Examples of a homonym: Learn About Homonyms, With Examples
Posted onWhat Is a Homonym? | Wonderopolis
LANGUAGE ARTS — Languages
Have You Ever Wondered…
- What is a homonym?
- What’s the difference between a homograph and a homophone?
- What is a capitonym?
Tags:
See All Tags
- capitonym,
- grammar,
- heterograph,
- heteronym,
- homograph,
- homonym,
- homophone,
- language,
- language arts,
- meaning,
- spelling,
- technology,
- words,
- writing,
- Capitonym,
- Grammar,
- Heterograph,
- Heteronym,
- Homograph,
- Homonym,
- Homophone,
- Language,
- Language Arts,
- Meaning,
- Spelling,
- Technology,
- Words,
- Writing
Today’s Wonder of the Day was inspired by Amber. Amber Wonders, “What is a homophone?” Thanks for WONDERing with us, Amber!
Did you hear about the man who left town by turning left at the stop light? He realized he forgot to use his arm to arm his house alarm. So he turned right at the light, because it was the right thing to do.
Words can be funny, can’t they? Did you notice that several words in the sentences above are spelled the same and pronounced the same, yet they have different meanings? We call those words homonyms. The word “homonym» comes from a Greek word that means “having the same name.»
When you begin to think about words, you’ll realize that there are a lot of words that are spelled the same, but have different meanings. There are also a lot of words that are pronounced the same, but have different spellings.
There are special terms for all of these types of words, and we’ll explain more about them here. It may seem confusing at first, but the important thing to remember is that just because two or more words sound the same or are spelled the same doesn’t mean they mean the same thing.
Words that are spelled the same but have different meanings are called homographs. Homographs can be further broken down into two groups depending upon if they’re pronounced the same.
Homographs that are pronounced the same are also homophones (and also homonyms, which are words that are spelled and pronounced the same, yet have different meanings). Examples of these words were seen above: right (direction) and right (correct). Homographs that are pronounced differently are called heteronyms. Examples of heteronyms include bow (to bend over) and bow (the hunting weapon).
Homophones are words that are pronounced the same but have different meanings. As already mentioned, homophones that are spelled the same are also homographs (and homonyms). If they’re spelled differently, they’re called heterographs. Examples of heterographs include to, too and two. You have to be careful with heterographs. Modern technology, such as spelling and grammar checkers, will not always catch when you use a heteronym incorrectly, since you probably spelled the wrong word right!
And just to make things even more fun, did you realize that there are words that are spelled the same but have different meanings when capitalized? We call these words capitonyms.
You may notice that people get these different terms confused very easily. People often call pairs of words homonyms when they’re really just homographs or homophones. Remember: homonyms are both homographs (spelled the same) and homophones (pronounced the same).
Wonder What’s Next?
We hope tomorrow’s fast-moving Wonder of the Day doesn’t make you sick!
Try It Out
Ready to have more fun with words? Recruit a friend or family member to help you check out the following activities:
I’m done. Too many people ate bananas for breakfast!
If you’re good with codes, you probably picked up that the hidden message was 1-2-8-4. Maybe that’s the combination for a secret locker! Here’s where those numbers were hidden:
I’m done. Too many people ate bananas for breakfast.
Do you see how heterographs like “too,» “ate,» and “for» were used? Can you make up your own challenging code? Give it a try and then challenge your friends and family members to unlock the code!
- Check out the fun Word Confusion game online to help Regan the Vegan make fresh salad. All you need to do is choose the correct word to complete each sentence!
- If you want to explore a huge list of homonyms, check out the Homonym Word Bank online. We bet you never realized there were so many homonyms! How many homonyms on the list did you already know? How many were new to you? Do you know of any homonyms not in the Homonym Word Bank? If you do, post them on Facebook to share with all your Wonder Friends!
- Did you know that spies can use words to create elaborate mathematical codes that can communicate things like phone and bank account numbers? It’s true! Check out the following sentence and see if you can find the hidden mathematical message:
Did you get it?
Test your knowledge
Wonder Contributors
We’d like to thank:
Alejandro and Drew
for contributing questions about today’s Wonder topic!
Keep WONDERing with us!
What are you wondering?
Wonder Words
- several
- meaning
- term
- confuse
- direction
- correct
- pronounce
- technology
- spelling
- grammar
- capitalized
- homonym
- homograph
- homophone
- heteronym
- capitonym
Take the Wonder Word Challenge
Rate this wonder
Share this wonder
×
GET YOUR WONDER DAILY
Subscribe to Wonderopolis and receive
the Wonder of the Day® via email or SMS
Join the Buzz
Don’t miss our special deals, gifts and promotions.
Share with the World
Tell everybody about Wonderopolis and its wonders.
Share Wonderopolis
Wonderopolis Widget
Interested in sharing Wonderopolis® every day? Want to add a little wonder to your website? Help spread the wonder of families learning together.
Add widget
You Got It!
ContinueNot Quite!
Try Again
Homonyms and Homophones — Javatpoint
|
next → The terms ate, and eight are homophones. Are they also homonyms? Perhaps they are neither — or perhaps they are both! Homonyms are words that are pronounced the same but have different meanings or are spelled the same but have different pronunciations. For example, «buy» and «by.» Homophones, on the other hand, are words that have the same sound but different spellings and meanings. It can be examined thoroughly using homophone instances. Homophones must be understood in order to improve one’s mastery of the English language. Learn the distinction between homonyms and homophones, as well as if they are synonymous with homographs. Differentiating Homonyms and HomophonesThe terms homonym and homophone are frequently used interchangeably. Both words contain the Greek prefix homo-, which means «the same,» and both indicate a connection between two or more words. Their definitions, however, differ slightly.
The words eight and ate, for instance, are homophones since they sound the same. Since they share the same spelling and pronunciation, the terms bar (a metal stick) and bar (a place that offers beverages) are homonyms. Another Meaning of HomonymAccording to some sources, a homonym is an umbrella term for homophones and homographs (a term that shares the spelling but have distinctive sounds). To be a homonym, a word pair must share either spelling or pronunciation, as per this definition. On the other hand, the stricter definition considers a homonym to be a homophone (share the same sound) and a homograph (share the spelling). What Is a Homonym: The Same Sound, Different Spelling?A homonym is Greek for «same name,» and it means that two words are spelled and spoken similarly. In other terms, homonyms are words with numerous meanings. Each homonym has a unique definition. Homonyms ExamplesInstances of homonyms include the following words :
Homophone Definition: Identical Sound, Distinct SpellingHomophones are any two words that share the same sound irrespective of spelling. Homophone ExamplesHere are some examples of homophones :
How Do Homographs Work?Homographs are antonyms for homophones. These terms have the same spelling but may sound distinct. Here are a few instances of homographs :
How to Distinguish Between Homonyms and HomophonesThe difference between homonyms and homophones can be found in their Greek roots. Homophones are words or sets of words that share the same sound but vary in meaning. Homonyms share the same spelling or pronunciation but distinctive meanings, as demonstrated by examples of homophones. Consider the cell phone. Consider your best friend’s phone. They would sound identical if they rang at the same moment. How were you supposed to tell them apart? They appear to be distinct — exactly like homophones. Understanding Your Word ConnectionsThe context of the statement — and the definition in your dictionary — determine whether a word is a homonym or a homophone. Whatever the name of the term relationship is, picking the proper word will assist you in explaining your message. Homonyms Homophones and HomographsWords that sound similar and may be spelled similarly yet have different meanings. Homonyms are regarded as synonyms for homographs and homophones. A homograph is a word that has the same spelling but alternate meanings, whether they are pronounced alike or not. For instance, Bass (instrument) and Bass (instrument) ( a fish). Simultaneously, homophones have the same sound and may have the same or distinct spelling, but they vary in meaning. There are homophones such as they’re, their, and there. As a result, homophones and homographs are classified as homonymy. Homonyms are frequently utilized, which confuses both novices and native speakers. They aren’t particularly vital, but understanding how to utilize them correctly is essential for creating excellent, understandable sentences. The distinctions between the three will aid in comprehending the message. At the same time, the word itself aids in identifying the distinction between these three. Homophones, homographs, and homonyms all start with the word «homo,» which indicates identical or similar. Simultaneously, «nyms» derived from homonyms determine the name. As a result, homonyms are both homographs and homophones. It’s also utilized as a synonym for both of these terms. Homonyms are more commonly used than homographs and homophones among these three. Your, you’re, to, and two categories of words generate uncertainty in comprehending their meaning since everyone pronounces them the same way in everyday life. These are examples of homophones that are commonly used when speaking English. Commonly confused homophones include:
While natural speakers have no difficulty communicating because they can easily recognize homophones, novices and pupils, have difficulty understanding them. Here are some examples of homophones. Both have the same pronunciation but alternate meanings.
ConclusionHomonyms are essential for comprehending the English language. Instead of comprehending the examples, comprehend their application and meanings, which will be beneficial to the general situation of homonyms. Homonyms are classified into two categories. Homophones and homographs vary in spelling and pronunciation, while homophones and homographs vary in sound. In comparison, both are significant in the language itself. As noted in the article, several examples of homophones are regularly used. All of the homonym details and brief annotations are part of language comprehension for speaking and writing. To avoid the misunderstanding caused by homonyms, it is essential to comprehend them. Homophones, homographs, and homonyms are among the most perplexing features of English, with which most people struggle. However, understanding the concept and practicing daily can help in mastering the concepts. Next TopicHomophones Sentences ← prev |
Homonyms
Homonyms are words similar in sound and spelling, but different in meaning. The word «homonym» comes from two Greek words: homos — the same, onymo — name.
Let’s read a conversation between two boys:
— And I have oatmeal at home.
— Just think, I also have oatmeal at home today.
— I love oatmeal!
— And I love it!
— She is yellow, so beautiful!
– And delicious! Especially with milk!
– How delicious is that? How about milk?
— Yes. Also good with butter or granulated sugar.
– What are you talking about?
– How is this about what? About oatmeal.
— About what kind of oatmeal?
— About the common oatmeal? What are you talking about?
— About the one that lived in our garden and sang songs.
— Did Kasha sing songs?
— What kind of porridge? Not porridge, but a bird. Bunting bird! Haven’t heard of this one, have you? Come to me to listen to my oatmeal!
– And then eat my oatmeal with me!
Of course, you guessed that the boys did not understand each other, because they were talking about different things, while calling them the same word. This is an example of homonyms. After all, oatmeal is a bird, and oatmeal is also a cereal.
Consider examples of homonyms, compare the sound, spelling and meaning of words.
At sea land strip
It is called a scythe,
And the girl has a braid
Colors of ripe oats.
There is dew on the grass —
The scythe mows the grass.
I have one question:
How many braids are there in the world?
Spit is a narrow shoal running from the shore.
Scythe — braided hair.
Scythe is a tool for mowing grass.
The porridge ripened in the meadow.
Cow Masha eats porridge.
Masha likes lunch:
Nothing tastes better!
Kashka — white clover.
Kashka – a dish of grains boiled in water or milk.
Say «spring» —
And here it is,
Runs in the green thicket
Merry murmuring key.
And we call the spring the key
(The key to the doors has nothing to do with it).
Key – spring.
Key — tool for the lock.
— Who are you?
— We are foxes,
— Friendly sisters.
— Well, who are you?
— We are foxes too!
– Like, with one paw?
— No, still with a hat.
Chanterelles — mushrooms.
Chanterelles — animals.
Come learn shooting with me
Look for me on the ridge.
I can hit a bird accurately,
And also I get into cabbage soup.
Onion — plant.
Bow — weapon.
All the words we have considered are the same in sound and spelling, but their lexical meaning is different.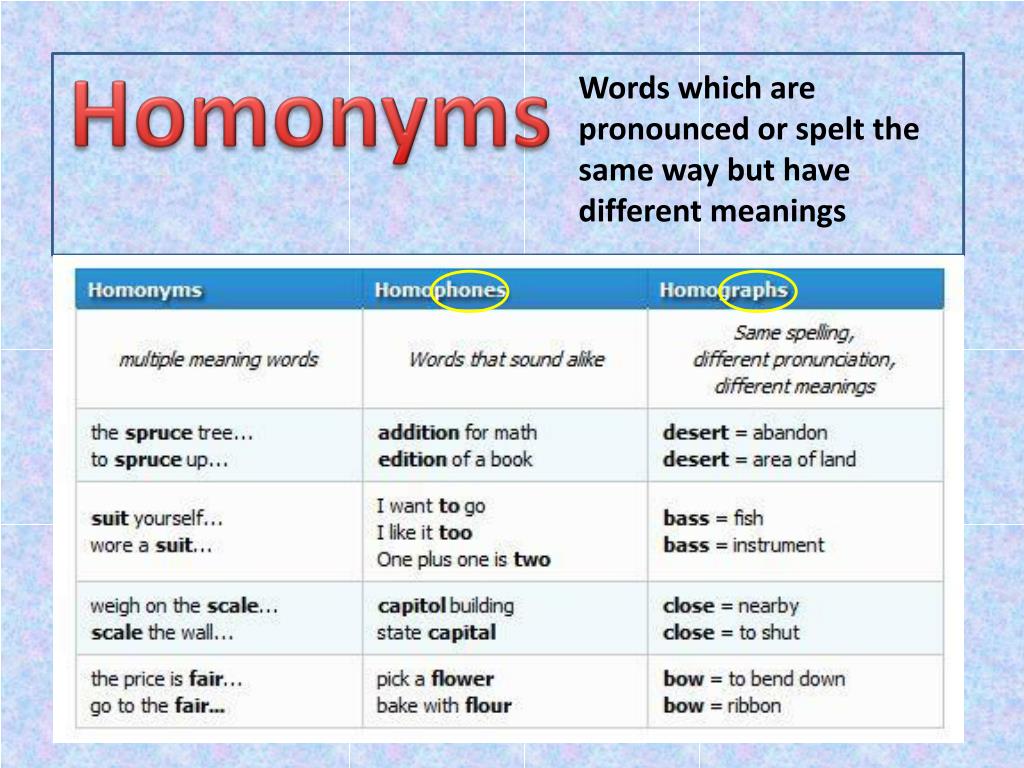
We already know that words carry lexical meaning . Single-valued words have one lexical meaning, multi-valued — several.
Let’s learn how to distinguish an ambiguous word from a homonym. Consider the lexical meaning of the word « bell «: bell is a flower; bell small bell. The word bell is ambiguous, because the objects have a similar shape.
Consider the lexical meaning of the word « dachshund «: dachshund — breed of dog; tax — fare. These words are homonyms, because they have different lexical meanings and have nothing in common.
Polysemantic words and homonyms are spelled the same. The main difference between them is that polysemantic words have something in common in their lexical meaning (color, shape), while lexical meanings of homonyms are completely different.
If you doubt the definition of a polysemantic word or homonym, an explanatory dictionary will come to your aid. Consider the difference in the entry of dictionary entries:
The root is a polysemantic word, has several meanings:
1. The underground part of plants.
2. The inner part of the hair, tooth.
3. Beginning, source of something (figurative).
4. Significant part of the word.
In the dictionary of a polysemantic word, each of its meanings is indicated by a number.
Consider how homonyms are represented in the dictionary. For example:
Stopcock is a shut-off device in the form of a tube for the release of liquid or gas.
Crane is a machine for lifting and moving loads over short distances.
In the dictionary, homonyms have a separate dictionary entry.
It is possible to determine the meaning of homonyms only when the word is used in a phrase or in a sentence.
return to the page «Russian language grade 2» >>>
If you liked it, share with your friends:
Join us at Facebook !
Spoken Russian – Real Language Club
See also:
- Russian texts with audio
- Dialogues in Russian
- Video in Russian with subtitles
- Pronunciation Exercises
- Russian tongue twisters in audio format
- Common phrases in Russian
- Russian slang expressions
- Jokes in Russian with translation into English
Preparation for Russian language exams:
- OGE in Russian
- USE in Russian language
- Exams for migrants (Patent, RVP, Residence Permit, Citizenship of the Russian Federation)
We recommend:
- Best Russian tutors
Essentials from theory:
- Russian Grammar
We offer online tests:
- Russian proficiency test
- Russian vocabulary test
- Russian grammar tests
- What language to learn?
Recommended articles and videos:
- How to successfully pass an interview in Russian
- TV — a means of learning a foreign language
- Interesting tests: find out your level of language proficiency
- Gymnastics for linguists: complex for correct pronunciation
- 5 rules for successful language learning
- How to improve your knowledge of a foreign language: three tips and five rules
- How to improve fluency
- Video: «How to improve pronunciation and understanding
More articles >>>
Please help.

?
|
Personnel is everything (Kodak advertising)
|
Haven’t moved in yet? (advertising for an auto insurance company)
Khoper-invest excellent company .
|
Thank you!
|
Philips has an advertisement for a clipper — dad and son are sitting at a football match, showing them against the background of the game, slogan:
Many beautiful heads!
|
You can’t even find fault with this!
The perfect case.

 It aids in the growth of a person’s lexical knowledge. When speaking, thousands of homophones are utilized, which causes difficulties for both native speakers and learners.
It aids in the growth of a person’s lexical knowledge. When speaking, thousands of homophones are utilized, which causes difficulties for both native speakers and learners.
 Right and write, for instance, are homophones since they sound identical but are spelled differently.
Right and write, for instance, are homophones since they sound identical but are spelled differently. Homonym implies «identical name» and refers to words that have the same sound and spelling. Homophone implies «same sound»; homophones are terms that sound the same.
Homonym implies «identical name» and refers to words that have the same sound and spelling. Homophone implies «same sound»; homophones are terms that sound the same.
 The homophone «phones» refers to the sound. And «graph» refers to the writing in the homograph.
The homophone «phones» refers to the sound. And «graph» refers to the writing in the homograph. As a result, several activities have been added to the topic assigned to pupils by professors.
As a result, several activities have been added to the topic assigned to pupils by professors.

 »
» 