: The email regarding the week’s work is coming Monday.
- Since: It has been a while since then.
- Through: The team ran through the arches and onto the field.
- Throughout: Throughout your life, you will meet many people.
- To: You can give the permission slip to the office.
- Toward: The dog ran toward its owner.
- Under: The ball fell under the dresser.
- Unlike: She, unlike Tracy, loves chocolate.
- Until: Don’t wait until tomorrow to do what you can today.
- Up: Look up because the clouds are beautiful.
- Upon: Once upon a time, the prince and princess fell in love.
- Versus: Traveling by air versus by car is faster.
- With: I will be with you in a moment.
- Within: Look within yourself to find the courage to finish the job.
- Without: Humans cannot survive without water for more than a few days.
Special Case: Gerunds as Objects
Propositional phrases do not have verbs, but sometimes they appear to do because of gerunds. A gerund is a verb that ends in -ing but functions as a noun in the sentence. Here is an example of a prepositional phrase with a gerund as the object:
- Before going to the store, please make a shopping list.
In this sentence, “going” is the object of the preposition “before” and functions as a noun. Here is another example:
- After installing the lights, he was excited to turn them on.
A Final Word on Examples of Prepositional Phrases
Prepositional phrases add meaning to sentences, and studying examples of them makes spotting them easier. Keep in mind that a prepositional phrase cannot have a subject or a verb. Rather, it has an object and the object’s modifiers.
The easiest way to spot prepositional phrases is to memorize or familiarize yourself with the prepositions.
FAQs About Examples of Prepositional Phrases
What are prepositional phrases?
Prepositional phrases have a preposition followed by an object and its modifiers. They function as adjectives or adverbs in the sentence.
What are some examples of prepositional phrases?
Here are some examples of prepositional phrases:
1. In the closet
2. Under the bed
3. Through the woods
4. Outside the house
5. Of mice and men
Join over 15,000 writers today
Get a FREE book of writing prompts and learn how to make more money from your writing.
Powered by ConvertKit
Author
Preposition & Prepositional Phrases — Examples
Preposition – What Is a Prepositional Phrase?
A preposition draws a relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in a sentence.
Common prepositional phrase examples include about, after, at, before, behind, by, during, for, from, in, of, over, past, to, under, up, and with.
Prepositional Phrase Examples Functioning as Adjective Phrases:
(With is the preposition, and with him is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adjective phrase, modifying boy.)
The bracelet in the storefront window is the one I want.
(In is the preposition, and in the storefront window is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adjective phrase, modifying bracelet.
We stayed at the cabin by the river.
(By is the preposition, and by the river is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adjective phrase, modifying cabin.)
The store at the corner sells sandwiches.
(At is the preposition, and at the corner is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adjective phrase, modifying store.)
(Behind is the preposition, and behind you is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adjective phrase, modifying broom.)
I adopted a black cat with white paws.
(With is the preposition, and with white paws is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adjective phrase, modifying cat.)
Prepositional Phrase Examples Functioning as Adverb Phrases:
When you get to the sign, take a left.
(To is the preposition, and to the sign is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adverb phrase, modifying get.)
We climbed up the hill to see the view.
(Up is the preposition, and up the hill is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adverb phrase, modifying climbed.)
It annoys me when people talk during movies.
(During is the preposition, and during movies is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adverb phrase, modifying talk.)
Hannah looked under the bed to see if she could find her necklace.
(Under is the preposition, and under the bed is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adverb phrase, modifying looked.)
I’ll meet you after school.
(After is the preposition, and after school is the prepositional phrase.
The sun rose over the mountain.
(Over is the preposition, and over the mountain is the prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase functions as an adverb phrase, modifying rose.)
Why are Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases Important?
Prepositions and prepositional phrases provide important details about the words they modify. This includes answering the following questions: Which one? What kind? How? Where? When? To what extent?
Learn more about prepositions and how to correctly use them in your writing with help from K12Reader!
Related Topics:
Prepositional Phrase Worksheets
Verbals
Infinitive Phrase
Participle Phrase
Gerund Phrase
Appositive Phrase
Adjective Phrase
Adverb Phrase
Verb Phrase
All Grammar Terms
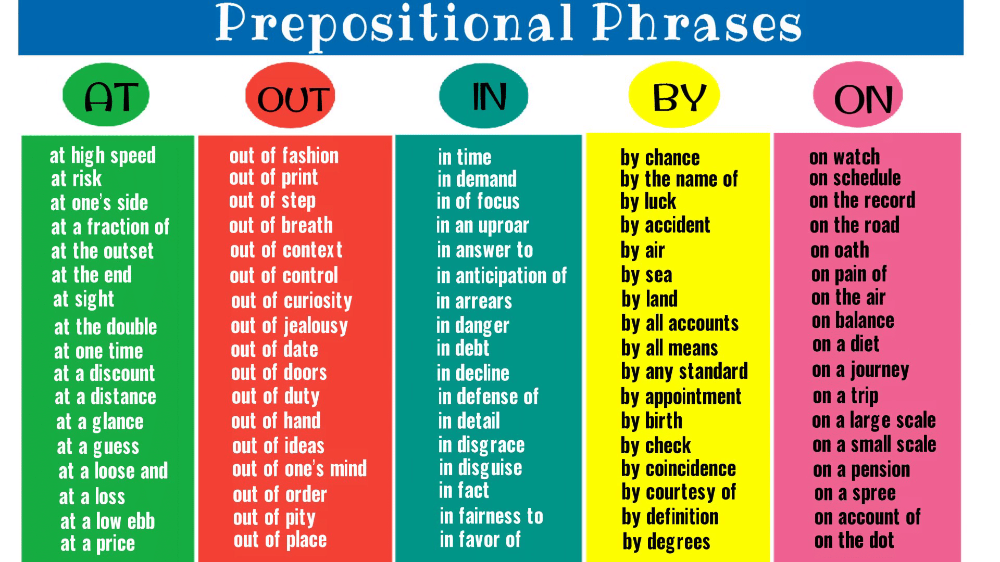
90,000 prepositional phrases in English (Prepositional Phrases)
Stable English phrases: prepositional phrases
AT
AT AT AT A DISCOUNT
AT A GLANCE
9000 at AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT AT ATA at a loss/profit
at a moment’s notice
at all costs
at all events
at an advantage
at any rate
at breakfast/lunch
2 at church/school
at ease
at first hand
at first sight
at hand (=closely)
at heart (=basically)
at home length
at liberty
at night (note: in the night)
at noon
at odds with
at one’s request (= because sb wishes it)
at peace/war
at present 9002 random
at risk
at sea
at speed
at age of
at the beginning (= when sth started)
at the end (=when sth finishes)
at the expense of
at the last possible time
at the moment
at the point of (= at that particular time)
at the present time
at the same time
at the time (= at a particular time)
at times (= sometimes )
at work
By
by accident
by all accounts
by all means
by birth
by bus/train/plane/car (but note: IN my own car, ON the 8 o’clock train)
by law
by luck (=luckily)
by marriage
by means of
by mistake
by name (= using a name)
by nature sb’s wish)
by sight (know sb by sight only, not as a friend)
by surprise
by the end (= before sth finishes)
by the time (= before reaching a certain point)
by the way (= incidentally) 9
for a moment (= for a short time)
for a visit/holiday
for a walk
for a while
for ages (
2 for ages) nothing for breakfast/lunch/dinner
for certain
for ever
for fears of (= in case sth happens)
for good (=forever)
for granted
for hire
for life
for once (= on one occasion)
for sale (= to be sold)
for sb’s sake
for short
for the moment (=for now.
from now on
from time to time
In
in a (good/bad) mood
in a hurry
in a mess
in a way 90 to some extent addition
in advance (of)
in AGONY
In All
In ANY CASE (= Anyway)
In Arrears
In Bed
In Blossom
in Cash
in Charge 9000 ( conclusion
in danger
in debt
in difficulty
in disguise
in disorder
in doubt
in fact
in favor of (= supporting)
003
in fear of (= afraid of)
in front of (= further forward than)
in the future
in name only (= not really)
in no time(= very quickly)
in one’s free time possession of (= owning)
in principle (= theoretically)
in prison/jail
in private/public in stock
in summer/winter
in tears
in the air
in the beginning (= originally)
in the case of (= in the event)
in the dark
in the end (= finally)
9
in the morning
in the mountains
in the name of (= on sb’s behalf)
in the news
in the right/wrong
in time (= early enough)
in time of (= during a particular time)
in touch
in tune with
in turn uniform
in use
in vain
in view of (=because of, taking into account)
On
on a diet
ON ISLAND
On Approval
ON AVERAGE
On Bail
ON BALANCE
OF
ON Credit
OND DUMAND 9000 OND DUTY
OND DUTI0003
on foot
on good/bad terms with
on holiday
on impulse
on leave
on loan
on no account (= under no circumstances)
on one’s mind
on one’s own
on order
on paper
on principle (= according to a particular belief)
on purpose
on sale (= reduced in price) nine0003
on strike
on the agenda
on the air
on the contrary
on the one/other hand
on the outskirts
on the phone
on the point of (=00002 on the point of (=00002) to2 to3) on the radio/TV
on the way
on the whole
on time (= at the correct time)
Out of
out of breath
out of control (= uncontrolled)
2 out if
3 danger
out of date
out of debt
out of doors
out of fashion
out of hand
out of luck
out of order
out of pity
out of place
out of practice
out of reach
out of season
out if sight (= beyond one’s range of vision)
out of stock
out of the question
out of town
out of use
out of work
Off
6
off colour
off duty
off school/work
off the record
off the road
Under
under age
under arrest
under control (= controlled)
under discussion
under one’s breath
under pressure
under repair
under the impression
under the weather0003
with difficulty
with luck (= hopefully)
with reference to
with regard to
with the compliments of
with the exception of
without delay
without fail
without success
without warning
Round
round the corner
To
to one’s astonishment0003
What are prepositions | Current literature
Prepositions help us organize our thoughts in a text in a coherent way.
But this is far from a tiresome article on the subject,
Also, An example of a prepositional phrase: “My sister likes chocolate”; the structure introduced by the preposition [my sister] is the prepositional phrase , in which case it actually contains the noun phrase [my sister]. Another example: «The killer was arrested by the police» [prepositional phrase: police].
However, prepositions in Spanish very often form sentences . Examples: «The girl I told you about the other day works at the municipal swimming pool» [prepositional phrases: the one I told you about / at the municipal swimming pool] / «Life in the city is better than I remembered» [phrase prepositional: o what he remembered.
Characteristics
Prepositions in Spanish: before, before, under, fits, with, against, from, during, between, to, before, through, for, according to, without, so, on, after, against and through .
Some of them are worn out . We can find them in some classical works or in legal texts. Here means «near» (farmhouse Cabe river) and so «bass». We will rarely use «fits» or hear it from someone else, but «so» is still common in legal or procedural language and therefore in the media: «Two women cannot return to their country. nine0005 so a death sentence.» For its part, «against» is an anglicism that should only be used at certain times (sports or games): «In today’s game they meet Real Madrid. compared to Atlético Madrid «.
Prepositions have the invariable form (they never change), so they have no gender or number and its function is relations between words, phrases and sentences, as we have already seen.
We usually use prepositions to express movement, place and time. . This is the most common: I went to Florence this vacation (traffic), I live in Madrid (place), The concert starts at nine (time).
We can also find prepositional adverbs . The adverb is a modifier of the verb, and prepositions can also often complete the verb. This is why we can find prepositional adverbs, especially for locating something. These are the most common hybrid prepositional adverbs: top/top, bottom/bottom, front/front, back/rear, inside/inside, outside/outside, opposite .
also There are also constructions that include prepositions, which are called prepositional phrases. , but also text links: due to, in order to, in spite of, with a goal, about, next to, around, before, in relation to, before, before, after, as for, in order to, in the middle, instead of, because of, regarding…
Usage and examples
A
Applications: way (I write a car because I like it) traffic (I travel a lot a Toledo because I work there), parts of the day (Come to check the boiler a noon ), direct person object (I understand a neighbor every morning), Edad (I married a 25 years old), exact time/time (Class a eight), place expression/ distance/day/temperature/frequency (Bathroom al background / have a 200 km / We a tuesday / We a 20s / I train twice a a week), an indirect compliment A ( my family loves Sea) Time (works from 9 a 8) Space (From Madrid a Alicante almost 500 km).
Bet
Applications: facing (Children bet director / Mary crashes rate problems)
Low
Applications: seat (Bicycle have low tree).
In person
Applications: instrument (I make all calls con my cell phone), company (Live con my boyfriend).
Against
Applications: opposition / shock (It is not correct that Mariana entered against his brother).
De
Applications: possession (This book de Manuel), material (Table de wood), Time (Library open de 9 to 8), origin de / 9005 origin home every morning / Hans de Germany), name supplement (bag de fruit / book de math), part (Do you want some de cake?), call (He died de cancer), space ( De From Madrid to Alicante almost 500 km / I’m going to turn off the TV de this room), part of the day in relation to the hour (It’s 5 de noon).
from
Applications: place ( from I can’t see the pharmacy from the balcony), time (I can’t see my brothers from Christmas), start of temporary action (Worked from from March to October).
During
Applications: temporary extension (Dolores did not smoke anything during pregnancy).
EN
Applications: place (we rested EN Mallorca / bed EN bedroom / Letters EN Table / socks Ennoye machine), Time (we will fly EN in June in Malaga / I’m doing my homework en 30 minutes). nine0003
Between
Applications: temporary relationships ( Between September and November the trees are beautiful) personal ( Between Rosa and Julian will drive me crazy) objects 9006 and 005 undecided ).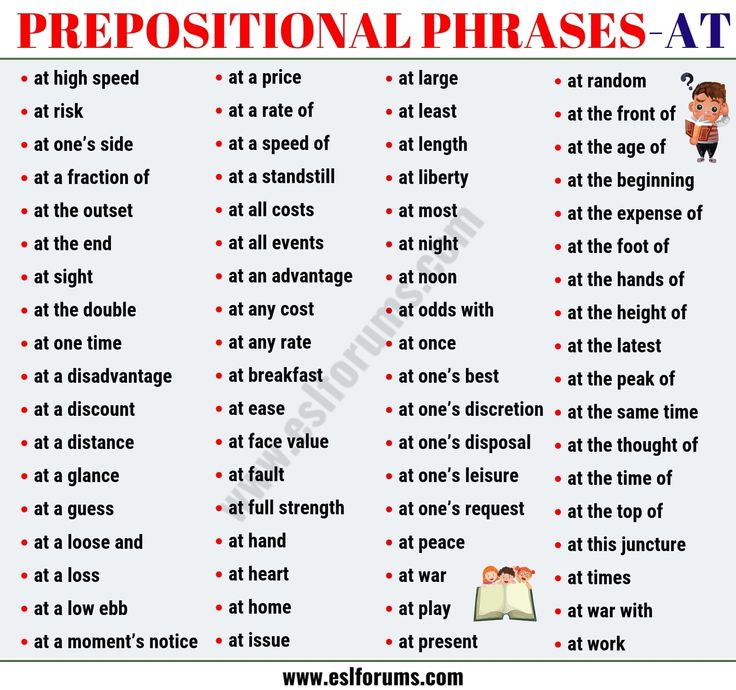
to
Applications: address (We must go to Salamanca), Approximate time (I was with March to six hours).
Hasta
Applications: action end point temporary or not / place (working from March to October / will work to six hours / we ate to get bored / I will walk to park and I will go home ).
Via
Applications: through / con (I made documents through electronic certificate).
to
Applications: finalidad (I train for get in shape), recipient (This dress is for Sarah), time lapse (I need to finish this for morning), address (I will go for Girona at the weekend), opinion ( For me that they won’t come to the wedding).
to
Applications: call (I study German to worked), part of the day ( to worked in the afternoon), time / approximate location (I will go to Madrid to November / I like to walk to beach), through (He left to main door) frequency (I give guitar lessons three times to a week), mid-month (I sail to Internet), change (he changed car to motorcycle), agreement / disagree ( to 900).00.0 nine0003
To
Applications: way (I’m going to do it Shogun tell me).
Sin
Applications: without (usually in the form of pipes without Salt).
About us
Applications: place (Camera is at bed), approach (we stayed at nine hours), link / about cinema).

 (“About the princess” modifies “story.”)
(“About the princess” modifies “story.”) (“In the morning” modifies the adverb “early.”)
(“In the morning” modifies the adverb “early.”)