Maths addition problems: Browse Printable Addition Worksheets | Education.com
Posted onAddition Worksheets
Welcome to the addition worksheets page at Math-Drills.com where we will add to your learning experience in many positive ways! On this page, you will find Addition worksheets from addition facts and two-digit addition to column addition and addition with games. In the first section, we’ve included a few addition printables that should help out the beginning student. Teaching addition facts is best done with some interesting teaching strategies.
Some teachers and parents use addition manipulatives to help students understand the basic addition facts. For example, adding groups of «Apple Jacks» (a breakfast cereal) by counting will quickly lead students to understand the concepts of addition. The sooner you can introduce base ten blocks to your students, the better. If you haven’t already used them for counting, use them for basic addition and show students how regrouping works.
Most Popular Addition Worksheets this Week
100 Single-Digit Addition Questions With Some Regrouping (709 views this week)2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition With Some Regrouping (25 Questions) (526 views this week)3-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition With Some Regrouping (25 Questions) (233 views this week)25 Single-Digit Addition Questions with No Regrouping (195 views this week)5-Digit Plus 5-Digit Addition With Some Regrouping (20 Questions) (115 views this week)
Addition Facts Tables
Disputably not a great way to learn addition facts, but undeniably a great way to summarize, addition facts tables are an invaluable resource in any home or school classroom.
Addition Tables
Addition works very well as a table since the addends can be sequential. Encourage students to look for patterns and teach them a variety of strategies to learn the addition facts. For students who have not yet memorized their addition facts but need to know them for a more advanced math lesson such as adding two-digit numbers, provide an addition facts table to them, so they can quickly look up addition facts. After a while, they will most likely learn the facts through the use of the table and become less reliant on it. To make the tables more durable, print them on card stock and laminate them. They can be displayed on a screen or enlarged and printed on poster paper for whole class use.
Addition Facts Table
Blank Addition Facts Table
Addition Facts Table With Zero
Blank Addition Facts Table With Zero
Left-Handed Addition Facts Table
Left-Handed Blank Addition Facts Table
All Addition Facts Tables
Addition Facts Tables With One Fact at a time highlighted
Addition Facts Tables in Gray 1 to 12
Addition Facts Tables in Color 1 to 12
Addition Facts Tables in Montessori Colors 1 to 12
Five Minute Frenzy Charts
Five minute frenzy charts are 10 by 10 grids for addition fact practice.
Called mad minutes or timed drills by some, five minute frenzies are meant to be timed to add a little more excitement to practicing addition facts. They are ideally used to increase a student’s ability to recall addition facts quickly which has all sorts of benefits later in their school life including preventing high school teachers from complaining about «how their students can’t even add single-digit numbers without using a calculator.»
A general goal to achieve would be to complete one chart in less than five minutes and score 98 percent or better, however, we recommend setting personal goals for students based on an initial test. If they are banging their head against the wall after a couple of minutes with only a few questions done, they really shouldn’t be completing a timed addition facts drill at the moment. They still have some learning to do. We would recommend breaking out the manipulatives at this point.
Five Minute
Addition Frenzies that include one addition chart per page
One-per-page addition frenzies are not the most efficient use of paper resources, but they are a good starting point especially for younger students who have not quite mastered their penmanship enough to fit their numbers into a smaller chart. They are also great for displaying on screens or monitors for group activities. For example, you might use an interactive white board to fill out the chart.
Addition Frenzy (1 to 10)
Addition Frenzy (11 to 20)
Addition Frenzy (21 to 50)
Addition Frenzy (51 to 100)
Left-handed Addition Frenzy (1 to 10)
Left-handed Addition Frenzy (11 to 20)
Left-handed Addition Frenzy (21 to 50)
Left-handed Addition Frenzy (51 to 100)
Five Minute
Addition Frenzies that include four addition charts per page
A wiser use of paper and photo-copy limits, having four charts on a page allows for multi-day practice, collaborative work or through the use of a paper-cutter, a quick stack of practice pages for students who finish early.
Four Addition Frenzies (1 to 10)
Four Addition Frenzies (11 to 20)
Four Addition Frenzies (21 to 50)
Four Addition Frenzies (51 to 100)
Left-handed Four Addition Charts Per Page (1 to 10)
Left-handed Four Addition Charts Per Page (11 to 20)
Left-handed Four Addition Charts Per Page (21 to 50)
Left-handed Four Addition Charts Per Page (51 to 100)
Most people would agree that being able to add single-digit numbers quickly and in your head is an essential skill for success in math. The various addition worksheets in this section focus on skills that students will use their entire life. These worksheets will not magically make a student learn addition, but they are valuable for reinforcement and practice and can also be used as assessment tools.
Vertically Arranged Single-Digit Addition
So, you need some practice sheets for addition facts? You’ve found them. Use these for practice, assessment, games or just for fun.
100 Single-Digit Addition Questions with Some Regrouping
81 Single-Digit Addition Questions with Some Regrouping
64 Single-Digit Addition Questions with Some Regrouping
50 Single-Digit Addition Questions with Some Regrouping
25 Single-Digit Addition Questions with Some Regrouping
12 Single-Digit Addition Questions with Some Regrouping
100 Single-Digit Addition Questions with No Regrouping
64 Single-Digit Addition Questions with No Regrouping
25 Single-Digit Addition Questions with No Regrouping
12 Single-Digit Addition Questions with No Regrouping
100 Single-Digit Addition Questions with All Regrouping
64 Single-Digit Addition Questions with All Regrouping
25 Single-Digit Addition Questions with All Regrouping
12 Single-Digit Addition Questions with All Regrouping
Horizontally Arranged Single-Digit Addition
100 Horizontal Addition Facts
50 Horizontal Addition Facts
Horizontal Numbers that Add to 10
Horizontal Adding up to 5 + 5
Horizontal Adding up to 6 + 6
Horizontal Adding up to 7 + 7
Horizontal Adding up to 8 + 8
Adding 3 Single-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding 4 Single-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding 5 Single-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding 10 Single-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Horizontal Addition Facts with No Regrouping 100 per page
Horizontal Addition Facts with No Regrouping and No Zeros 100 per page
Horizontal Addition Facts with No Regrouping 50 per page
Horizontal Addition Facts with All Regrouping 100 per page
Horizontal Addition Facts with All Regrouping 50 per page
Make Ten Addition Strategy
The make ten addition strategy involves «spliting» the second addend into two parts.
Make 10 Addition Strategy
Make 20 Addition Strategy
Make 30 Addition Strategy
Make 40 Addition Strategy
Make 50 Addition Strategy
Make 60 Addition Strategy
Make 70 Addition Strategy
Make 80 Addition Strategy
Make 90 Addition Strategy
Make Multiples of 10 Addition Strategy
Single-digit addition questions with
focus numbers
Focusing on one number at a time is necessary for some students.
25 Adding 0s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 1s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 2s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 3s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 4s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 5s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 6s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 7s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 8s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 9s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
25 Adding 1s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 2s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 3s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 4s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 5s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 6s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 7s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 8s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
25 Adding 9s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions With Sums Limited to 12
50 Adding 0s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 1s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 2s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 3s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 4s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 5s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 6s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 7s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 8s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 9s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
50 Adding 1s and 2s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 1s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 2s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 3s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 4s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 5s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 6s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 7s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 8s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
100 Horizontal Adding 9s to Single-Digit Numbers Questions
Multi-Digit Addition Worksheets
A variety of strategies can be used to learn multi-digit addition; it isn’t necessary to rely only on paper and pencil methods.
Multi-Digit Addition with
SOME regrouping
Classic addition worksheets with some steps requiring regrouping and others not. Versions with ALL regrouping and NO regrouping follow this section. Versions with thousands separators are a little further down the page.
2-Digit plus 1-Digit Addition
2-Digit plus 1-Digit Addition (Sums Less Than 100)
2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition
3-Digit Plus 1-Digit Addition
3-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition
3-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition
4-Digit Plus 1-Digit Addition
4-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition
4-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition
4-Digit Plus 4-Digit Addition
5-Digit Plus 5-Digit Addition
Various 2-digit to 4-digit Addition
Various 2-digit to 5-digit Addition
Various 3-digit to 5-digit Addition
6-Digit Plus 6-Digit Addition
7-Digit Plus 7-Digit Addition
8-Digit Plus 8-Digit Addition
9-Digit Plus 9-Digit Addition
3-Digit Expanded Form Addition
Multi-Digit Addition with
ALL regrouping
Regrouping is what long addition is all about; these worksheets give students a lot of practice since every step requires regrouping.
2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
3-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
4-Digit Plus 4-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
5-Digit Plus 5-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
6-Digit Plus 6-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
7-Digit Plus 7-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
8-Digit Plus 8-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
9-Digit Plus 9-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
(OLD) 2-Digit Plus 1-Digit Addition with ALL Regrouping
Multi-Digit Addition with
NO regrouping
If you haven’t quite mastered all the addition facts or the long addition algorithm, this might be the section for you. These worksheets don’t require any regrouping, so they provide an extra in-between skill for students who require a little more guidance.
2-Digit Plus 1-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
3-Digit Plus 1-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
3-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
3-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
4-Digit Plus 1-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
4-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
4-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
4-Digit Plus 4-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
5-Digit Plus 5-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
6-Digit Plus 6-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
7-Digit Plus 7-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
8-Digit Plus 8-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
9-Digit Plus 9-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
Horizontally arranged addition
Horizontal addition can encourage students to use mental math or other strategies to add numbers.
Adding to 20 with the Second Addend Greater
2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Horizontal Addition with no Regrouping
2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Horizontal Addition with some Regrouping
3-Digit Plus 2-Digit Horizontal Addition
3-Digit Plus 3-Digit Horizontal Addition
Various-Digit (2 to 3) Horizontal Addition
4-Digit Plus 3-Digit Horizontal Addition
4-Digit Plus 4-Digit Horizontal Addition
Various-Digit (2 to 4) Horizontal Addition
Adding 3 Two-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding 4 Two-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding 5 Two-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding 10 Two-Digit Numbers Horizontally
Adding
focus numbers greater than 9
These worksheets include numbers greater than the ones further up the page.
25 Adding 10’s Questions
50 Adding 10’s Questions
50 Adding 11’s Questions
50 Adding 12’s Questions
50 Adding 13’s Questions
50 Adding 14’s Questions
50 Adding 15’s Questions
50 Adding 16’s Questions
50 Adding 17’s Questions
50 Adding 18’s Questions
50 Adding 19’s Questions
50 Adding 20’s Questions
Multi-Digit Addition with
Comma-Separated Thousands
Using a comma to separate thousands is the most common way to format large numbers in the English world.
Adding 4-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated)
Multi-Digit Addition with
Space-Separated Thousands
Using a space to separate thousands in large numbers is common in some languages.
Adding 4-Digit Numbers (Space Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers (Space Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers (Space Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers (Space Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers (Space Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers (Space Separated)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated)
Multi-Digit Addition with
Period-Separated Thousands
Using a period as a thousands separator is not generally seen in English-speaking countries, but since there are people from around the world who use these addition worksheets, they are included.
Adding 4-Digit Numbers (Period Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers (Period Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers (Period Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers (Period Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers (Period Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers (Period Separated)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated)
Adding 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated)
Large-Print Multi-digit Addition
For various reasons, sometimes you need addition questions in a larger font.
LP 2-digit Plus 1-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 3-digit Plus 1-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 4-digit Plus 1-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP Various Plus 1-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 2-digit Plus 2-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 3-digit Plus 2-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 4-digit Plus 2-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP Various Plus 2-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 3-digit Plus 3-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 4-digit Plus 3-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 4-digit Plus 4-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 5-digit Plus 5-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP 6-digit Plus 6-digit Addition with SOME Regrouping
LP Adding 2-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping
LP Adding 3-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping
LP Adding 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping
LP Adding 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping
LP Adding 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping
LP 2-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 3-Digit Plus 2-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 3-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 4-Digit Plus 3-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 4-Digit Plus 4-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 5-Digit Plus 5-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 6-Digit Plus 6-Digit Addition with NO Regrouping
LP 2-Digit Addition with Sums up to 99 (25 Questions)
LP 2-Digit Addition with Sums up to 99 (12 Questions)
Various Other Addition Worksheets
Column Addition Worksheets
Column addition is not just an exercise in accounting, it also develops mental addition skills that are useful in everyday life.
Adding Three Single-Digit Numbers
Adding Four Single-Digit Numbers
Adding Five Single-Digit Numbers
Adding Six Single-Digit Numbers
Adding Three Two-Digit Numbers
Adding Four Two-Digit Numbers
Adding Five Two-Digit Numbers
Adding Six Two-Digit Numbers
Adding Three Three-Digit Numbers
Adding Four Three-Digit Numbers
Adding Five Three-Digit Numbers
Adding Six Three-Digit Numbers
Adding Three Four-Digit Numbers
Adding Four Four-Digit Numbers
Adding Five Four-Digit Numbers
Adding Six Four-Digit Numbers
Adding Three Various-Digit Numbers
Adding Four Various-Digit Numbers
Adding Five Various-Digit Numbers
Adding Six Various-Digit Numbers
Adding With Grid Support
Adding with grid support helps students who have trouble lining up place values themselves.
Adding 2-Digit + 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 3-Digit + 3-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 3-Digit + 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 4-Digit + 4-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 4-Digit + 3-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 4-Digit + 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit + 5-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit + 4-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit + 3-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit + 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding Various Digit Numbers on a Grid (2 Addends)
Adding 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (3 Addends)
Adding 3-Digit Numbers on a Grid (3 Addends)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers on a Grid (3 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers on a Grid (3 Addends)
Adding Various-Digit Numbers on a Grid (3 Addends)
Adding 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (4 Addends)
Adding 3-Digit Numbers on a Grid (4 Addends)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers on a Grid (4 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers on a Grid (4 Addends)
Adding Various-Digit Numbers on a Grid (4 Addends)
Adding 2-Digit Numbers on a Grid (5 Addends)
Adding 3-Digit Numbers on a Grid (5 Addends)
Adding 4-Digit Numbers on a Grid (5 Addends)
Adding 5-Digit Numbers on a Grid (5 Addends)
Adding Various-Digit Numbers on a Grid (5 Addends)
Adding With
Games
These adding worksheets also help students develop mental addition skills, but use a game context for familiarity and interest.
Adding 2 Playing Cards
Adding 3 Playing Cards
Adding 4 Playing Cards
Adding 5 Playing Cards
Adding 6 Playing Cards
Adding 7 Playing Cards
Adding 8 Playing Cards
Counting Cribbage Hands
Identify and Count Yahtzee! Combinations
Adding complements of various amounts
Finding complements of numbers can help students a great deal in developing mental arithmetic skills and to further their understanding of number.
Adding Complements of 9 (Blanks in First or Second Position Mixed)
Adding Complements of 9 (Blanks in First then Second Position)
Adding Complements of 9 (Blanks in First Position Only)
Adding Complements of 9 (Blanks in Second Position Only)
Adding Complements of 9 (Blanks in Any Position, Including Sums)
Adding Complements of 99
Adding Complements of 999
Adding Complements of 10
Adding Complements of 100
Adding Complements of 1000
Adding Complements of 11 (Blanks in First or Second Position Mixed)
Adding Complements of 11 (Blanks in First then Second Position)
Adding Complements of 11 (Blanks in First Position Only)
Adding Complements of 11 (Blanks in Second Position Only)
Adding Complements of 11 (Blanks in Any Position, Including Sums)
Adding
Doubles of Numbers
Using an adding doubles strategy can help students to process addition questions more quickly using mental math.
Adding Doubles (Up to 9)
Adding Doubles Plus One (Up to 9)
Adding Doubles Plus Two (Up to 9)
Adding Doubles Minus One (Up to 9)
Adding Doubles Minus Two (Up to 9)
Adding Doubles Mixed Variations (Up to 9)
Adding Doubles (Up to 15)
Adding Doubles Plus One (Up to 15)
Adding Doubles Plus Two (Up to 15)
Adding Doubles Minus One (Up to 15)
Adding Doubles Minus Two (Up to 15)
Adding Doubles Mixed Variations (Up to 15)
Adding Doubles (Up to 30)
Adding Doubles Plus One (Up to 30)
Adding Doubles Plus Two (Up to 30)
Adding Doubles Minus One (Up to 30)
Adding Doubles Minus Two (Up to 30)
Adding Doubles Mixed Variations (Up to 30)
Adding in
other base number systems
Not commonly taught in modern schools, adding in other base number systems can stretch students’ minds and have quite a few important applications, especially in technology.
Adding Binary Numbers (Base 2)
Adding Ternary Numbers (Base 3)
Adding Quaternary Numbers (Base 4)
Adding Quinary Numbers (Base 5)
Adding Senary Numbers (Base 6)
Adding Octal Numbers (Base 8)
Adding Duodecimal Numbers (Base 12)
Adding Hexadecimal Numbers (Base 16)
Adding Vigesimal Numbers (Base 20)
Adding Hexatrigesimal Numbers (Base 36)
Adding Various Numbers (Various Bases)
Addition Worksheets
The addition worksheets on this page introduce addition math facts, multiple digit addition without regrouping, addition with regrouping (we used to call this ‘carrying’ in my day), addition with decimals and other concepts designed to foster a mastery of all things addition.
One Minute Timed Addition Worksheets
104 Addition Worksheets
These addition worksheets are similar to the RocketMath, Wolf Swamp or Mastering Math Facts addition worksheets used at many schools. These are typically one minute, timed tests. Try my super entertaining online timer if you or your kids are into silly sounds!
Spaceship Math
Two Minute Tests
60 Addition Worksheets
These 80 and 100 problem addition worksheets are designed to incrementally build addition fact competency. Use these as two minute timed addition tests, which are great at-home practice even if your school is only doing one minute tests.
Two Minute Tests
Circle Addition Facts Worksheets
32 Addition Worksheets
These addition worksheets emphasize groups of related facts and there are variations with the facts in order to facilitate skip counting, or with random products that help facilitate fact memorization.
Addition Fact Circles
Spiral Addition Facts
52 Addition Worksheets
Tired of the same old math fact worksheets with rows and rows of problems? Time to try something unique. These worksheets present the addition facts in a spiral layout that provides fun a twist on memorization. They use the same fact layouts as the spaceship math addition worksheets above, so try the first two sets worksheets if you are looking for the full set of addition facts or practice without the easier problems, or look at the others for an incremental approach to learning the facts.
Spiral Addition Facts
Addition Sequence Facts
4 Addition Worksheets
These addition worksheets allow students to practice simple sequences of addition to arrive at a final answer to a problem.
Sequence Addition Worksheets
Bullseye Addition
8 Addition Worksheets
Get on target with those addition math facts! These fun worksheets provide some additional kinesthetics over and above your usual math fact practice. Hopefully you will find these addition worksheets are spot-on when you need a change of pace!
Bullseye Addition
Dice Addition
8 Addition Worksheets
Get on target with those addition math facts! These fun worksheets provide some additional kinesthetics over and above your usual math fact practice. Hopefully you will find these addition worksheets are spot-on when you need a change of pace!
Dice Addition
Place Value
20 Addition Worksheets
These place value addition worksheets are good first steps towards multi-digit addition problems.
Place Value
No Carry
8 Addition Worksheets
These addition worksheets contain multi-digit addition problems without regrouping. Getting comfortable with these will prepare students for full multi-digit addition where regrouping (carrying) is required to find the sum.
No Carry
Multi-Digit Addition Worksheets
24 Addition Worksheets
Each of these addition worksheets provide exercises for progressively more complex types of addition problems with multiple digit addends, as well as problems with more than two addends.
More Complex
Applications
20 Addition Worksheets
These addition worksheets provide sample programs that should help develop skills for specific applications of addition (addition with time, money, multiples of 5, etc.
Applications
Addition with Decimals
16 Addition Worksheets
One digit (tenths) and two digit (hundredths) addition worksheets.
Addition with Decimals
Addition Multiples
24 Addition Worksheets
Addition worksheets that introduce multiples and skip-counting. These addition worksheets are an excellent stepping stone to multiplication.
Addition Multiples
Doubling Addition
60 Addition Worksheets
Practice addition worksheets for doubling values. Includes worksheets for single digit addition, two digit addition that require no borrowing (mental addition) and for addition worksheets for factor of five. These addition worksheets are great tools for place-value concepts.
Doubling Addition
Addition Worksheets for Math Practice!
It all starts here with addition! Learning addition is the first step on your way to subtraction, and makes up the foundation of all of the strategies used to teach multiplication.
Picture Math Addition
Addition Flash Cards
Addition and Subtraction Grid Puzzle Worksheets
Math Worksheets
Addition
This index page will link you to all types of addition worksheets, including basic facts, 2-digit addends, 3-digit addends, 4-digit addends, fraction addition, decimal addition, fact families, and money addition.
Addition: Basic Facts
Worksheets with basic, single-digit addition facts (sums up to 18).
Addition: 3-Digit Addends
Practice adding 3-digit numbers together with these printable worksheets, task cards, and games.
Addition: 4 and 5-Digit Addends
Challenge your students to solve addition problems with 4 and 5-digit numbers.
Addition: 3 or More Addends
Column addition problems with 3 or more addends of 1, 2, 3, and 4-digit numbers.
Addition and Subtraction Mix: Basic
The worksheets, flashcards, and number lines on this page have a mix of basic, single-digit addition and subtraction problems.
Addition: Fractions
Add fractions and mixed numbers with like denominators, as well as unlike denominators.
Addition Properties
These worksheets were made to teach students about the commutative and associative properties of addition.
Addition Squares
Build logical thinking skills with these addition square brainteaser worksheets.
Addition-Subtraction Fact Families
Basic fact family triangles, number bonds, and fact squares worksheets for addition and subtraction.
Addition: Sum Game (Basic addition)
On these printable game boards, students color pairs of numbers that equal a given sum.
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Write algebraic expressions, learn to identify independent/dependent variables, solve for variables in equations, work with inequalities, and more.
Angles: Types and Measuring
Using protractors to find measurements of right, acute, and obtuse angles.
Angles: Complementary, Supplementary, Vertical
Download worksheets to practice geometry concepts related to vertical, complementary, and supplementary angles.
Area of Triangles
Use the formula A = 1/2 x (b x h) to calculate the area of triangles
Area Worksheets
Calculate the area (in square units) of the shapes on these worksheets.
Box Plots (Box-and-Whisker Diagrams)
Use these worksheets to help students learn about statistics and creating box-and-whisker plots.
Calendars (Math)
Calendars to help students with years, months, weeks and days on a calendar.
Capacity Worksheets
Volume or capacity worksheets (gallons, quarts, pints, & cups).
Circles: Radius, Diameter, Circumference
Calculate the diameter and radius of circles; also includes circumference and area worksheets.
Color-by-Number Worksheets
Color the mystery pictures according to the number key at the bottom.
Counting Money (Australian)
Use these worksheets to practice counting Australian money.
Counting Money (Canadian)
Count toonies, loonies, quarters, nickels, and dimes with these Canadian currency worksheets.
Counting Money (UK Pounds)
Learn to count pounds and pence, coins used in the United Kingdom.
Counting Money (USA)
Practice counting American money (pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters).
Counting Worksheets 0-30 (Very Basic)
Learn to count and write numbers up to 30.
Counting Worksheets (More Advanced)
Learn how to accurately count two, three, and four-digit numbers. Complete the number lines, tell what number comes before, and skip counting.
Daily Math Review
This page will link you to over 100 daily review practice worksheets («Math Buzz»), leveled for grades 1 through 5.
Daily Word Problems
This area has math daily word problems for grades 1 through 5. There are hundreds of graphical word problems for students to solve, with plenty of space to show their work.
Decimal Addition and Subtraction
Add and subtract decimal numbers with tenths, hundredths, and thousandths place values.
Decimal Division
Practice long division with decimal numbers.
Decimal Multiplication
Practice multiplication problems that have decimal factors and products.
Decimal Worksheets
Naming and working with decimal numbers.
Division Worksheets: Basic
Basic division facts worksheets, games, and activities.
Division Worksheets: Long Division
Long division worksheets with 2, 3, and 4-digit dividends.
Equations (Basic Algebra)
Learn to balance simple algebraic equations and find the value of variables.
Even and Odd Worksheets
Identifying odd and even numbers
Exponents Worksheets
Find the exponents of single-digit numbers on these printable worksheets and task cards.
Factoring Worksheets
Complete factor trees, find greatest common factors, and least common multiples.
Fraction Worksheets (Advanced)
Reducing fractions, ordering fractions, equivalent fractions, and comparing fractions.
Fraction Worksheets (Basic)
Identifying basic fractions, fraction strips, fraction manipulatives.
Fractions: Addition
Find sums of fractions and mixed numbers. Includes worksheets with like-denominator fractions, as well as unlike-denominator fractions.
Fractions: Division
Divide fractions and mixed numbers. Many of these worksheets include illustrated problems, graphical model problems, as well as word problems.
Fractions: Mixed Numbers
Practice basic mixed number skills.
Fractions: Multiplication
Multiply the fractions and mixed numbers. Many worksheets include models and diagrams, as well as word problems.
Fractions: Reciprocals
Print these worksheets to help students learn about reciprocal fractions.
Fractions: Subtraction
Practice subtracting fractions and mixed numbers. Includes like and unlike denominators.
Frames and Arrows Practice
Use frames and arrows activities to build up logical thinking skills.
Graphing: Bar Graphs
Read the bar graphs on the worksheets and answer questions.
Graphing: Line Graphs
Interpret the line graphs on the worksheets and answer questions.
Graphing: Line Plots
Line plots are a special type of number line that represents frequency of data.
Graphing: Pictographs
Study the pictographs on the worksheets and answer questions.
Graphing: Pie Graphs
Analyze the pie graphs on the worksheets and answer questions.
Greater than, Less than Worksheets
Compare numbers greater than, less than, and equal to.
Hundreds Charts
Use these helpful place value charts, hundreds charts, ninety-nines charts.
In and Out Boxes
Complete these printable input and output boxes, or rule boxes.
Inequalities
Solve and graph the inequalities. Includes single-variable, one-step, and two-step inequalities.
Integers (Basic)
Compare, order, add, and subtract the positive and negative numbers.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Determine the least common multiple of each set numbers
Lines, Segments, Rays
Learn about lines, line segments, rays, parallel lines, and perpendicular lines.
Math Crossword Puzzles
Solve the math problems and use the answers to complete the crossword puzzles.
Math Riddles
Solve the math problems to decode the answer to funny riddles. Includes a wide variety of math skills, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, place value, rounding, and more.
Math Story Passages
This page has a set of whole-page reading passages. Students use information from the passages to solve math problems. These are much longer than «regular» word problems.
Mean (Averages) Worksheets
Calculate the mean, or average, of numbers.
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
Calculate the mode, median, mean, and range of the given numbers.
Measurement Index
Select the types of measurement worksheets you’re looking for, including linear measurement, capacity, and temperature.
Measurement: CM, MM, and M
Practice metric linear measurement: centimeters, millimeters, and meters.
Measurement: Feet, Yards, Inches
Learn American linear measurement; inches, feet, and yards.
Measurement: Grams and Kilograms
Measure the weight and convert to and from grams and kilograms.
Measurement: Liters and Milliliters
Estimate and convert capacity measurements in liters and milliliters.
Measurement: Pounds and Ounces
Measure the weight and convert to and from ounces and pounds.
Middle School Math
This index page will link you to dozens of middle school math topics on this site. Topics include inequalities, absolute value, algebra, and more.
Minute Math Drills
Drill-and-practice sheets for basic adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing.
Multiples
These worksheets will help students learn to find and identify multiples of numbers.
Multiplication (Properties)
Learn about the associative, distributive, commutative, and identity properties of multiplication.
Multiplication Tables
Print these multiplication charts and tables for students to use as reference.
Multiplication Worksheets: Advanced
Solve two and three-digit multiplication problems.
Multiplication Worksheets: Basic
Learn basic multiplication facts with these worksheets, mystery pictures, and games.
Multiplication-Division Fact Families
Basic number bonds, fact family worksheets and triangles for division and multiplication.
Multiplication: Lattice Multiplication
Multiply by 2, 3, or 4 digit numbers with a lattice grid.
Mystery Graph Art
Plot the ordered pairs to reveal mystery pictures.
Mystery Math Pictures
Solve the addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division facts to reveal a mystery picture.
Number Detective (Secret Numbers)
Students will used the clues posted each day to figure out the weekly secret number.
Number Lines
Printable number line worksheets for teaching counting, addition, subtraction, number patterns, fractions, and decimals.
Order of Operations
Practice order of operations: parenthesis and exponents, then multiply and divide, then add and subtract.
Ordered Pairs; Coordinate Planes
Coordinate planes and ordered pair worksheets.
Ordinal Numbers
Ordinal numbers define position in a series. (examples: first, second, third, fourth, etc.)
Patterns: Number
Students must list the numbers that come next in these patterns.
Patterns: Picture
Students determine which pictures come next in the patterns.
Percent Worksheets
Convert from decimal numbers and fractions to percents.
Perimeter Worksheets
Add to find the perimeters of polygons on these worksheets.
Place Value Worksheets
Finding the value of the underlined digit value; standard and expanded form; rounding.
Prime & Composite Numbers
Learn the differences between prime and composite numbers. Also, learn to identify and find prime numbers by factoring, or by using the Sieve of Eratosthenes.
Polygons Worksheets
Identifying and working with polygon shapes.
Probability Worksheets
Determine the probability of certain outcomes.
Puzzle Match Math Games
Printable puzzle pieces that you can cut out for students to match up. Great for learning centers, small group activities and independent practice.
Pythagorean Theorem
Find the lengths of the sides of a right triangle with the Pythagorean theorem formula.
QR Code Worksheets
Students use an iPad or smartphone to scan QR codes to complete or check problems on each of these math worksheets.
Ratios
Practice comparing pairs of quantities using ratios.
Reflection, Rotation, and Translation
Identify the reflected, rotated, and translated shapes.
Roman Numerals
Learn to read and write Roman numerals with these printable worksheets and activities.
Rounding Numbers Worksheets
Rounding numbers to the nearest tens and hundreds.
Scientific Notation
Learn to write numbers in scientific notation.
Secret Code Math
On these worksheets, students will use the key to decode the secret numbers in each addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division problem.
Similar and Congruent Worksheets
Identify similar and congruent shapes.
Skip Counting by 100s
Use these worksheets to teach students about skip counting by hundreds.
Skip Counting by 10s
Review counting by tens with these printables.
Skip Counting by 11s
Count elevens, multiply by elevens, and fill in missing numbers.
Skip Counting by 12s
Fill in empty boxes and word problems by counting by twelves.
Skip Counting by 25s
Skip counting by twenty-fives is important if you’re teaching your students to count money.
Skip Counting by 2s
Use these printables to teach students to skip count by intervals of two.
Skip Counting by 3s
The set of worksheets on this page will help students learn to count by threes.
Skip Counting by 4s
If you’re teaching students to count by fours, try these worksheets.
Skip Counting by 5s
When you teach students to count nickels or count by fives, these worksheets may be helpful to you.
Slides, Flips, and Turns Worksheets
Tell whether the shapes were flipped, slid, or turned.
Slope
On these worksheets, students will use graphs, ordered pairs, and tables to calculate the slopes of straight lines.
Solid Shapes Worksheets
Name the geometric solid shapes: rectangular prisms, cubes, spheres, and cylinders.
Special Numbers
These worksheets cover a variety of place value concepts, including even/odd, finding the value of digits, and writing numbers in expanded form.
Subtraction
Single and multi-digit subtractions. Includes 1, 2, 3, and 4-digit numbers. There are links to decimal and money subtraction too.
Subtraction: Basic
Practice basic, single-digit subtraction facts; concept and drill worksheets.
Subtracting Fractions
Practice subtracting fractions and mixed numbers with these printable worksheets and task cards.
Surface Area
Calculate the surface area of rectangular prisms and other three-dimensional shapes.
Symmetry Worksheets
Find the lines of symmetry, identify symmetrical figures, and complete the symmetrical shapes.
Tally Marks
Learn to count objects with tally marks.
Temperature Worksheets
Read the Celsius and Fahrenheit thermometers and state the temperature.
Ten-Frame Math
Printable ten-frame activities for teaching counting, basic addition, and simple subtraction.
Tessellation Worksheets
Teach students to recognize geometric tessellation of two-dimensional shapes.
Time Worksheets
Learn about telling time to the nearest minute, hour, and quarter hour.
Time: Elapsed Time
Determine the amount of time that has passed.
Venn Diagrams (Math)
This page has math Venn Diagram worksheets.
Volume — Graduated Cylinders
These worksheets feature pictures of graduated cylinders.
Volume Worksheets
Calculate the volume of solid shapes. Includes volume «counting cubes,» rectangular prisms, cones, cylinders, and spheres.
Word Problem Worksheets (by Type)
Practice word problems for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Word Problem Worksheets (Mixed)
Review mixed word problem skills at different grade levels.
Word Problems (Multiple Steps)
These word problems have multiple steps, and require students to use critical thinking skills.
Math Index Pages
Addition Worksheets
Here you can link to all types of addition worksheets, including basic facts, fraction addition, 2-digit, 3-digit, and 4-digit addition.
Fraction Worksheets
Index of our basic and advanced-level fraction worksheets.
Geometry Worksheets
Learn area, perimeter, symmetry, polygons, solid shapes, and more.
Graphing Worksheets
Choose from pie graphs, bar graphs, and line graphs.
Skip Counting Worksheets
Count by 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 10s, 25s, or 100s.
Subtraction Worksheets
Here’s an index page that links to all of the subtraction sections of our website.
Math Skills Worksheets
This page contains only a partial index of the math skills worksheets on S.T.W.
Full Website Index
View the complete index of all Math, ELA, Spelling, Phonics, Grammar, Science, and Social Studies worksheets found on this website.
Addition Problems – Free Addition Problems for Kids – Math Blaster
Math Blaster has a large collection of addition worksheets, addition word problems and addition activities — all free, all printable.
Add the Slow Snails
‘Add the Slow Snails’ is a cute addition worksheet that’s replete with cute pictures of little snails! See more
More Numbers Make it Fun!
If your kids love solving addition worksheets, download and give her this one to solve! She’ll love the…See more
The more Addends, the more Fun!
We all know it get a little tougher as kids gravitate from one grade to another. This particular addition worksheet … See more
Add Here and There
Once elementary addition worksheets are mastered, kids can gradually gravitate towards such worksheets …See more
Add the Strawberries in the Bush
How many strawberries can you find in the bush? Download this free addition printable and ask them this question! See more
The Car Trains of Gridlokia
Help the traffic police manage Gridlokia’s traffic by solving the math problems and letting them know how many cars can be joined to form each train.
A Penny for Your Name
With values for each letter, students add the values of the letters in their names to find out whose name is the most valuable. See more
Beautiful Butterflies
In this math worksheet, students practice adding and subtracting to balance equations as they put each of the beautiful butterflies in their right places. See more
Boat Ride
In this math worksheet, students must figure out how many glasses of orange juice, grapefruit juice and apple juice to fetch for the passengers on the ferry. See more
Calculator Match
Test your mathematical ability by solving math problems and comparing your answers with the calculator’s in ‘Calculator Match’. See more
Up a Tree
Give kids some addition practice with ‘Up a Tree’, a fun addition worksheet for kids. See more
Ring Toss
Help kids sharpen their addition skills with ‘Ring Toss’, a challenging addition worksheet for kids.
Space Numbers
Help your kids understand the concept of fact families with ‘Space Numbers’, a fun worksheet on addition and subtraction fact families. See more
Bug Capture
Bug Capture is an addition game based on luck. Players roll two dice and add up the total, trying to get the right sum in each round. This game is perfect for practicing mental math. See more
Target 50
Target 50 is a challenging math game that can be used to help kids develop their problem solving skills, addition and subtraction skills and mental math skills. See more
Chain of Clues
In Chain of Clues, players must read the clues on each other’s shirts and figure out the answer to each one, collecting signatures as they solve the clues. There’s a lot of addition and subtraction involved, making this game great for practicing mental math. See more
Secret Code
It’s time to crack the code! Solve all the addition and subtraction problems in our free math worksheet and figure out the ‘Secret Code’! See more
Highway 99
Give kids some math practice by having them solve addition problems in ‘Highway 99’, our fun math activity for 1st graders.
Frankie Goes Shopping
Teach first graders to solve double-digit addition problems with ‘Frankie Goes Shopping’, a fun math activity for kids! See more
Even or Odd
Even or Odd is a fun printable card game, great for practicing mental math, addition and/or subtraction. See more
Add it Up!
Figure out how much equipment to order in our fun, free and printable addition worksheet for kids, ‘Add it Up!’. See more
Though addition problems are one of the first math problems a child encounters in school, kids continue to use this basic skill throughout their adult years. Further, as kids grow older they learn to add more and more complex mathematical numbers. But for this, it is essential that they have no difficulty solving basic addition problems.
Practicing Addition Problems
Addition is much like an introduction to mathematics. Children who have difficulty solving addition problems will find it very difficult to learn other skills in mathematics.
Addition Word Problems
Addition word problems may be a bit trickier than simple addition problems because they require reading and comprehension skills apart from addition skills. In order to solve addition word problems, children must be able to understand how addition is used in everyday life. For most children, this concept is not difficult to understand at all. As with simple math problems, enough practice solving addition word problems will remove difficulties children may have with them. Parents can easily find large collections of addition word problems online for their kids.
Fun Games with Addition Problems
Many free online games are designed to allow children to learn while having fun.
Addition Worksheets | Free — Distance Learning, worksheets and more: CommonCoreSheets
|
Want to help support the site and remove the ads? Become a patron via patreon or donate through paypal. |
|
|
Jump to a Heading
Filter
k
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
No Filter
Understanding Addition
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
koa1Matching Addition ★
Each worksheet has 10 problems matching a numeric equation to a visual equation.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
koa3Which Equals ★
Each worksheet has 8 problems determining which equations equal a number.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
koa2Addition Boxes (to ten) ★M
Each worksheet has 12 problems identifying the missing number.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Finding 1 More and 1 Less ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding 1 more or 1 less than a number.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
koa4Adding to Ten ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding the missing number that makes 10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1nbt2bBreaking Apart Tens and Ones ★
Each worksheet has 18 problems breaking apart a two digit number into tens and ones.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa5Counting Up and Down ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems counting up or down within 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Traditional Addition
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
koa5Adding & Subtracting Within 5 ★M
Each worksheet has 16 problems adding within 5.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa6Adding Within 20 ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding within 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa6Adding Within 20 (horizontal) ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding the sum of numbers within 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1nbt42nbt5Adding Within 100 ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding the sum of numbers within 100.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1nbt4Adding Within 100 (horizontal) ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding the sum of numbers within 100.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1nbt4Adding Multiples of Ten ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding (within 100) a 2 digit number and a multiple of ten.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1nbt4Adding Multiples of Ten (Horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding (within 100) a 2 digit number and a multiple of ten.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Adding Multiples of Ten to Multiples of Ten ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding a multiple of ten to a multiple of ten.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa8Solving Mixed Problems within 20 (+ -) ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems solving addition and subtraction problems.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt5Solving Mixed Problems within 100 (+ -) ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems solving addition and subtraction problems.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt73nbt2Solving Mixed Problems within 1000 (+ -) ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems solving addition and subtraction problems.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2oa2Adding and Subtracting within 20 ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding and subtracting within 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt7Adding Within 1,000 ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding the sum of numbers within 1,000.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
4nbt44 Digit Plus 4 Digit ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems with addends between 1,000 and 9,999.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
4nbt44 Digit Plus 4 Digit (horizontal) ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems with addends between 1,000 and 9,999.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Addition (Vertical) ★
Each worksheet has 15 problems solving mixed addition problems.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Addition (Horizontal) ★M
Each worksheet has 12 problems solving addition equations.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Addition and Subtraction (Horizontal) ★M
Each worksheet has 12 problems adding and subtracting.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Finding Missing Addend (Within 10) ★M
Each worksheet has 15 problems finding the missing addend with the sum being less than 10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Adding Multiples of Ten to Multiples of Ten ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding a multiple of ten to a multiple of ten.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Addition and Subtraction with Regrouping ★M
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding and subtracting with regrouping.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Word Addition
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
koa2Word Addition Within 10 ★M
Each worksheets has 12 problems finding the result of an addition problem.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa1Word Addition Within 20 ★M
Each worksheets has 12 problems finding the result of an addition problem.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2oa1Word Addition Within 100 ★M
Each worksheets has 12 problems finding the result of an addition problem.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Finding Sum with Rounding
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
Finding Sums with Rounding ★M
Each worksheet has 10 problems determining the sum with rounding to either tens or hundreds.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Multiple Addends
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
1oa2Adding with Multiple Addends (3 Addends Less than 20) ★M
Each worksheet has 15 problems adding 3 digits. Sum is less than 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa2Adding Multiple Addends (3 Addends Less than 20) (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems adding with twenty.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa23 Addends (Less than 20) Word ★M
Each worksheet has 10 problems adding 3 digits. Sum is less than 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa3Combining Addends ★M
Each worksheet has 14 problems filling in a blank to make an equal problem.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt6Three Addends (2 Digit) ★M
Each worksheet has 14 problems adding three addends with each addend having two digits.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt6Four Addends (2 Digit) ★M
Each worksheet has 14 problems adding four addends with each addend having two digits.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
3nbt2Multiple Addends (3 Digits) Word ★
Each worksheet has 10 problems with 3 addends with each addend between 100 and 999.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Addition Strategies
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
1oa6Creating Tens ★
Each worksheet contains 7 problems breaking an addition problem into an adding with ten problem.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa6Finding Equivalent Addition Problems with 10 ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Finding Missing Digit ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems finding the missing digit to make an equation true.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Finding Sum with Rounding ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems using rounding to find the sum mentally.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Finding Sums with Rounding ★M
Each worksheet has 10 problems determining the sum with rounding to either tens or hundreds.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2md6Finding Sum And Differences with Numberlines ★
Each worksheet has 10 problems using a numberline to find the answer to a problem.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt9Addition Strategies ★
Each worksheet has 11 problems using addition place value strategies to solve.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Creating Equations ★
Each worksheet has 20 problems determining the sign to make an equation true.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
4nbt4Addition Using an Open Numberline ★M
Each worksheet has 8 problems using an open numberline to find the difference.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Addition Drills
link
Drag ⇄ to Scroll
Click to Open
1nbt5Finding Ten More and Ten Less ★
Each worksheet has 50 problems finding ten more or ten less than a two digit number.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1oa6Add and Subtract (Within 20) ★
Each worksheet has 50 problems adding and subtracting below 20.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2nbt8Adding-Subtracting 10s and 100s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems finding 10 more, 10 less, 100 more and 100 less than a number between 100 and 900.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Customize
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Adding 9s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems adding a number plus 9.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Adding to Multiples of Ten ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems identifying what must be added to equal a multiple of 10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
0s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 0+1 up to 0+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 1+1 up to 1+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 2+1 up to 2+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
3s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 3+1 up to 3+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
4s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 4+1 up to 4+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
5s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 5+1 up to 5+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
6s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 6+1 up to 6+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
7s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 7+1 up to 7+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
8s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 8+1 up to 8+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
9s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 9+1 up to 9+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
10s ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 10+1 up to 10+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Mixed ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 1+1 up to 10+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
0s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 0+1 up to 0+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
1s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 1+1 up to 1+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
2s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 2+1 up to 2+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
3s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 3+1 up to 3+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
4s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 4+1 up to 4+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
5s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 5+1 up to 5+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
6s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 6+1 up to 6+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
7s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 7+1 up to 7+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
8s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 8+1 up to 8+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
9s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 9+1 up to 9+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
10s (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 10+1 up to 10+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Mixed (horizontal) ★
Each worksheet has 100 problems ranging from 1+1 up to 10+10.
Create New Sheet
One atta Time
Flash Cards
Share
Distance Learning
Select a Worksheet Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Version 5 Version 6 Version 7 Version 8 Version 9 Version 10Grab ’em AllCreate New Sheet
Advertisement
Types of Addition and Subtraction Problems Samples use whole numbers
Overview
- Join problems
- Separate problems
- Part-part-whole problems
- Compare or equalize problems
- Samples to classfiy
Join Problems
(start number + change number = sum or result)
Missing Sum or Result Unknown
(start number + change number = ____________)
- Pete had 3 apples.
Ann gave Pete 5 more apples, How many apples does Pete have now?
- Sandi had 7 dimes. Mike gave her 4 more. How many dimes does Sandi have altogether?
Missing Change Addend Unknown
(start number + ____________ = sum or result)
- Kathy had 5 pencils. How many more pencils does she have to put with them so she has 7 pencils altogether?
- Sandi has 7 dimes. Mike gave her some more. Now Sandi has 11 dimes. How many did Mike give her?
Missing Start or Initial Addend Unknown
(____________ + change number = sum or result)
- Bob got 2 cookies. Now he has 5 cookies. How many cookies did Bob have in the beginning?
- Sandi has some dimes. Mike gave her 4 more. Now Sandi has 11 dimes. How many dimes did Sandi have to begin with?
Separate Problems
(start — change = difference or sum or result)
Resulting Difference or Sum Unknown
(start number + change number = ____________)
- Sandi has 11 dimes.
She gave 4 dimes to Mike. How many dimes does Sandi have now?
- Joe had 8 marbles. Then he gave 5 marbles to Tom. How many marbles does Joe have now?
Missing Change Addend/Subtrahend Unknown
(start number + ____________ = difference or sum)
- Sandi had 11 dimes. She gave some to Mike. Now she has 7 dimes. How many did she give to Mike?
- Fred had 11 pieces of candy. He lost some of the pieces. Now he has 4 pieces of candy. How many pieces of candy did Fred lose?
Initial Addend/Minuend Unknown
(____________ + change number = difference or sum)
- Sandi had some dimes. She gave 4 to Mike. Now Sandi has 7 dimes left. How many dimes did Sandi have to begin with?
- Karen had some word problems. She solved 2 of them. She still has 3 word problems. How many word problems did she have to start with?
Part — Part — Whole Problems
(part + part = whole)
Missing Whole or Sum Unknown
(part + part = ____________
- There are 6 boys and 8 girls on the volleyball team.
How many children are on the team?
- Bobbi has 3 dimes and Azzie has 5. If they put them together how many do they have?
- Mike has 5 pennies and 10 dimes. How many coins does he have?
- Mike has 5 dimes and Sandi has 10 dimes. They put there dimes into a piggy bank. How many dimes did they put into the bank?
- Sara has 6 sugar donuts and 9 plain donuts. Then she puts them all on a plate. How many donuts are there on the plate?
Missing Part Unknown
(part + ____________ = whole) or
( ____________ + part = whole)
- Carlos had 8 quarters in his pocket. He reaches in and pulls out four. How many are still in his pocket?
- Brian has 14 flowers. Eight of them are red and the rest are yellow. How many yellow flowers does Brian have?
- Bobbi and Sandi put 12 dimes into a change purse.
Sandi put in 8. How many did Bobbi put in? or Mike and Sandi put 11 dimes into a piggy bank. Mike put in 7 dimes. How many dimes did Sandi put in?
- Mike has 10 coins. 7 of his coins are dimes, and the rest are pennies. How many are pennies?
- Joe and Tom have 8 marbles when they put all their marbles together. Joe has 3 marbles. How many marbles does Tom have?
Compare or Equalize Problems
(one value + or — difference = second value)
Difference Unknown
(one value + or — difference = second value)
(one value — second value = difference)
- Joe has 3 balloons. His sister Connie has 5 balloons. How man more balloons does Connie have than Joe?
- Janice has 8 sticks of gum. Tom has 2 sticks of gum. Tom has how many sticks less than Janice?
- Mike has 11 dimes and Sandi has 5. How many more dimes does Mike have than Sandi?
- Mike has 11 dimes.
Sandi has 5 dimes. How many fewer dimes does Sandi have than Mike?
Larger Unknown
(one value + difference = second value)
(second value — difference = first value)
- Luis has 6 goldfish. Carla has 2 more goldish than Luis. How many goldfish does Carla have?
- Dad bought 18 bottles of milk on Sunday and on Monday he brought 6 bottles less. How many bottles did he bring on Monday?
- Mike has 4 more dimes than Sandi. Sandi has 7 dimes. How many dimes does Mike have?
- Sandi has 4 fewer dimes than Mike. Sandi has 7 dimes. How many dimes does Mike have?
- Jane has 7 dolls. Ann has 3 dolls. How many dolls does Jane have to lose to have as many as Ann?
- Connie has 13 marbles. If Jim wins 5 marbles, he will have the same number of marbles as Connie. How many marbles does Jim have?
Smaller Unknown
(one value + difference = second value)
(second value — difference = first value)
- Maxine has 9 sweaters.
She has 5 sweaters more than Sue. How many sweaters does Sue have?
- Jim has 5 marbles. He has 8 fewer marbles than Connie. How many marbles does Connie have?
- Sandi has 4 fewer dimes than Mike. Mike has 11 dimes. How many dimes does Sandi have?
- Mike has 4 more dimes than Sandi. Mike has 11 dimes. How many dimes does Sandi have? Susan has 8 marbles.
- Fred has 5 marbles. How many more marbles does Fred have to get to have as many marble s as Susan has?
Where would you put these?
- There were 6 boys on the soccer team. Two more boys joined the team. Now there is the same number of boys as girls on the team. How many girls are on the team?
- There were 11 glasses on the table. I put 4 of them away so there would be the same number of glasses as plates on the table. How many plates were on the table?
- There were some girls in the dancing group.
Four of them sat down so each boy would have a partner. There are 7 boys in the dancing group. How many girls are in the dancing group?
- Jim has 7 quarters. Ann has 3 quarters. How many quarters does Jim have to spend to have as many as Ann?
Ideas originated from: Research on Whole Number Addition and Subtraction. Karen C. Fuson in Handbook of Research on Mathematics Teaching and Learning. Ed. Douglas A. Grouws. Macmillan Publishing Co. 1992.
Dr. Robert Sweetland’s notes
[Home: thehob.net ]
Lesson 22. problem solving. addition and subtraction table with the number 2 — Mathematics — Grade 1
Mathematics, Grade 1. Lesson 22
Problem solving. Addition and subtraction table with the number 2.
List of questions addressed in the lesson:
- Drawing up addition and subtraction problems according to a drawing, diagram, table, table.
- Solving problems in one action to increase (decrease) the number by several units.
- Explanation based on the illustration of adding to the number by 2, subtracting from the number by 2.
- Calculations of the form + 2, — 2.
- Supplementing the conditions of the problems with missing data or a question.
Glossary on the topic
Task components — condition, question, solution, answer.
Addition and subtraction problems.
Task in the form of a diagram, table or diagram.
The relationship between the condition and the question of the problem.
Calculations of the form + 2, — 2.
Keywords
Text problem; the task; task question; the solution of the problem; addition to the number by 2; subtraction from the number by 2.
Basic and additional literature on the topic of the lesson :
- Moro M. I., Volkova S. I., Stepanova S. V. Mathematics.
Textbook. 1 class At 2 hours, part 1. — M .: Education, 2017. — p. 90 – 93.
2.MoroM. I., Volkova S. I. Mathematics workbook. 1 class 1 hour — M .: Enlightenment, — p. 35 – 36.
At the lesson we will learn how to make a table for adding and subtracting the number 2. We will learn to compose problems according to pictures and solutions, explain and justify the action chosen to solve the problem. Let’s solve problems in one action to increase (decrease) the number by several units.
Main content of the lesson
Read the entry:
A bird was sitting on a branch, two more flew to it.
Can this entry be called a task.
This is only a condition of the problem, no question.
Compose a question for the problem.
How many birds have become?
Solve the problem.
Two added to one makes three.
How to answer the problem question?
Answer: there are three birds on the branch.
|
Conditions of the problem |
sat on the branch, another 2. |
|
|
Problem question |
How many birds are there? |
|
|
Problem solution. |
1 + 2=3 (p.) |
Answer: 3 birds. |
Make another problem from this picture so that it can be solved by subtraction.
3 birds were sitting on a branch. Two birds have flown away. How many birds are left on the branch?
How to solve such a problem?
Subtract two from three and you get one.
How to answer the problem question?
Answer: there is only one bird left on the branch.
|
Condition of the problem |
Three birds were sitting on a branch. |
|
|
Problem question |
How many birds are left on the branch? |
|
|
Problem solution. |
3 — 2=1 (p.) |
Answer: 1 bird. |
What number did we add and subtract in these problems?
The number two
The theme of our lesson: “Problem solving. Addition and subtraction table with the number 2.
Look at the following picture and write the appropriate addition example.
|
2+2=4 |
|
|
2 + 2 = 4 |
4 — 2 = 2 |
Consider the following drawings. Write the appropriate addition and subtraction examples for each picture.
|
3 + 2 = 5 |
5 — 2 = 3 |
|
9000 9000 9 + 2 = 6,0004 ,0005 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 6 — 2 = 4 |
|
5 + 2 = 7 |
7 — 2 = 5 |
|
6 + 2 = 8 |
— 2 = 6 |
|
9000 9000 + 2 = 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 — 2 = 7 |
|
8 + 2 = 10 |
10 — 2 = 8 |
See what happened?
This is an addition and subtraction table with the number two.
Look at the left column of the table, how was it compiled?
Two were added to the result.
And the right column?
Subtracted two from the result.
Look at the number series
It is very easy to add or subtract the number two with it.
When we add or subtract the number two, we jump over one number.
Try it yourself, add two to one.
We start moving from point one to the right, jump over one number, stop at point three, we get …
Three.
|
1 + 2 = 3 |
8 — 6 = 2 |
out of eight deduct two.
We start moving from point eight to the left, jump over one number, we get …
Six.
|
1 + 2 = 3 |
8 — 2 = 6 |
Parsing of training tasks.
Solve examples using the number series:
Answer:
Write down the missing numbers, fill in the chips with the appropriate color. Remember how they are compiled and fill in the tables for addition and subtraction with the number 2.
Answer:
Look at the picture. What expressions fit it.
Highlight matching expressions with color.
Answer:
Hint: think about what condition of the problem can be made according to the picture and what questions to answer.
Fill in the gaps so that the equalities are true.
Answer:
Solve math chains:
Answer:
Connect the dots in order. Who succeeded, write down the answer.
Answer: Elephant.
paint over the red color of the expression, the values of which are 6. Green — values of which are 7.
|
5 + 2 |
9000 9000 — 1 |
9000 9000 9000 + 1 |
7 + 2 |
8 — 1 |
6 — 2 |
|
6 — 0 |
9 — 2 |
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 5 + 1 |
4 + 2 |
0 + 7 |
Answer:
|
5 + 2 |
9000 9000 — 1 9 — 1 9 — 1 |
6 + 1 |
7 + 2 |
8 — 1 |
9000 |
9 — 2 |
8 — 2 |
5 + 1 |
4 + 2 |
Read the condition, the question of the problem and solve it.
They circle above the flowers.
And the same number of dragonflies.
How many insects circle over the flowers?
Answer:
Mark the correct answer.
How many triangles are in the picture:
Answer:
Find the pattern. Insert the missing trailer. Indicate the corresponding numbers on all trailers.
Answer:
Look at the picture. Paste the data into the empty boxes.
Answer:
Match the condition and the solution of the problems. Insert the missing words in the problem statements. Natasha had a It became 2 …. How many carrots did Natasha have?
4 + 2
Serezha had . It became 2 …. How many apples did Seryozha have?
3 — 2
Was in a vase. It became 2 …. How many daisies are in the vase?
5 — 2
There was .
SOLUTION
Natasha had . It became 2 more. How many carrots did Natasha have?
4 + 2
Serezha had . It became 2 less. How many apples did Seryozha have?
3 — 2
Was in a vase. It became 2 less. How many daisies were in the vase?
5 — 2
There was . It became 2 more. How many cucumbers were on the plate?
4 + 2
Hint: the words greater than or less than.
Complete the table.
Three school environmental groups took part in the action «Plant a tree!». The table records the number of trees they planted. Mark with a sign which unit planted the most trees.
Answer:
Hint: first count how many trees each unit planted, and then tick off.
Look at the picture and choose the correct answer.
Will this money be enough to buy 2 small chocolates and a bun.
Answer:
Mathematics: lessons, tests, tasks.
- Items
-
-
Start control
-
Color, shape, size
-
Item Comparison
-
Point, straight line, curve and segment
-
Features of polygons
-
Spatial and temporal representations
-
Combining objects into groups and pairs
-
Comparison (more, less, same)
-
Comparison and action marks
-
Addition
-
Subtraction
-
-
-
many and one
-
Number 1.
Number 1
-
Number 2. Number 2
-
Number 3. Number 3
-
Number 4. Number 4
-
Number 5. Number 5
-
Numbering.
How? 1 to 5
-
Examples for addition and subtraction from 1 to 5
-
Comparison of numbers from 1 to 5
-
Text problems (from 1 to 5)
-
Tasks for ingenuity (from 1 to 5)
-
-
-
Number 6.
Number 6
-
Examples for the amount
-
Text problems (sum)
-
Points, lines, borders and areas
-
-
Commutative law of addition
-
-
Difference Examples
-
Text tasks (difference)
-
Line segment.
Parts of a cut
-
Number 7. Number 7
-
Broken line. Polygons
-
Expressions
-
Number 9. Number 9
-
Parts of figures (parts and whole)
-
-
Addition table.
Numbers 1 to 9
-
-
Number 0. Number 0
-
Numbering. How? 0 to 10
-
Examples 0 to 10
-
Comparison of numbers from 0 to 10 and expressions
-
Text problems (from 0 to 10)
-
Tasks for ingenuity (from 0 to 10)
-
Equal figures.
Numbering (alphabetic, Roman)
-
-
Enlarge/reduce by…
-
-
Measure of length — centimeter
-
Measure of length — decimeter
-
Weight
-
Volume
-
-
How much more? How much less?
-
-
Counting in tens
-
Counting round numbers
-
-
-
Numbering.
How? 11 to 20
-
Examples 11 to 20
-
Comparisons of numbers from 11 to 20
-
Tasks for comparison
-
Text problems (from 11 to 20)
-
Tasks for ingenuity (from 11 to 20)
-
Solving compound problems
-
The equation
-
Two-digit numbering
-
Addition and subtraction of two-digit numbers
-
Addition table within 20
-
-
Numbers from 20 to 100.
Numbering. Numbers and numbers
-
-
Associative law of addition. Parentheses
-
Addition table. Numbers 0 to 18
-
Subtract the amount from the number
-
Rules for adding and subtracting numbers within 20 with a transition through a dozen
-
Adding and subtracting numbers within 100 without going through ten
-
Rules for adding and subtracting numbers within 100 with a transition through a dozen
-
Rules for adding and subtracting numbers within 100
-
-
-
Finding the perimeter
-
Solving problems in two steps
-
-
-
Measure of length — meter
-
Kilogram
-
Liter
-
-
-
Equation (sum)
-
Equation (difference)
-
-
-
Concept of multiplication
-
Commutative law of multiplication
-
Multiplication by 2 (table)
-
Multiply by 3 (table)
-
Multiplication by 4 (table)
-
Multiply by 5 (table)
-
-
Division
-
Even and odd numbers
-
-
Expressions without brackets
-
Expressions with brackets
-
-
-
Learn about the beam
-
Figure angle and its characteristics
-
Characteristics of right, obtuse and acute angles
-
-
-
Digital Olympiad
-
International Olympiad YaKlass
-
-
-
Zoom in.
.. Zoom in… Zoom out… Zoom out…
-
More by… More by… Less by… Less by…
-
-
-
Multiply by 6 (table)
-
Multiplication by 7 (table)
-
Multiply by 8 (table)
-
Multiply by 9 (table)
-
-
-
Finding the unknown multiplier
-
Finding an unknown dividend
-
Finding the unknown divisor
-
-
-
Polyline Properties
-
Triangles.
Types of triangles
-
-
-
Multiplication and division by 0, 1, 10. Dividing a number by itself
-
Perform multiplication and division of a round number by a single digit
-
Rules for dividing a round number by a round number
-
-
-
Multiply the amount by the number
-
Multiply a two-digit number by a one-digit number
-
-
-
Rules for dividing a sum by a number
-
Rules for dividing a two-digit number by a one-digit number
-
Rules for dividing a two-digit number by a two-digit number
-
Rules for division with a remainder
-
-
-
Finding a fraction of a number
-
Compare shares
-
Finding a number by fraction
-
-
-
Three digit numbers.
Numbering
-
Addition and subtraction of three-digit numbers
-
We perform multiplication and division of a three-digit number by a single-digit number
-
Relationship between quantities
-
-
Calendar
-
-
Numbering
-
Rules for adding and subtracting multi-digit numbers
-
Rules of the associative law of multiplication
-
Multiplying and dividing numbers by 10, 100, 1000
-
Round numbers (multiplication and division)
-
-
-
Time units (hour, minute, day)
-
Millimeter
-
Kilometer
-
-
-
Finding the area of a figure, a rectangle
-
Area units
-
-
-
Digital Olympiad
-
International Olympiad YaKlass
-
-
-
Solution of inequality.
Sets of Solutions
-
Signs ⩽ and ⩾
-
double inequality
-
Estimated amount
-
Difference estimation
-
Evaluation of the work
-
Private valuation
-
Estimating the results of arithmetic operations
-
-
-
Multiplication by a single number.
Distributive law of multiplication with respect to addition
-
Multiply a round number by a single number
-
Performing multiplication by a round number
-
Performing multiplication of round numbers
-
Performing a two-digit multiplication
-
Performing a three-digit multiplication
-
-
-
Dividing a multi-digit number by a single-digit number
-
Dividing a round multi-digit number by a single-digit number
-
Division of a multi-digit number by 10, 100, 1000 with a remainder
-
Dividing a multi-digit number with a remainder by a single-digit number
-
Divide a 3 digit number by a 2 digit number
-
Division with a remainder of a three-digit number by a two-digit number
-
Dividing a multi-digit number by a two-digit number
-
Division with a remainder by a two-digit number
-
Perform division by a three-digit number
-
Division with a remainder by a three-digit number
-
Dividing a round number by a round number
-
-
-
Time units.
Minute. Second
-
Units of mass and area. Hectare. Centner. Ton
-
Approximate calculation of areas
-
Area of a right triangle
-
-
-
Interest
-
The concept of a fraction
-
Compare fractions
-
Fractions.
Finding a part of a number
-
Fractions. Finding a number by its part
-
Division and fractions
-
Finding the part of one number from another
-
Addition of fractions
-
Subtraction of fractions
-
Proper and improper fractions
-
Correct and incorrect parts of quantities
-
Tasks in parts
-
Mixed numbers.
Extracting the integer part from an improper fraction
-
Converting a mixed number to an improper fraction
-
Addition through 1
-
Subtraction with transition through 1
-
Properties of actions with mixed numbers.
Problem solving
-
-
-
Scales
-
number beam
-
coordinate beam
-
Distance between points of the coordinate beam
-
Movement along the coordinate beam
-
Approach speed
-
Removal speed
-
Solving problems for finding speed, time, distance
-
Solving problems on finding work, time, productivity
-
Solving problems to find the price, quantity, cost
-
Operations with composite named numbers
-
New area units
-
-
-
Digital Olympiad
-
International Olympiad YaKlass
-
-
-
Decimal number system.
Roman numeration
-
Numeric and alphabetic expressions
-
Basic geometric concepts: straight line, segment, ray, polyline, rectangle
-
Definition of a coordinate beam
-
Rounding numbers.
Estimating and evaluating the results of calculations
-
Laws of arithmetic operations. Multi-Digit Calculations
-
Solving text problems in an arithmetic way
-
Formulas. Equations. Expression simplification
-
Mathematical language and mathematical model
-
-
-
Division with remainder.
The concept of an ordinary fraction
-
Basic property of a fraction. Reduction and expansion of fractions
-
Proper and improper fractions. Mixed numbers. Concept, writing and reading
-
Comparison of ordinary fractions
-
Addition and subtraction of common fractions and mixed numbers
-
Multiplication and division of an ordinary fraction by a natural number
-
Finding a part of a whole and a number by its part
-
Geometric concepts: circumference and circle
-
-
-
Corner.
Angle measurement
-
Angle bisector. Angle bisector property
-
Triangle. Area of a triangle
-
property of the angles of a triangle. Dimensions of objects of the surrounding world (scale)
-
Distances between two points.
Scale. Scale types
-
Perpendicularity of lines. The distance from a point to a line. Midperpendicular
-
-
-
The concept of decimal fraction. Representing a decimal as a fraction and vice versa
-
Decimals. Comparison
-
Decimals.
Addition and subtraction
-
Decimals. Multiplication
-
Degree with a natural indicator
-
Decimals. Arithmetic mean, division by a natural number
-
Decimals.
Decimal division
-
Interest. Tasks for percentages: finding a percentage of a value and a value by its percentage
-
-
-
Rectangular parallelepiped. Definition, properties
-
Rectangular parallelepiped. Scan
-
Rectangular parallelepiped.
Volume
-
-
-
Digital Olympiad
-
International Olympiad YaKlass
-
-
-
Solve and get TOP points!
-
-
-
Divisibility of natural numbers
-
Signs of divisibility by 2, 3, 5, 9, ten
-
Prime and composite numbers.
Decomposition of a natural number into prime factors
-
Greatest Common Divisor and Least Common Multiple
-
-
-
Positive and negative numbers. Definition of a coordinate line
-
opposite numbers. The absolute value of a number. Integers and rational numbers
-
Comparison of rational numbers
-
Addition of rational numbers using the coordinate line
-
Algebraic sum.
Properties
-
Algebraic sum of rational numbers with the same signs
-
Algebraic sum of rational numbers with different signs
-
Multiplication and division of rational numbers
-
Multiplication and division of ordinary fractions
-
Fractional Expressions
-
Coordinates.
Coordinate plane, point coordinates
-
-
-
The ratio of two numbers
-
Proportion. Basic property of proportion
-
Direct and inverse proportionality
-
Solving Problems with Proportions
-
Miscellaneous tasks
-
-
-
Simplifying expressions, expanding parentheses
-
Solving linear equations
-
Stages of solving linear equations
-
-
-
Basic concepts and facts of the geometry course
-
Parallelism of lines
-
Central and axial symmetry
-
Circle and circle.
Pi. Circumference. Area of a circle
-
Visual representations of the ball, sphere. Formulas for the surface area of a sphere and the volume of a sphere
-
-
-
Digital Olympiad
-
International Olympiad YaKlass
-
-
Collection of interactive models
entertaining tasks and examples in pictures with answers and solutions
Entertaining
mathematics
Grade 1
Why do kids love LogicLike tasks more than tasks from math textbooks?
The professor and his team will teach each child to click both typical and non-standard
math problems.
Select the child’s age
to get started!
Preschooler
First grader
LogicLike.com
children learn to reason, develop logic, ability to mathematics
and cognitive interest.
Recommended thematic courses
online for grade 1
Logic course
and thinking
To begin
Entertaining mathematics
To begin
Why do children and parents choose LogicLike?
What kind of mathematics do children need in grade 1?
The following story often happens: when preparing for the 1st grade
the child liked to solve entertaining tasks, puzzles, examples and tasks.
a quarter and a capable child begins to get bored of the monotonous or too simple for him
assignments.
If you were looking for a mental counting simulator or want to check how much your child has learned
school curriculum, you will love the collection of math tests for grade 1 from
LogicLike.
The LogicLike team knows how to captivate a first grader
mathematics and charge with the desire to learn how to solve any problems. We have more
3500 entertaining tasks, awards, achievements, student rating, personalized certificates.
Try the full fun math course
and logics from LogicLike
- Flexible Mind
and confidence! When children decide
tasks and puzzles on LogicLike, they train the «wiggles»
and develop ingenuity. - Foundation
for IT! Algorithms,
patterns, logic — we have all this. We teach to work with
information, train memory and thinking — we form the potential for success in
IT professions. - We increase
progress! Regular
classes of 20-30 minutes develop logical and mathematical
capabilities. As a result — high grades at school, prizes
at olympiads and competitions, interest in learning increases.
Start the course!
Entertaining mathematics for first graders online
Mathematics classes on LogicLike begin with entertaining logical problems, unusual
examples, puzzles and other tasks in pictures that you want to solve.
mathematical and logical problems, patterns, figures in space and other types
assignments.
Popular categories of assignments for grade 1
Selections from the training course
LogicLike
- Simple addition and subtraction
- Enlargement, reduction by several
units - Composite tasks
- Text logic and
math - Examples for addition and
subtraction for 1st grade - Math puzzles
for 1st class
Addition and Subtraction Problems
Simple problem of finding
sums
To decide
click Start!
Three girls took 1 balloon in each hand.
How many balls do they have?
Watch
answer
Answer:
6.
Mindfulness task
To decide
click Start!
There are two sweets, one cake and three pears on the plate.
How many fruits are on the plate?
Watch
answer
Answer:
3.
Subtraction problem
To decide
click Start!
There were 7 liters of water in a 12-liter barrel, and 8 liters in a bucket.
Water from a bucket filled the barrel to the top.
How many liters of water are left in the bucket?
Find out the answer
Answer:
3.
We have everything you were looking for
Text
and logical tasks
Tasks
mathematics
Examples and tasks
Shapes in space:
2D and 3D
Start classes!
We have built the educational process in an understandable and exciting way for anyone
child format, from simple to complex.
Tasks to increase and decrease the number by several units
What will be the result?
To decide
click Start!
Find out the answer
Answer:
5 apples.
Age problem
Yura was born 2 years earlier than Vanya.
Yuri is now 5 years old.
How old is Vanya?
Find out the answer
Answer:
3.
Finding the Unknown
term and difference
To decide
click Start!
An evil virus hid the numbers in the examples.
Put the correct numbers back in their places.
Find out the answer
Answer:
2 + 3=5
3 − 2 = 1
You can see examples of Olympiad tasks for 1
class or start
to
activities on the site.
Day after day more
100,000 children
pass 10-20 tasks
on the LogicLike website. And how much can you?
Solve problems
Downloads: tasks for developing counting skills
For those who do not currently have the opportunity to study online, we have prepared small selections
assignments for paperwork. You can download and print tasks for practicing oral skills
invoices in pdf format.
To «warm up» the child’s interest in mathematics, we recommend starting with 1 sheet a day.
- Entertaining
tasks for grade 1 for addition and subtraction within 10. - Entertaining
tasks for first graders: addition and subtraction up to 10.
What is the best online course?
We recommend that future and present first graders practice 15-20 minutes a day.
Compound tasks for first graders
Tasks in two or three actions develop memory, logic and mathematical speech.
Composite difference problem
comparison
To decide
click Start!
Condition:
The purple monster ate 4 whole oranges, and the red monster ate 7 halves of the same
oranges.
Question: Who
ate more oranges?
Show
solution
Answer:
Violet.
Solution
1 whole orange = 2 halves.
4 whole oranges = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8 halves.
8 > 7 means Purple ate more than Red.
Multi-action task on
balancing
To decide
click Start!
Condition:
A rabbit is 2 kg lighter than a puppy.
Questions: What
the scale will be higher if the puppy is placed on the left side of the scale, and the rabbit on
right? How after that you need to place the weights on the scales so that they come to
equilibrium?
Find out the answer and
solution
Solution
1.(101).jpg)
the bowl with the rabbit will rise up.
2. In order for the balance to balance, the weight on the bowl
rabbit should be 2 kg heavier than the kettlebell that
we will add to the puppy.
It turns out that you need to put on a bowl with a puppy
weight in 1 kg, and on a bowl with a rabbit — in 3 kg.
Suggested tasks are part of the LogicLike educational platform. Start learning!
Develop logic and mathematical thinking
- Child-friendly theory .
Video tutorials, tips and
hints will help the student to independently deal with even very complex tasks. - Making math fun . game form
and step-by-step methodology make the learning process interesting and effective. - All materials on one site . 17 categories,
over 3500 exciting challenges! The LogicLike team creates new ones every week
interesting tasks that help children understand and love logic and mathematics.
Text Boolean
Fedya has equal number of sisters and brothers.
Who is more in the family: sons or daughters?
Show
answer
Answer:
more sons
(Fedya is also a son).
To decide
click Start!
Kolya and Nadia have the same items.
Anya has a jump rope.
Distribute items to all children.
Find out the answer
Answer:
Kolya and Nadi
— balls. Ira and Anya have jump ropes.
Want more examples of similar tasks? See logic puzzles
for 1 class.
Take the full course from LogicLike!
- 3 steps to start the path to the heights of logic
😎: - 1. Solve 5 problems
- 2. Save account
- 3. Show the platform to the child and solve together 10-15
tasks.
Math tasks for logic
Task with figures on
verbal-logical thinking
To decide
click Start!
Condition:
The professor thought of a figure and gave two clues:
— it is not square and not blue;
— it is round or triangular.
Question: What
did the Professor guess?
Find out the answer
Answer:
orange
triangle.
Take
hint
Prompt
Solving similar mathematical puzzles
promotes the development of verbal-logical
thinking , trains possession skills
basic methods of thinking: highlighting essential
and insignificant features of objects, generalization,
comparison, derivation of the investigation and others.
Continue the pattern
To decide
click Start!
Find a pattern and continue the series with numbers.
Find out the answer
Answer:
20.
Comment:
The difference between each successive number and the previous one
increases by 1 (+1, +2, +3…).
You can see other rules
for 1st grade or start training.
Did you like the material? Share with friends!
Connect to LogicLike!
More than 150,000 children from all over the world have already
do math and logic at LogicLike.com.
Start learning!
Start learning
We will teach a child
Reasoning and making decisions
Solve any logic problem
Think flexible
and non-standard
Other collections of tasks by age
Tasks for preschoolers
Tasks for grade 2
Tasks for grade 3
Tasks for grade 4
You are here: LogicLike Math and Logic Online Simulator
in mathematics for grade 1
Simple problems for 5-6 years —
Contents
Simple problems for 5-6 years
Sasha is taller than Misha, but shorter than Vasya.
Masha turned 5 years old two years ago, and Vanya will be 7 years old in a year. Which one is older?
Several birds were sitting on a branch. Then four flew away, and only 2 birds remained. How many were there at the beginning?
Chickens were walking around the fence. I see that there are 6 chicken legs. How many chickens are there?
Cats and hens walked around the fence, and in total they had 8 legs. How many chickens could there be, and how many cats?
What if they only have 2 heads? 3 heads? 4 heads?
One car has 4 wheels. How many wheels do two cars have? Three cars?
Sasha and Mitya draw with red and blue pencil. Sasha doesn’t paint in blue.
What color does Mitya draw?
The cat is walking from the sixth floor to the third.
Vanya thought of a number. It is greater than 6 but less than 8. What is this number?
Playing in a store — we buy toys for fun, counting coins, discussing change
Playing in a cafe — everyone decides what to buy and calculates the amount — how much it will cost
One corner of a square table has been sawn off. How many corners does this table have now? Draw a picture to explain your answer.
Mathematics for children aged 5-6
The requirements of the modern school curriculum are such that by the time a child enters the first grade, elementary mathematical concepts must be formed. These include knowledge of numbers and basic signs, the ability to count within ten and cope with simple math problems in which children 5-6 years old need to perform addition and subtraction. At the same time, as you know, preschoolers learn much faster and easier information that is presented in a playful way. The specialists of the Razumeikin development site sought to take these factors into account when preparing online tasks for teaching mathematics to children aged 5. All exercises are presented in an easy and interesting way.
The section «Other Mathematical Concepts» introduces the child to the basic signs («greater than», «less than» and «equal to») and teaches them how to use them. With the help of our site, you can easily and productively study. Completing tasks in mathematics, preschoolers of 6 years old learn ordinal counting and the basics of measuring length, mass and volume.
When developing a set of exercises for toddlers of senior preschool age, our specialists tried to make them not only as understandable and exciting as possible, but also really useful in practical terms. Almost all online math tasks for children aged 6 are built in the form of a game and have detailed explanations. You can find them in the training video before the exercise. An explanation for the test tasks in the section «Mathematics for preschoolers 5-6 years old» is also given if the answer that the child derived turned out to be incorrect or insufficiently complete.
Features of the presentation of material
In order for the process of teaching mathematics to children of 6 years old not cause difficulties, the specialists of the developing site «Razumeikin» prepared special thematic pictures and voiced text for each task.
How are results evaluated?
For completing tasks in mathematics for preschoolers 5 years old, the Razumeykin website provides a whole system of rewards. We are convinced that it allows you to increase children’s interest in learning and form positive motivation.
Toddlers are rewarded for completing tasks in the Math for Preschoolers 5 Years section. Our website provides medals, cups, pennants and diplomas.
Almost all tasks-games in the section «Mathematics for children 6 years old» are evaluated depending on the attempt at which the child gave the correct answer. If necessary, you can return to the completed exercise. Having done the task in the section «Mathematics for preschoolers 5-6 years old» again, the child will be able to improve the previous result and get a higher reward.
Before starting the exercises in the section «Mathematics for children 5-6 years old», we recommend that you take a test.
Math for children 4, 5, 6, 7 years old
Here you can find a lot of useful materials on the topic «Math for children for children 4, 5, 6, 7 years old», which you can print on a printer and engage with children, both at home and in preschool and school institutions. Learning math in a playful way is a very interesting activity even for those children who do not show much love for learning. Also, such tasks are great for little fidgets who cannot sit in one place for 5 minutes. Each game task is designed for a younger child — it is designed in such a way that the child does not get tired, and at the same time receives a useful portion of knowledge and skills. The main thing is not to solve all the tasks at once, only one at a time!
Mathematics for children 4, 5, 6, 7 years old — choose a section for learning
Mathematics for children is presented here in several sections, each of which develops certain skills in teaching a child.
Learn to Count to 10 — Fun Picture Activities
In this section, we learn to count to 10 with fun picture activities for preschoolers. Learning to count in a playful way is a very interesting activity even for those children who do not show much love for learning.
Learn to count to 20 — Game tasks in pictures
Here we learn to count to 20 by completing interesting game tasks in pictures.
Fun math pictorial tasks for kids
Here are some interesting and colorful math pictorial tasks for kids who are getting ready for school or are in 1st grade. Assignments can be very useful for teachers in kindergartens and elementary schools to teach children about mathematical expressions more effectively.
Geometric shapes for children — Interesting tasks
Here you can download and print geometric shapes for children in the form of interesting tasks in pictures, the implementation of which will not only benefit the child, but also a lot of fun.
Numbers for kids — Download, print and cut!
Numbers for children are presented here in various designs — numbers in the form of flowers, three-dimensional, gold, with various textures, ice, puzzle numbers, as well as simple numbers in black and red.
Mathematical signs and symbols — Picture tasks
Learning math signs and symbols with interesting picture tasks.
Other interesting sections with mathematics
Educational games «Math for kids»
quick memorization of numbers, and also allow the child to understand the complex technology of counting for his age.
Math games for children from 4 to 6 years old
Games designed to prepare a preschooler for the first mathematical knowledge and numeracy. Here you will find interesting colorful games in which the child will need to find and count the specified number of objects or living beings. Children of this age really like to count, especially in a playful way.
Math examples online
A great opportunity for younger students to practice their knowledge of mathematics. After all, in these tasks you need to be able to quickly solve examples, because a certain time is allocated for the passage of each task.
All educational materials presented in the section «Mathematics for children 4, 5, 6, 7 years old» are very useful for preschoolers to prepare for school, as well as for younger students to practice and test their knowledge.
Riddles in poetry and logical tasks for children aged 6-7 | Material on mathematics on the topic:
Tasks for logic. Grade 1 , , , , , , , , , , , , , How many socks did Nina’s grandmother knit?
Chickens walk around the yard. Petya counted 6 legs for all chickens. How many chickens?
Tolya has 2 pairs of mittens. How many mittens on the left hand?
What is the smallest number?
There are four children in the family: there are as many sisters as there are brothers and sisters. How many sisters?
From the barrel they took 2 times 2 full buckets of water. How many buckets of water did you take?
Kittens are sitting in a basket.
6 guys rode on the hill. The two left for lunch, but after dinner they returned to the hill. How many guys were on the hill?
Spider has 4 pairs of legs. How many legs does a spider have?
Yura has 3 dice and Serezha has 2 dice. There is a box on the table that contains 4 cubes. Will the boys be able to fit all their blocks into this box?
The beetle has 3 pairs of legs. How many legs does a beetle have?
There were 8 buds on the bush in the morning. By the middle of the day, all the buds have blossomed and become beautiful roses. How many buds are left unopened on this bush?
There are red and yellow apples in the bag. 4 red and 5 yellow apples were taken from the bag, and the bag was empty. How many apples were in the bag?
Dima won 2 games of chess against Alyosha, and Alyosha won 3 games. How many games did the boys play?
Each of the three adults leads two children by the hand.
How many whole loaves of bread can be made from six halves?
5 children are walking one by one along the road. Every boy, except the last, is followed by a girl. How many girls are walking down the road?
I came up with two numbers. When I added them up, I got 6. When I subtracted the other from one, I got 6 again. What are these numbers?
Box contains 8 cakes. How many cakes must be taken from the box so that there are 5 cakes left in it?
Katya thought of a number, added 5 to it and got 15. What number did Katya think of?
There are two children in the family. Sasha is Zhenya’s brother, but Zhenya is not Sasha’s brother. Could it be? Who is Zhenya?
There were 10 apples on the apple tree. The gardener allowed the children to pick 1 apple from the apple tree. There are 6 apples left on the apple tree. How many children were there?
The train consists of 10 cars. Petya got into the fifth car from the beginning of the train, and Fedya got into the fifth car from the end.
Chocolate bar consists of 6 square pieces. How many breaks do you need to make to break this tile into separate slices?
Peter is the son of Sergei, and Sergei is the son of Fedor. Who is Pyotr Fedor related to?
There are 3 more apple trees than pears in the garden. Apple trees 7. How many pears?
Several sheets fell out of the book. The first page that falls out is number 5, and the last page is number 10. How many sheets fell out of the book?
Zina has 4 postcards less than Galya. Zina has 6 postcards. How many postcards does Gali have?
My name is Ivan Sergeevich, and my grandfather (my father’s father) is Petr Nikolaevich. Write down the name and patronymic of my father.
The red cord is 1m longer than the green one and 2m longer than the blue one. The length of the green cord is 5m. Find the length of the green cord.
Hats hanging on a hanger; 1 more hats than berets. Hats 8. How many hats and how many berets?
The minuend is greater than the subtrahend by 2.
Guess how old my grandfather is if we celebrate his 70th birthday in 15 years.
The difference of two numbers is equal to the subtracted one. Think of such numbers and write an example.
The difference between two numbers is 0. Think of and write down an example.
Grandma put 12 pears on a plate. After the grandchildren took 1 pear from the plate, 8 pears remained. How many grandchildren does the grandmother have?
At a mathematics lesson Olga Petrovna asked Gosha to name all numbers less than 7, and Vitya — all numbers greater than 3 and less than 9. What identical numbers did the boys name?
|
Answers A 4 sock 3 chickens 2 mittens Number 0, because of any natural number 2 sisters 2+2 = 4 buckets 3 kitten 6 children 8 feet No 6 feet 0 4+5=9 apples 1+1+1=3 or 1+2=3 2+2+2=6 children 3 2 6 and 0 4 socks 3 chickens 2 mittens Number 0, because of any natural number 2 sisters 2+2 = 4 buckets 3 kitten 6 children 8 legs No 6 feet 0 4+5=9 apples 1+1+1=3 or 1+2=3 2+2+2=6 children 3 2 6 and 0 3 cakes Number 10 Sister four children no 5 4 pears 3 sheets 10 Cards Sergey Petrovich 5+1 = 6, 6-2 = 4M 31. 2 70-15=55(years) 6-3=3, 14-7=7 etc. For example: 8-8 = 0 12-8 = 4 grandson 4, 5, 6. |
Answers A 4 Noska 3 chickens 2 mittens Number 0, because of any natural number 2 sisters 2+2 = 4 buckets 3 kitten 6 children 8 legs no 6 feet 0 4+5=9 apples 1+1+1=3 or 1+2=3 2+2+2=6 children 3 2 6 and 3 cakes Number 10 Sister four children No 5 Grandson 4 pears 3 sheets 10 postcards Sergey Petrovich 5+1=6, 6-2=4m 8-900 caps and 6 berets 2 70-15=55(years) 6-3=3, 14-7=7 etc. For example: 8-8=0 12-8=4 grandchildren 4, 5, 6. |
B
How many left mittens and how many right mittens?
2.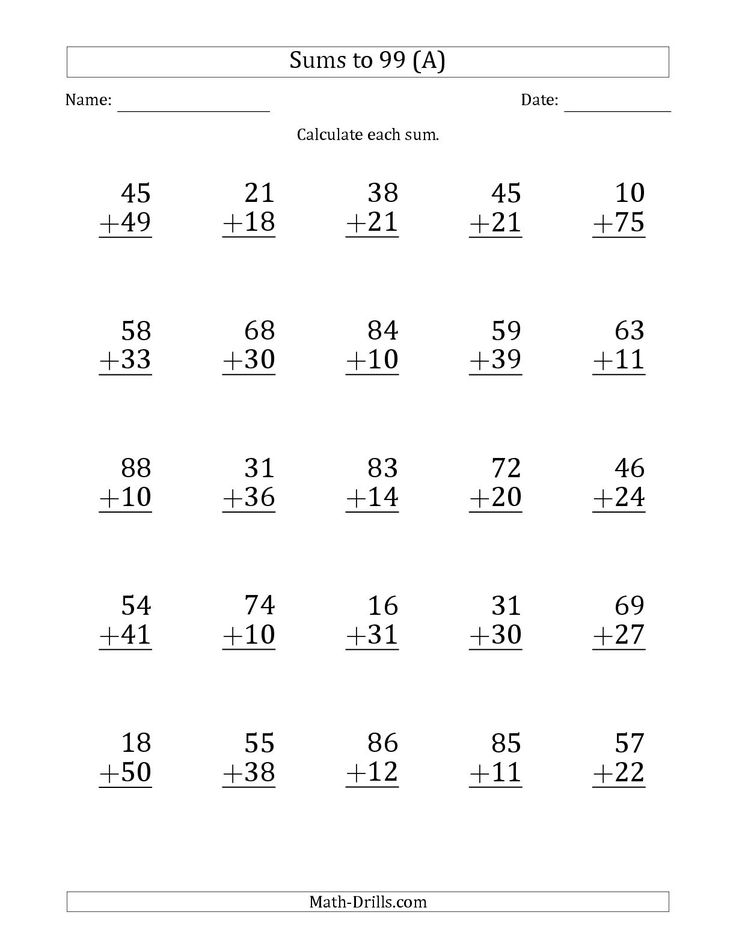
3. The apartment has 2 rooms. They made two out of one room. How many rooms are in the apartment?
4. Yura asked the library for Nafanya magazines from the second to the sixth issue. How many magazines did the librarian give him?
5. The apartment has 4 rooms. Two rooms were connected together and made one large room out of them. How many rooms are in the apartment?
6. Yulia counted 10 legs of all the chickens that were sitting in the basket. How many chickens were in the basket?
7. Tanya said that she had more than 4 dolls and less than 7. How many dolls could Tanya have?
8. Kolya is older than Seryozha, and Seryozha is older than Misha. Write down the name of the boy who is the youngest.
9. There were 8 green tomatoes on the windowsill. After 3 days they turned red. How many green tomatoes are left?
10. Rabbits sit in a cage so that their ears are visible.
11. The blacksmith shod two horses. How many horseshoes did he need?
12. Alyosha was treated to sweets. He decided to give his sister 4 sweets and take 3 for himself. How many sweets did they give Alyosha?
13. Masha and Vanya each have 9 lollipops. Masha ate 4 lollipops and Vanya did the same. How many lollipops does Vanya have left?
14. Nina thought of a number. She first added this number to 7, and then subtracted it from 7. The answer turned out to be the same — 7. What number did Nina think of?
15. Roma was presented with as many badges as he already had. Roma counted all the badges, there were 8 of them. How many badges did Roma have at first?
16. To seat 7 children in a room, 2 chairs are missing. How many chairs are in the room?
17. A spider has 4 pairs of legs, and a beetle has 3 pairs of legs. How many more legs does a spider have than a beetle?
18.
19. Sister is 1 year older than brother. How many years older will the sister be than the brother in 5 years?
20. Can the sum of two numbers be equal to the summand?
21. Can the difference of two numbers be equal to the one being reduced?
22. Write down the number less than 20, in which the number of tens is 4 less than the number of units.
23. I pasted 4 decals on each page of the album. How many pages did 8 pictures take up?
24. The sum of two numbers is 8 and their difference is 4. Guess what these numbers are?
25. My name is Nina Aleksandrovna, and my grandfather (my father’s father) is Ivan Nikolaevich. What is my father’s name?
26. On the left pan of the scales there is a bag of flour and a weight of 1 kg. On the right pan of the scales is a 3 kg weight. Scales in balance. Find a mass of bags of flour.
27. In the shoe section of the department store there is a sign: “Shoes 37 — 42 sizes”. Is it possible to buy shoes in size 39 in this department?
28. What two-digit numbers can be written using the numbers 5 and 6?
29. Granulated sugar is sold packaged in bags of 1 kg, 2 kg, 3 kg. Mom knocked out a check at the cash desk for the purchase of 7 kg of sugar. The saleswoman gave her 3 bags of sugar. How much sugar was in each of the packets? Consider possible cases.
30. Compare the numbers *2 and 95 Record using one of the < or > signs.
31. Yulia and Marina found an equal number of mushrooms in the forest. Yulia had 4 mushrooms that turned out to be wormy, and on the way home she threw them away. And Marina found 5 more mushrooms. How many more mushrooms did Marina have than Yulia?
32. There is money in the desk drawer. With this money you can buy 2 chairs of the same price or one chair. What is more expensive chair or chair?
33.
34. There are 12 red and green balls in a box. Take 3 red and 4 green balls from the box. After that, there are no green balls left in the box. How many red balls are left in the box? 35. There are 5 more apples in the basket than in the bag. 7 apples were taken from the basket. Where are more apples left: in a basket or in a bag, and by how much?
36. The wizard made 3 keys for three locks: copper, silver and gold. Only one key fits each lock. The copper key does not fit either the first or the second lock. The silver key does not fit the second lock. Which lock fits each key?
37. Petya has 4 less sweets than Seryozha. Mom gave Petya 5 more sweets. Who has more sweets and by how much?
38. The green ribbon is 3 m longer than the red one. 5 m were cut off from the green tape, and 2 m from the red one.
39. Yura has enough money to buy 4 waffles or 2 sweets. Will he be able to buy 1 candy and 4 waffles with his own money?
40. Write down 6 numbers according to this rule: the first is 1, the second is 2, and each next is equal to the sum of the previous two.
41. Olya can buy 4 pencils and 3 notebooks with her own money. Will she have enough money to buy 3 pencils or 3 notebooks?42. Grandfather allowed each of the three granddaughters to pick one rose from four bushes. How many roses did all the granddaughters pick?43. Write down 5 numbers according to this rule: the first is 18, the second is 10, and each next is equal to the difference of the previous two.
44. Half the number of apples on the plate was taken for compote. How many apples are left on the plate if the compote was cooked from 6 apples?
45. Bought a package of yogurt. Half of all the yogurt that was in the bag was drunk by Masha and Dasha.
46. Melon is heavier than watermelon and lighter than pumpkin. What is the heaviest?
47. There are vegetables on the table: turnips are 1 less than cucumbers, and cucumbers are 1 less than tomatoes. How many fewer turnips are there than tomatoes?
48. The red ribbon is shorter than the blue ribbon and longer than the green one. Which tape is the shortest?
49. Dima is 1 year older than Serezha, and Serezha is 1 year older than Roma. How many years is Dima older than Roma?
50. Every minute 10 liters of water is poured into the bath from the tap. During the same time, 2 liters of water is poured out through a hole in the bottom of the tub that is not tightly covered with a cork. Is the amount of water in the bath increasing or decreasing, and by how many liters every minute?
51. Petya took 3 cubes and put them one on one so that it turned out to be a “tower”.
52. A tower was built from three cubes. The yellow die is placed above the blue and below the red. Which cube is the tallest?
53. The cake was cut into 4 identical parts, and then each part was cut into 2 identical parts. How many people will the cake last if everyone puts one piece on a saucer?
54. There are gingerbread and waffles in the box: there are 2 less gingerbread than waffles. How many waffles if there are 6 gingerbread cookies?
55. Mitya is 2 years older than Gena. Mitya is 10 years old. How old is Gene?
56. The sum of two numbers 9. The sum is 5 more than the first term. What is the second term equal to?
57. 6 girls and 2 boys were skating at the rink. Soon the three children were called to dinner and they went home. Was there even one girl left on the rink?
58. Bought a can of grape juice.
60. Melon is 3 kg lighter than watermelon. A piece weighing 1 kg was cut from a melon, and 9 from a watermelon.0005
3 kg piece. What is left more: melon or watermelon, and by how many kilograms?
|
Answers b 3, 3 7 3 5 3 5 or 6 Misha 8-8 = 0 9000 5 2222222 4+4=8 4+3=7 9-4=5 0 4 7-2=5 chairs 3+3=6(k) > top shelf 1 way: 12-4=8, 8-3=5. 2 way: 3+4=7. 12-7=5 In a bag of 2 apples >. Copper key for 3 locks, silver key for 1 lock, gold key for 2 locks. Petya has 1 The lengths are No. 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13. Yes. 4+4+4=12 roses 18 10 8 2 60002 For 2 years 10-2=8(years) increases Green cube Red For 8 people 6+2=8 10-2=8(years) 5 57 Yes. 4+4=8 glasses Watermelons per 1 kg >. |
Answers B 3, 3 7 3 5 3 5 5 or 6 Misha 9chairs 0002 8-8=0 5 4+4=8 4+3=7 9-4=5 2 or 4-3=1 one pair is two legs 4+3=7 6<7 no, not allowed for 1 year Yes. If one of the terms is zero. For example: 5+0=5 Yes. When subtracted is 0. 7-0=7 15 2 6 and 2 Alexander Ivanovich 3-1=2(kg) Yes 55, 56, 65, 66 1) 3kg, 3kg, 1kg; 2) 2kg, 2kg, and 3kg *2 < 95 4+5=9 Armchair 3+3=6(k) > top shelf 1 way: 12-4=8, 8- 3=5. 2 way: 3+4=7. 12-7=5 In a bag of 2 apples >. Copper key for 3 locks, silver key for 1 lock, gold key for 2 locks. Petya has 1 The lengths are No. 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13. Yes. 4+4+4=12 roses 18, 10, 8, 2, 6. 6 4 Pumpkin on 2. Green tape by 2 years 10-2 = 8 (l.) Increases Green cube Red For 8 persons 6+2=8 10-2=8(years) 5 57 Yes. 4+4=8 glasses Watermelons per 1 kg >. |
B 3, 3 7 3 5 3 5 5 or 6 Misha 8-8 = 0 5 4+4 = 8 4+3 = 7 9-4=5 0 4 7-2=5 chairs 8-6=2 or 4-3=1 one pair is two legs 4+3=7 6< 7 no, not allowed for 1 year Yes. If one of the terms is zero. For example: 5+0=5 Yes. When the subtrahend is 0. 7-0 = 7 15 2 6 and 2 Alexander Ivanovich 3-1 = 2 (kg) Yes 55, 65, 66 1) 3kg, 3kg, 3kgg, 3kg, 3kgg, 3kg , 1 kg; 2) 2kg, 2kg, and 3kg *2 < 95 4+5=9 Armchair 3+3=6(k) > top shelf 1 way: 12-4=8, 8- 3=5. 2 way: 3+4=7. 12-7=5 In a bag of 2 apples >. Copper key for 3 locks, silver key for 1 lock, gold key for 2 locks. Petya has 1 The lengths are None. 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13. Yes. 4+4+4 = 12 roses 18, 10, 8, 2, 6. 6 4 pumpkin on 2. Green tape for 2 years 10-2-2-2-2-2-2-2-2-2 \u003d 8 (l.) increases Green cube Red For 8 people 6 + 2 \u003d 8 10-2 \u003d 8 (years) 5 57 Yes. 4+4=8 glasses Watermelons per 1 kg >. |
Mathematics for children from 5 years
Publication date: .
Mathematical tasks for children from 5 to 6 years old. Download free in pdf, print or use online
Tasks for: counting from 1 to 10 with pictures, recognition of basic geometric shapes (circle, oval, square, rectangle, trapezium, rhombus, pentagon, hexagon), writing numbers from 0 to 9, basic arithmetic operations (addition and subtraction) using pictures, quantitative comparison
What a child should be able to do at this age (mathematics):
1.
2. Know how to count from 1 to 10 (both direct and reverse).
3. Confidently count objects up to 10.
4. Compare objects both quantitatively and qualitatively (higher, lower, shorter, longer, etc.).
5. Apply basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, equals).
Dear users, do not forget to leave your comments, feedback, suggestions. All materials are checked by an antivirus program.
Geometric shapes
Show a circle.
Show square.
Show triangle.
Show the diamond.
Show an oval.
Show a quadrilateral.
Name the figures.
Color different shapes with different colors.
Show the pyramid.
Show cube.
Show the ball.
Show figures of the same color.
Show figures of the same size.
Show figures that are identical in shape.
Circle the shapes and continue the row.
Show symmetrical figures.
Copy the shapes.
Copy the shapes.
Cross out the extra figure. Explain why it is redundant.
Continue the series of figures.
Addition with pictures
Add up the number of objects and write the sum.
Add up the number of items and write the sum.
Add the number of figures and write the sum.
Add the items and write the sum.
Adding numbers up to 10
Page 1.
|
Date: __________________ Name: _______________________________ Rating: __________ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Add two single digit numbers. Sum of numbers up to 105 | 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 3 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 | + | 6 | = | __ | 8 | + | 0 | = | __ | 0 | + | 0 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 1 | + | + | +8 = | __ | 5 | + | 0 | = | __ | 2 | + | 4 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 0 | + | 3 | = | __ | 1 | = | __ | |||||||||||||
| 7 | + | 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 3 | = | __ | 2 | + | 7 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 5 | + | 4 | = | __ | + | 1 | 8 4 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||
| 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 7 | + | 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 5 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 3 | 5 | = | __ | 1 | + | 4 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 | + | 8 | = | __ | 4 | + | 0 | = | __ | 1 | + | 7 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 6 | + | ° | ’ | ’ | 10252 | 3 | + | 3 | = | __ | 1 | + | 0 | = | __ | ||||||||||
| 5 | + | 0 | = | __ | 2 | + | 0 | = | __ | 1 | + | 3 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 4 | + | 1 | = | __ | 0 | + | 9 | = | __ | 3 | + | 5 | = | __ | |||||||||||
Adding numbers up to 10.

Page 2.
|
Date: __________________ Name: _______________________________ Rating: __________ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Add two single digit numbers. Sum of numbers up to 10. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | + | 6 | = | __ | 2 | + | 6 | = | __ | 2 | + | 1 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | + | 6 | = | __ | 1 | 6 | = | 0095 | + | 7 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | + | 0 | = | __ | 4 | + | 5 | = | __ | 3 | + | 3 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| + | 0 | __ | +0098 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 5 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | + | 5 | = | __ | 3 | + | 0 | = | __ | 0 | + | 0 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | +0095 | __ | 6 | + | 3 | = | __ | 1 | + | 8 | = | __ | |||
| 8 | + | 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 0 | = | __ | 0 | + | = | 0091 | 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 6 | + | 1 | = | __ | 1 | + | 5 | = | __ | ||||||||||
| 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 4 | + | 0 | __ | + | +5 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | + | 9 | = | __ | 4 | + | 3 | = | __ | 3 | + | 1 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | + | 1 | = | __ | 5 | + | 4 | = | __ | 2 | + | 3 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | + | 1 | = | __ | 4 | + | 1 | = | __ | 0 | + | 8 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Addting numbers to 10.

p. 3.
|
Date: __________________ Name: _______________________________ Rating: __________ 95 | + | 5 | = | __ | 2 | + | 3 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | + | 1 | = | __ | 6 | + | 3 | = | __ | 2 | + | 5 | = | 0098 7 | = | __ | 2 | + | 4 | = | __ | 1 | + | 7 | = | __ | ||||||||||
| 6 | + | 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 1 | = | __ | 2 | + | = | = | = | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 3 | + | 4 | = | __ | 3 | + | 2 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | + | 1 | = | __ | 0 | + | 90 | 8 + | 0 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | + | 1 | = | __ | 2 | + | 0 | = | __ | 2 | + | 6 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | + | 5 | = | = | __ | 3 | + | 3 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | + | 0 | = | __ | 5 | + | 4 | = | __ | 3 | + | 3 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | + | 1 | = | __ | 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 1 | + | 5 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | + | 1 | = | __ | 3 | + | 0 | = | __ | + | 7 | = | __ | __ | __8 = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | + | 0 | = | __ | 0 | — | 0 | = | __ | 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | — | 2 | = | __ | + | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0095 | 2 | — | 2 | = | __ | ||
| 10 | + | 0 | = | __ | 2 | — | 1 | = | __ | 2 | + | 7 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | — | 0 | = | 52525252525252525252525252525252525252525252525252525252525252525252525AC0095 | + | 2 | = | __ | 3 | — | 1 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | + | 7 | = | __ | 3 | — | 1 | = | __ | 0 | + | = | 0098 1 | = | __ | 8 | + | 1 | = | __ | 8 | — | 3 | = | __ | |||||||||||
| 8 | + | 2 | = | __ | 1 | — | 0 | = | __ | 4 | + | = | = | = | = | = | = | = | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | — | 2 | = | __ | 8 | + | 0 | = | __ | 4 | — | 4 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | + | 3 | = | __ | 6 | — | = | __ | __ | 8 + | 3 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | — | 5 | = | __ | 7 | + | 1 | = | __ | 8 | — | 8 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | + | 3 | = |
9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009 9009
9009EV5 | __ | 2 | + | 6 | = | __ | 7 | — | 5 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | + | 2 | = | __ | 2 | — | 1 | = | __ | 1 | + | = | 0091 | 0 | — | 0 | = | __ | 8 | + | 0 | = | __ | 9 | — | 8 | = | __ | ||||||||
| 9 | + | 1 | = | __ | 4 | = |
7 | +5 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | — | 0 | = | __ | 7 | + | 0 | = | __ | 3 | — | 0 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| + | 1 | = | __ | 3 | 4 | + | 4 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | — | 3 | = | __ | 6 | + | 2 | = | __ | 9 | — | 8 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 7 | — | 1 | = | __ | 2 | + | 2 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | — | 3 | = | __ | 7 | + | 3 | = | __ | 10 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0095 | 0 | = | __ | 4 | — | 4 | = | __ | 7 | + | 1 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | — | 5 | = | __ | 4 | + | 5 | = | __ | — | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 4 | — | 2 | = | __ | 5 | + | 5 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Adding and subtracting numbers up to 10.

Page 3.
|
Date: ________________ Name: _________________________________ Rating:_________ | 1 | = | __ | 4 | + | 3 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | — | 2 | = | __ | 9 | + | 0 | = | __ | 7 | — | 7 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | +0095 | __ | 6 | — | 3 | = | __ | 10 | + | 0 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | — | 2 | = | __ | 9 | + | 1 | = | __ | 1 | — | = | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | + | 4 | = | __ | 6 | — | 1 | = | __ | 8 | + | 0 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | — | 7 | = | __ | + | 2 | 0095 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | + | 0 | = | __ | 0 | — | 0 | = | __ | 4 | + | 1 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | — | 8 | = | __ | 8 | + | 1 | = | __ | 6 | — | 0 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | + | 0 | = | __ | 5 | — | 0 | = | __ | 1 | + | 1 | = | __ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | + | 4 | = | __ | 5 | — | 4 | = | __ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | + | 5 | = | __ | 1 | — | 1 | = | __ | 4 | 1 | = | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Link | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 5 | . | . |
| term | 9 | 6 | 8 | . | . | 2 | 1 |
| total | . | . | . | 9 | 8 | 9 | 7 |
— How many columns does the table consist of? How
what are these graphs called? Look at column 1.
known? What is unknown? How to find?
Output What are the names of the components when
addition? How to find 1 term? 2 term?
Amount?
— Guys, look around this house
scattered leaves. But they are not quite ordinary. On the
the reverse side contains examples that we
you need to write down and decide.
(1 student reads the example and 2 writes on
blackboard.)
4 plus 2; 6 minus 4; 5 increase by 3; 9 decrease by
4;1 term 4, 2 term 4, find the sum; sum
numbers 6 and 4.
— Thank our assistant and go
further along our fabulous street. We’ll get through
bridge and find ourselves on the other side of the street.
slide 6
— 3rd gnome should be waiting for us. Houses with what
do we need to go through the numbers? But he has terribly no time and
so he left us a note with a task.
Practical work with geometric
material.
(there are 2 stripes on the desks: red and blue)
— Which strip is longer? shorter? How was it determined?
Conclusion You can compare objects,
overlapping each other, measuring with
rulers.
slide 7
— Trees grow near the next house. And for
them — 1 more gnome. What’s the score? (4) He us
points to the trees. And I think it offers
create a task. What are the parts of the task?
(Condition, question, solution, answer)
(Children compose and solve the problem with the teacher)
— There were 2 pine trees near the house, and 4 more near the bridge.
How many pine trees grew near the bridge?
— Let’s make a drawing for our problem. (1 student at
boards)
— What do we need to find in the problem? How will we find? Which
shall we write down the answer? Write down the solution and the answer of the problem
themselves. (Student — at the blackboard)
Cross checking.
IV. Fizminutka.
(to cheerful music)
Gnomes came out once
See what time it is.
One, two, three, four —
Dwarfs pulled the weights.
Then there was a terrible ringing
The gnomes ran out.
— And our next assistant thought and did not know
how to complete the task. Let’s help him.
slide 8 table
Reduced 10 — So we helped this dwarf.
— And now we will go to house number 4.
Another envelope with a task.— Solution of examples in groups on sheets (No. 5
page 5)— Checking at the board the solution of examples of each
groups. Discussion.— We go further to the house number 2. This gnome also
prepared the task.(On the board) Problem.
- It is necessary — 10 pr.
- Decided — … pr.
- Remaining — ? project
— Tell me, can we solve the problem right away?
What data are we missing?— Instead of points, insert any number and solve
on one’s own.Check.
— Here we come to the last house.
This is a house
No. 6 and the gnome is already waiting for us here. He offers
choose the fastest counter.Variant tests. Write down only the answers.
1st option 6+4 7+3 8+2 9-6 4-4 10-1 5+5 3+4 8-5 0-0 7-6 2 Option
1 7 -5 8-8 4+6 10-7 3+5 3+3 6-5 1-1 6+4 61 61 61 61 61 -3 Self test .
(Answers on the board)
— So, who quickly and without errors completed
exercise?V. Reflection of learning activities in the classroom.
— And now we will return to Snow White,
thank her for her helpers, for
an interesting tour of the fabulous city. BUT
Snow White has prepared prizes for your active
assistance in completing assignments.Problems for addition and subtraction within 20 Pages 1 — 6 — Flip PDF Download
0002 1Tasks for adding and subtracting numbers within 20 1. In February, Dima attended 6 lessons in the pool, and in March — 3 lessons more. How many classes did Dima attend in March? Drawing: F. 6 3 M. ? Solution: Answer: classes. 2. Julia took 7 books from the library, and Eva took 3 books less. How many books did Eva take from the library? Drawing: Y. 7 3 E. ? Solution: Answer: books.
2 3. Misha scored 2 goals and Oleg scored 4 goals. How many goals did Misha and Oleg score in total? Drawing: 24 ? Solution: Answer: goals.
4. When Katya made friends with 4 classmates, she became 9friends. How many friends did Katya have at first? Drawing: ? 4 9 Solution: Answer: friends.
13 25. Dad assembled the kit in 2 minutes, and son in 9 minutes. How many minutes faster did dad assemble the constructor? Drawing: Solution: Answer: minutes faster. 26. Anton has a birthday. His parents gave him 3 gifts, and his friends gave him 4 more gifts. How many gifts did Anton’s friends give? Drawing: Solution: Answer: gifts.
16 31*. Ruslana has 7 transparent beads. She exchanged 4 transparent beads for 2 blue ones. How many transparent beads does Ruslana have left? How many beads did the girl have in total? Drawing: 1) ? 4 2) 32 P. P. + S.? 7 Solution: 1) 2) Answer: beads. 32*. Dasha is 7 years old, and Masha is 12 years old. How much older is Masha than Dasha? How old will Dasha be when Masha turns 15? Drawing: 1) 7 2) ? 5 D.D.M.? 15 12 Solution: 1) 2) Answer: years.
We offer simulators for everyone who wants to know mathematics perfectly! The ability to quickly and easily solve mathematical problems is one of the key skills that a child should master in the 1st grade.
The simulator helps develop this skill and lay a solid foundation for the successful study of mathematics in the future. Grade 1 Grade 2■ Digit composition of numbers up to 10; ■ Digit composition of numbers up to 100; ■ Addition and subtraction of numbers within 10; ■ Addition and subtraction within 100; ■ Comparison of numbers within 10; ■ Comparing numbers within 100; ✔ Tasks for adding and subtracting numbers ■ Performing actions with values; ■ Tasks for actions with numbers within 100. within 20. Grade 4 Grade 3■ Addition and subtraction within 1000; ■ Numeric expressions and simple equations; ■ Multiplication and division within 1000; ■ Units of measure for mass, length, time; ■ Performing actions with quantities; ■ Tasks for determining speed, time ■ Tasks for addition, subtraction, multiplication and distance; and division; ■ Tasks to determine the perimeter and area.■ Tasks to find the fraction of a number. ISBN 978-985-565-556-6 pshop.by
Methods for studying addition and subtraction within 10 — Megatutorial
Place of study of the topic: 1st grade
Goals:
9022 addition and subtraction;
Build strong computing skills; Learn to solve simple problems of addition and subtraction of various types (finding the sum, remainder, increasing and decreasing the number by several units, difference comparison, finding the unknown term) Tasks:
- Acquaintance with computational techniques and the formation of the ability to apply them when compiling addition and subtraction tables.

- Learning addition and subtraction tables in close connection with the assimilation of the composition of the number within 10. Formation of addition skills.
Visual aids and didactic material
0091
term term sum + = 2) A set of movable numbers and signs
3) A set of geometric shapes of various types and colors
4) A set of cards with numerical figures illustrating the numbers 1-5
5) Sets of subject pictures for compiling problems
Content and features of the study of the topic
Addition and subtraction within 10 form the basis for performing oral and written calculations outside the first ten.
The specific meaning of addition and subtraction is realized by children in the course of actions with sets of objects and is used in solving problems.
Addition is considered as the union of sets that do not have common elements. Subtraction is like removing part of a set. Addition is associated with an increase in the number of elements of a given set; subtraction — with a decrease in the number of elements of a given set.
A significant place in this topic is given to familiarity with the names of the components and results of actions and the understanding of the relationships between them, as well as the assimilation of the properties of arithmetic operations.
Elements of algebra and geometry are also included: children get acquainted with mathematical expressions (sum, difference), learn to read and write them, begin to compare expressions, on the basis of which they obtain numerical equalities and inequalities of the form: 4 + 2> 7, 7-3 <7+3, 3+2=2+3. Here, students get acquainted with equations of the form x-3=7, 5+x=9and learn how to solve them. The ability to draw and measure segments is consolidated, tasks are included for composing geometric shapes from given ones, and for isolating familiar geometric shapes from a given figure.

The study of addition and subtraction within 10 is carried out according to the following plan:
1. Preparatory stage: revealing the specific meaning of addition and subtraction, writing and reading examples, cases of adding and subtracting 1, where the results are based on knowledge of the properties of the natural series of numbers ( when we add 1 to a number, we get the number following it when counting, and when we subtract from the number 1, we get the previous number).
2. Studying methods of counting and counting one by one and in groups for cases 2, 3, 4.
3. Studying the method of rearranging terms for cases + 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. Addition table and composition of numbers from terms.
4. study of the subtraction technique based on the knowledge of the relationship between the sum and the terms for cases — 5,6, 7, 8, 9.
Preparatory work for the study of addition and subtraction begins with the first lessons of considering numbering.
By repeatedly performing operations on sets, children understand that the operation of combining corresponds to the action of addition, and the operation of removing part of the set corresponds to the action of subtraction. Children’s attention is also drawn to the fact that when they add, it becomes more than it was; when subtracted, it becomes smaller.
By the end of the study of numbering, students should have a solid understanding of how to form any number of the first ten by counting and counting one, and using this technique (not counting), freely add and subtract with one. Gradually, children summarize their conclusions and formulate conclusions: to add 1 number means to name the number following it; To subtract 1 from a number is to name the number that precedes it. In a specially designated lesson, all cases are brought into the system, under the guidance of a teacher, children draw up tables «add 1» and «subtract 1» and then memorize them.
At the second stage , cases of addition and subtraction of the form are considered, the results of which are found by counting or counting in parts.

Work on computing skills is based on the following plan:
1) preparatory exercises;
2) familiarity with the methods of calculation;
3) consolidation of knowledge of techniques, development of computational skills;
4) compiling and memorizing tables.
Consider the method of familiarization with the computational technique «add and subtract 2».
At the preparatory stage, children learn to solve examples in two actions 2 + 1 + 1, 9-1-1, in order to consolidate the ability to add and subtract one and accumulate observations: if we add (subtract) 1 and 1 more, then we will add (subtract) the total ) 2.
At the lesson on familiarization with new calculation methods, the teacher sets a goal for the children — to learn how to add and subtract the number 2. The solution of the first examples is based on an objective action. The 4+2 example is being solved. Let these bouquets on the window represent the number 4, and these 2 bouquets on the table — the number 2.
Show how to attach 2 bouquets to those 4 (the student transfers the flowers to the window: first one bouquet, then the second). Let’s write down what Vova did. How much did you add to 4 first? How much did it turn out? How can you add 2 to 4? To add 2 to 4, you must first add 1 to 4, you get 5, and then add 1 to 5, you get 6.
Write on the board:
4 + 2 = 6
4 + 1 = 5
5 + 1 = 6
-2 and, based on their practical work (first they colored 1, and then another 1 apple), they explain how to subtract 2.
In the same plan, several more tasks are considered, then they move on to solving examples with an explanation of calculation methods.
Techniques are revealed with the help of similar exercises. Calculation techniques are also illustrated by actions with objects, and at first several examples are solved with a detailed note on the board
4 + 3 = 7 9 – 3 = 6 4 + 2 = 6 9 — 1 = 8 6 + 1 = 7 8 — 2 = 6 For receptions, the entry may be the same, but it is more expedient to start writing in a different way: 5 + 4 = 5 + 2 + 2 = 9, 10 — 4 = 10 — 2 — 2 = 6.

First, the examples are solved with detailed explanations aloud, the explanations are gradually reduced, then they are spoken briefly to themselves. In order to develop skills, oral exercises are included (oral counting, games «silent», «relay», «ladder», «circular examples»). Very useful arithmetic dictations. Creative exercises are especially useful: compose problems, examples, correct incorrectly solved examples, insert a missing number or action sign — 3 = 7, 8 — = 6, 8 + = 10; 6 * 4 = 10, 6 * 4 = 2.
Effective for the formation of computational skills are exercises with equalities and inequalities: compare expressions and insert signs: 7 + 2 * 7, 10 — 3 * 4; check if the signs are correct: 6 + 4<10, 6 +3>10.8 +2 =10; insert the appropriate number to make the correct entry: 10 — 4<, 5 + 2>, 5 + 3=.
Comparison of expressions is performed on the basis of comparison of their values, therefore, children with the help of such exercises consolidate their calculation skills.

Completes the work on each of the methods of compiling and memorizing tables. Part of each table is compiled collectively under the guidance of a teacher, part — independently. Simultaneously with addition and subtraction tables, it is useful to compile tables of the composition of numbers from terms, for example:
2 + 2 = 4 4 = 2 + 2 4 — 2 = 2 3 + 2 = 5 5 = 3 + 2 5 — 2 = 3 4 + 2 = 6 6 = 4 + 2 6 — 2 = 4 … … … 8 + 2 = 10 10 = 8 + 2 10 — 2 = 8 At this stage, students are introduced to the terms addition, subtraction, term, sum, and later with terms — reduced, subtracted, difference.

At the third stage we study the method of addition for the cases of «add 5, 6, 7, 8, 9». If we apply a permutation of the terms in the calculations, then all these cases will be reduced to the previously studied types a + 1, a + 2, a + 3, a + 4. To do this, get acquainted with the commutative property of addition.
It is possible to reveal the method of permutation of terms, that is, to show exactly when the commutative property is used in calculations when solving a practical problem. For example, you need to put together 2 bags and 7 bags of flour, standing apart. How is it more convenient to do this: bring 2 bags to 7 or 7 bags to two? Based on such exercises, children come to the conclusion: it is easier to add a smaller number to a larger number, and you can always rearrange the numbers — the amount will not change from this.
Then they show how to use the method of rearranging terms when solving examples and addition problems within 10. After that, an addition table within 10 is compiled.
The children themselves can explain why only these cases are included and why the others are not included.
At the fourth stage , we study the subtraction technique based on the relationship between the sum and the terms to find the results in the cases “subtract 5, 6, 7, 8, 9”. The relationship between the sum and terms is discussed in the topic «Finding an unknown term». Operating with specific subject sets (demonstration and individual visual aids), students independently come to the conclusion: if one term is subtracted from the sum of two terms, then we get another term (inductive method: incomplete induction).
In the course of working on a topic, children get acquainted with the problems of increasing (decreasing) the number associated with comparing two sets of objects. They must understand what the expressions “the second is 2 more (less) than the first” mean, learn how to reduce problems of this type to problems of finding the sum and remainder based on the reasoning: “2 more means the same and 2 more «,» 3 less means the same amount without 3.

In the process of studying addition and subtraction, the formation of the concept of the number zero continues. By performing operations on sets, students gradually learn that the number zero is a characteristic of an empty set. At the end of the work on the topic, cases of addition and subtraction with zero 6 + 0, 6 — 0 are included.
Lesson 22. problem solving. addition and subtraction table with the number 2 — Mathematics — Grade 1
Mathematics, Grade 1. Lesson 22
Problem solving. Addition and subtraction table with the number 2.
List of questions addressed in the lesson:
- Drawing up addition and subtraction problems according to a drawing, diagram, table, table.
- Solving problems in one action to increase (decrease) the number by several units.
- Explanation based on the illustration of adding to the number by 2, subtracting from the number by 2.
- Calculations of the form + 2, — 2.

- Supplementing the conditions of the problems with missing data or a question.
Glossary on the topic
Task components — condition, question, solution, answer.
Addition and subtraction problems.
Task in the form of a diagram, table or diagram.
The relationship between the condition and the question of the problem.
Calculations of the form + 2, — 2.
Keywords
Text problem; the task; task question; the solution of the problem; addition to the number by 2; subtraction from the number by 2.
Basic and additional literature on the topic of the lesson :
- Moro M. I., Volkova S. I., Stepanova S. V. Mathematics. Textbook. 1 class At 2 hours, part 1. — M .: Education, 2017. — p. 90 – 93.
2.MoroM. I., Volkova S. I. Mathematics workbook. 1 class 1 hour — M .: Enlightenment, — p. 35 – 36.
At the lesson we will learn how to make a table for adding and subtracting the number 2.
We will learn to compose problems according to pictures and solutions, explain and justify the action chosen to solve the problem. Let’s solve problems in one action to increase (decrease) the number by several units.
Main content of the lesson
Read the entry:
A bird was sitting on a branch, two more flew to it.
Can this entry be called a task.
This is only a condition of the problem, no question.
Compose a question for the problem.
How many birds have become?
Solve the problem.
Two added to one makes three.
How to answer the problem question?
Answer: there are three birds on the branch.
Condition Condition
on the branch sat 1ptic, another 2.
Problem question
How many birds are there?
Problem solution.

1 + 2=3 (p.)
Answer: 3 birds.
Make another problem from this picture so that it can be solved by subtraction.
3 birds were sitting on a branch. Two birds have flown away. How many birds are left on the branch?
How to solve such a problem?
Subtract two from three and you get one.
How to answer the problem question?
Answer: there is only one bird left on the branch.
Condition of the problem
3 birds were sitting on a branch. Two birds have flown away.
Problem question
How many birds are left on the branch?
Problem solving.
3 — 2=1 (p.)
Answer: 1 bird.
What number did we add and subtract in these problems?
The number two
The theme of our lesson: “Problem solving.
Addition and subtraction table with the number 2.
Look at the following picture and write the appropriate addition example.
2 + 2=4
2 + 2=4
4 — 2=2 Write the appropriate addition and subtraction examples for each picture.
3 + 2=5
5 — 2 = 3
4 + 2 = 6
6 = 4
5 + 2 = 7 7 — 2 = 5
6 + 2 = 8
9000 — 2 = 6
9009 9009
7 + 2 =
9 — 2 = 7,0004
9000 9000 9000 9000 + 2 = 10,000,000,000,000,000 9000 2=8 See what we got?
This is an addition and subtraction table with the number two.
This table must be known by heart.
Look at the left column of the table, how was it compiled?
Two were added to the result.
And the right column?
Subtracted two from the result.
Look at the number series
It is very easy to add or subtract the number two with it.
When we add or subtract the number two, we jump over one number.
Try it yourself, add two to one.
We start moving from point one to the right, jump over one number, stop at point three, it turns out …
Three.
1 + 2=3
We start moving from point eight to the left, jump over one number, we get …
Six.
1 + 2 = 3
— 2 = 6
Parsing of training tasks.
Solve examples using the number series:
Answer:
Write down the missing numbers, fill in the chips with the appropriate color.
Remember how they are compiled and fill in the tables for addition and subtraction with the number 2.
Answer:
Look at the picture. What expressions fit it.
Highlight matching expressions with color.
Answer:
Hint: think about what condition of the problem can be made according to the picture and what questions to answer.
Fill in the gaps so that the equalities are true.
Answer:
Solve math chains:
Answer:
Connect the dots in order. Who succeeded, write down the answer.
Answer: Elephant.
paint over the red color of the expression, the values of which are 6. Green — values that are 7.
5 + 2
— 1
6 + 1
7 + 2
8 — 1
6 — 2
9000
8 — 2
5 + 1
4 + 2
0 + 7,0004
Answer:
9009 9009 9009
5 + 2
7 — 1
6 + 1
+ 2 — 1 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 6000 6 — 2
6 — 0
9 — 2
8 — 2 5 + 1 9000 9000 9000
0003 4 + 2
0 + 7
Read the condition, question of the problem and solve it.

They circle above the flowers.
And the same number of dragonflies.
How many insects circle over the flowers?
Answer:
Mark the correct answer.
How many triangles are in the picture:
Answer:
Find the pattern. Insert the missing trailer. Indicate the corresponding numbers on all trailers.
Answer:
Look at the picture. Paste the data into the empty boxes.
Answer:
Match the condition and the solution of the problems. Insert the missing words in the problem statements. Natasha had a It became 2 …. How many carrots did Natasha have?
4 + 2
Serezha had . It became 2 …. How many apples did Seryozha have?
3 — 2
Was in the vase. It became 2 …. How many daisies are in the vase?
5 — 2
There was . It became 2 …
. How many cucumbers were on the plate?
4 + 2
Answer:
Condition
Decision
Natasha had . It became 2 more. How many carrots did Natasha have?
4 + 2
Serezha had . It became 2 less. How many apples did Seryozha have?
3 — 2
Was in the vase. It became 2 less. How many daisies were in the vase?
5 — 2
There was . It became 2 more. How many cucumbers were on the plate?
4 + 2
Hint: the words greater than or less than.
Complete the table.
Three school environmental groups took part in the action «Plant a tree!». The table records the number of trees they planted.
Mark with a sign which unit planted the most trees.
Answer:
Hint: first count how many trees each unit planted, and then check the box.
Look at the picture and choose the correct answer.
Will this money be enough to buy 2 small chocolates and a bun.
Answer:
Consolidation. Addition and subtraction within 10. Problem solving
Journey to a fairy tale. Mathematics lesson in grade 1 on the topic: “Reinforcement. Addition and subtraction within 10. Problem solving”
Objectives: to consolidate knowledge of the addition and subtraction tables and the composition of a number from two terms. Continue the work of teaching children how to compose and solve problems ..
Expected result: children learn to live and work in a team, evaluate themselves and their friends.
UUD training: the ability to generalize and concretize when building an answer to a question, to clearly and correctly express one’s thoughts.

Lesson scenario:
Inclusion in learning activities
-Guys, today we have an unusual lesson. I’ll tell you a secret: we will be filmed with a hidden camera, how we will work with you in the lesson, follow the rules of conduct. And then show your parents.
2. Actualization of knowledge
Logical warm -up
How many triangles
and how many quadrangles
Work in pairs
Make one figure
3. Summary of activity
Work in the group
4000 2 Work on the topic of the lesson
Well done, you have completed the task, we are setting off on a journey with fairy-tale heroes. Guys, let’s remember what fairy-tale characters are in this fairy tale.
And who was the first to come to the tower.
Slide №2
There is a teremok in the field. A mouse runs past. I saw a teremok, stopped and asked: -Teremok, teremok! Who lives in the terem?
Nobody answered her.
I wanted to open the door, but there was an inscription on the lock: Only the one who answers what the task consists of and solves the tasks will open.
Well, what can the guys help?
Slide №3,4,5
Problem solving
Slide №6
A mouse entered the house and began to live in it. Jumped to the tower Who? Frog-quack and asks: -Teremok, teremok! Who lives in the terem?
-I’m a mouse — norushka, and who are you?
And I’m a frog!
-Come live with me. The frog wanted to open it, and there was an inscription on it: There are many flowers around the tower, and they fall asleep at different times of the day. Guess what time different flowers fall asleep.
Slide #7
Slide #8
A frog jumped and they began to live together. Jumped to the tower Who? Runaway Bunny and asks: -Teremok, teremok! Who lives in the terem?
-I’m a mouse — norushka!
And I’m a frog, and who are you?
-And I’m a Runaway Bunny!
-Come live with us!
Hare at the door, there is a task on the door.

Slide #9
Choose the equation that matches the picture
Slide #10
A bunny jumped and the three of them began to live. Goes to the tower Who? Chanterelle-sister and asks: -Teremok, teremok! Who lives in the terem?
-I’m a mouse — norushka!
And I’m a frog!
— I’m a Runaway Bunny!
— who are you?
-I’m a fox-sister!
-Come live with us!
Chanterelle at the door, task on the door.
First you need to unravel the mystery — the door will open.
Slide #11
Children work in notebooks
PHYSMINUTKA (Musical physical minute)
Slide №12
The fox entered the teremok and they began to live. Ran to the tower Who? Top gray barrel and asks: -Teremok, teremok! Who lives in the terem?
-I’m a mouse — norushka!
And I’m a frog!
— I’m a Runaway Bunny!
-I’m a fox-sister!
— who are you?
-And I’m a spinning top Gray barrel!
-Come live with us!
A spinning top at the door, and a drawing on the door.

Slide No. 13
Number series
Slide No. 14
The wolf entered the teremok and they began to live. Goes past to the tower Who? Bear clumsy and asks: -Teremok, teremok! Who lives in the terem?
-I’m a mouse — norushka!
And I’m a frog!
— I’m a Runaway Bunny!
-I’m a fox-sister!
-And I’m a top gray barrel!
— who are you?
— I’m a clumsy bear!
-Come live with us!
a bear at the door and a picture on the door.
Slide No. 15
Sharada
Slide No. 16
Reflection
Our journey came to the end of
and I will show you where the hidden camera
is honestly evaluate your work in front of the camera.
— Show your salute how you liked lesson
Topic: “Solving examples and problems within 100”
Technological map of the lesson
Mukhtarova Lutfiya Tukhtamuradovna primary school teacher Municipal budgetary educational institution secondary school 69 with in-depth study of individual subjects Republic
More details
in mathematics Grade 2
MOU Bolshebykovskaya secondary school Open lesson in mathematics in grade 2 Topic: «Repetition and generalization of what was studied in grade 2» «Journey to a fairy tale» Prepared by a teacher of elementary
More
Open lesson in mathematics in the 2nd grade Honored Teacher of the Russian Federation Furagina
More
Abstract of a lesson in mathematics.

Summary of the lesson in mathematics. Teacher: Vissarionova I.E. Class: 2 «A» Date: 12/24/2018 Subject: mathematics UMK «School of Russia» Topic: «What did you learn. What have you learned.» Unit: Oral Calculus Lesson 54 Type:
More details
Stages, time 1 Org. moment
OPEN LESSON IN MATH Topic: «Division» Objectives: — to introduce the concept of division; — consider simple division problems (into parts and by content) and compare their solutions; — establish a connection between actions
Read more
Subject: “More. Less. The same number”
Technological map of the lesson in mathematics Grade 1 “Planet of Knowledge” Topic: “More. Less. The same number” Galetskaya Victoria Alexandrovna GBOU gymnasium 426 primary school teacher Topic: “More. Less.
Read more
«Solving motion problems»
Branch of MBOU Bolsheokulovsk secondary school Pozdnyakovskaya secondary school Synopsis of a lesson in mathematics in grade 4 «Solving motion problems» Prepared by: primary school teacher Chukhnina O.
M. The purpose of the lesson: — creating conditions
More
7*:: 2 31 4*
Open mathematics lesson in grade 3 Topic: «Multiplying a number by a product» lesson to consolidate the material Lesson objectives: Educational: Summarize the material on the topics «Multiplication of multivalued numbers into single digits»,
More
School of Childhood Association
MBUDO CDT Phoenix School of Childhood Association Additional general education program for the formation of mathematical concepts in preschool children «Counting» (third year of study).
Read more
Mathematics lesson flow chart.
Technological map of the lesson of mathematics. Subject of the teaching materials Time of the lesson Class Full name of the teacher Theme of the lesson Type of the lesson Purpose of the lesson Tasks of the lesson Teaching methods Pedagogical technologies Forms of organization of work
Read more
Topic: “Names of numbers in multiplication.
”
Municipal educational institution Padovskaya secondary school Mathematics lesson in grade 2 Topic: «Name of numbers in multiplication.» Teacher: Noskova O.N. 2010 Topic: “Name
More
Summary of a lesson in mathematics in grade 7
Municipal special (correctional) educational institution for students with disabilities, Kola special (correctional) general education school of the VIII type of Municipal
Read more
Personal results
Technological map of the lesson of mathematics Class 6b Date 30. 11.2018 Mathematics teacher Maslennikova Maria Vasilievna Topic Types of triangles. Construction of an equilateral triangle. Lesson type Lesson of receiving
Read more
Topic: “Addition of fractions with the same
Math lesson. 4th grade. Program «School 2100». according to the textbook by L.G. Peterson (grade 4, part 2, lesson 3) Topic: «Addition of fractions with denominators.
» A lesson in discovering new knowledge. Prepared by: Moiseeva E.R.
More
Grade 3 (1-4). The program of Istomina N.B.
Grade 3 (1-4). The program of Istomina N.B. Topic: «FIVE-DIGITAL AND SIX-DIGITAL NUMBERS». (First lesson.) The purpose of the lesson: to introduce the concept of «five-digit» numbers, to teach how to read and write such numbers. Tasks: EDUCATIONAL:
More
Mathematics lessons in the 6th grade.
Mathematics lessons in the 6th grade. Decomposition into prime factors (h) Lesson 11. Decomposition into prime factors Objectives: to introduce the decomposition into prime factors of a number; repeat the power of a number; form
Read more
Subtract up to 10 worksheets
Welcome to the Subtract up to 10 worksheets section.
Here you will find a wide range of free printable math assignments for kindergarten,
which will help your child learn to subtract up to 10.
Worksheets start at an easy level and get progressively more difficult.
Here you will find our range of free kindergarten subtraction sheets.
The following tables use subtraction skills. sheets carefully
so that the easier sheets come first and the level of difficulty gets progressively more difficult.Using these worksheets will help your child:
- subtract with numbers up to 10.
All of the addition worksheets in this section correspond to elementary math kindergarten tests.
Take a look at some more of our worksheets similar to these.
We also have some more kindergarten subtraction worksheets with numbers within 10.
The sheets on the page below are at an easier level than the sheets on this page.
Worksheets include subtraction facts up to 5 and also use images to support subtraction up to 10.
Here you will find a range of free printable materials for kindergarten.
Addition and subtraction worksheets.
The following charts include addition and subtraction up to 10.
Using these worksheets will help your child:
- add and subtract up to 10.
Once your child has learned to count things up to 10 and write down their numbers, he is ready start counting one more and one less.
The worksheets provided here will help your child count one more/one less.
Most of the worksheets focus on counting up to 10. There are also some worksheets that go up to 25.
Here you will find a number of free printable math worksheets for kindergarten.
to study numerical facts.The following worksheets include various kindergarten maths.
activities such as counting, coloring and learning to write numbers.Using these sheets will help your child:
- reading and writing numbers up to 25;
- compare numbers with 10.
All math worksheets in this section are compiled
tests in elementary mathematics for kindergarten.
Here is our selection of bond number worksheets up to 10.
The worksheets in this section will help your child learn number pairs up to 10.
Math Salamanders hope you enjoy these free printable math worksheets.
and all our other math games and resources.We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets in the Facebook comment box at the bottom of every page.
131 Addition and Subtraction Worksheets (K-4)
Listed below are all the Addition and Subtraction worksheets available on the site. There are fact family worksheets up to 9. Addition and subtraction worksheets include both numbers up to 10 and numbers up to 20. There is also a universal worksheet generator that allows you to ask an unlimited number of addition and/or subtraction questions.
Worksheet Generator
Addition and Subtraction Worksheet Generators allow you to create a wide range and unlimited number of tasks by specifying many parameters.
These include options for creating worksheets with large print and limiting the number of questions that can meet the varying needs of students. Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator (adding and/or subtracting zeros, ones and/or doubles) Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator (Cuisenaire Rod-like) Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator Addition and subtraction with 3 numbers (e.g. gram 5) + 6 + 3 = 14, 12 — 3 + 7 = 16) Regroup ten subtraction (includes base decimal block visuals) Regroup subtraction (with place value blocks) Custom addition worksheet generator Addition and subtraction tables Custom subtraction worksheet generator
Bond number up to 10
The Number Link Worksheets are basic activities that help students with Number Links develop an understanding of how numbers can be added or broken apart.
Number of bonds
More numeric bonds with multiples of 10 to 100.
Facts of Families
Facts of Families help students learn arithmetic facts and at the same time strengthen the connection between addition and subtraction.
Examples: 3 + 4 = 7, 4 + 3 = 7, 7-3 = 4, 7-4 = 3
Addition and Subtraction Facts
This worksheet series was developed by Susan Greenwald, MA Ed. and taken from her workbook Two plus two is not five . Learn more about Susan Greenwald here.
K 10
Addition and subtraction within 10.
Jumper
Students’ ability to be able to overcome more than 10 and more than multiples of 10 can be practiced using the worksheets below.
K 20
Slightly different
Worksheets that present addition and subtraction in alternative ways and in various formats.
K 100
Large numbers
These worksheets usually include numbers greater than 100.
Three or more
Addition with 3 or more numbers
Third/Fourth grade
years and older — and includes addition and subtraction with numbers greater than 1000.
Most worksheets include a «Show Answer» option that you can select to allow viewing and printing of answer sheets.

Basic subtraction within 10 (worksheets)
In this math card game, students take turns matching each subtraction fact to its answer.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Registered members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets to save their favorite worksheets.
Quick access to your most used files AND custom worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to take advantage of this helpful feature.
Print out a subtraction bingo board for each student in your class. The teacher names the subtraction facts and the class marks the answers on their boards.
Kindergarten & 1st Grade
This is a fun single player dice game. Your student will roll two dice and write the numbers in the squares (higher number first) and solve the subtraction problem.
Kindergarten and 1st grade
Players take turns rolling a pair of dice. After each roll, the player subtracts the smaller number from the larger number.
The player with the highest margin wins the round. All lows and responses are 10 or less.
Kindergarten and 1st grade
Students roll a die and compare the number rolled to the column in the subtraction table. They read and answer all subtraction facts in a column as accurately and quickly as possible. All lows and responses are 10 or less. (Example: 7-3 = 4)
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
This printable worksheet has 4 word problems with illustrations to help students solve the subtraction problem.
Kindergarten & 1st Grade
Use counter pictures to help you solve basic subtraction problems.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Solve basic subtraction problems by drawing chips in the space provided and circling the chips to form the reduced number.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
On this sheet, students will determine how many tokens are missing from the problem and draw them to complete the subtraction problem.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
On this worksheet, students can draw pictures to help them solve subtraction problems.

Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Using pictures of fruit as a visual aid, the student will solve these four basic subtraction problems.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Use pictures of animals to help you solve basic subtraction facts.
Kindergarten and Grade 1
Students will find the difference for each of these tasks. Use scissors and glue to match the numbers to the correct boxes.
Kindergarten and Grade 1
Cut the puzzle pieces. Match the subtraction problems with their answers. Make a great learning center. (Note: There is an alternative full color version of this exercise. If you would like a color version, click the alt button below.)
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Students can practice basic subtraction with this printable puzzle.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Ask students to figure out which subtraction problems are shown on each number line.
Kindergarten to 2nd Grade
These printable number line worksheets serve as visual aids to help students identify the subtract in each subtraction fact.

Kindergarten to 2nd Grade
Students will «count down» the number lines to find the missing subtract in each subtraction fact.
Kindergarten to Grade 2
This worksheet has number lines to help students solve subtraction facts.
Kindergarten to 2nd grade
Students will use the number bar to identify an addition or subtraction problem and write it on a line.
Kindergarten and 1st Grade
Fact Subtraction Practice
Write answers to the subtraction facts on the caterpillar. All facts have minimum values and quotients of 10 or less. (Example: 7-3)
Kindergarten and Grade 1
Tell me which facts are correct and which are not. If the fact is incorrect, cross out the difference and write the correct answer.
Kindergarten and 1st grade
Find the differences for these subtraction facts, then color according to the key.
Kindergarten to Grade 2
Your students will have fun solving subtraction problems and coloring the cryptic picture to find school supplies on the table.

Kindergarten to Grade 2
In this worksheet, students will solve basic subtraction problems by 10 or less. The finished painting will show a reading bird sitting on its nest.
Kindergarten up to Grade 2
After writing the differences for the problems on the page, color the sea monster (dragon) according to the color code at the bottom of the picture.
Kindergarten to Grade 2
Ask students to solve these easy subtraction problems. They will then use the color key to color the puzzle to see the seashells on the beach.
Kindergarten to 2nd Grade
After the students find the answers to the subtraction facts, they can color each space according to the key to see the gray whale and the blue whale.
1
______
0
4. Draw what will be further in the siz.
5. Fill in the field.
__________ + 8 = 10
6.
Complete the concatenation of the numbers that add to 10.
7. Write a number sentence to model the picture.
________ + ________ = _________
8. Fill out the form.
6 + __________ = 10
9. Write a number sentence to model the picture.
______ __ ______ = _______
10. Write a number sentence to model the picture.
______ __ ______ = _______
11. Sam had 5 apples. He ate 3 apples. How many apples does Sam have now? Write a number sentence to answer the question.
______ __ ______ = _______
12. Draw a picture in a box to model a number sentence. 95
0
4
4. Draw what will be next in the pattern.
5. Fill in the field.
2 + 8 = 10
6. Complete the concatenation of the numbers that add to 10.
7. Write a number sentence to model the picture.

3 + 7 = 10
8. Fill out the form.
6 + 4 = 10
9. Write a number sentence to model the picture.
6–4 = 2
10. Write a number sentence to model the picture.
4 + 2 = 6
11. Sam had 5 apples. He ate 3 apples. How many apples does Sam have now? Write a number sentence to answer the question.
5–3 = 2
12. Draw a picture in a box to model a number sentence.
1 + 4 = 5
Show all the ways to make six. Use a pattern. Use numbers and pictures.
Show all the ways to make six. Use a pattern. Use numbers and pictures.
Combinations in this particular order from top to bottom should include 6 and 0, 5 and 1, 4 and 2, 3 and 3, 2 and 4, 1 and 5, and 0 and 6 with pictures to support these numbers. Students should be able to describe the descending order of the numbers in the first column and the ascending order in the second column.
They must also show an understanding that the two columns are related. That is, when an object is removed from a set and placed in another set on the same row, one number decreases and another increases.
Points
Description
Written and verbal explanations are detailed and clear. The student demonstrates an excellent understanding of questions, mathematical concepts and processes. The student goes beyond the requirements of the task. The student may be using multiple methods/solutions. The image is suitable, excellent quality and creative. 3
- The math is correct in the work shown.
- Written and verbal explanations are detailed and clear.
- The student demonstrates a good understanding of questions, mathematical concepts and processes.
- The student meets all requirements of the task.

- The image is good, high quality and neat.
2
- Math is correct with or without minimal work.
- Written and oral explanations are present, but do not contain some details.
- The student demonstrates a partial understanding of questions, mathematical concepts and processes.
- The student meets most of the requirements of the task.
- The graphic is complete, but there may be errors.
1
- Math is wrong, some work is shown.
- Written and verbal explanations are incomplete and not detailed enough.
- The student has a poor understanding of questions, mathematical concepts and processes.
- The student does not meet most of the requirements of the task.
- The image is incomplete, does not match the situation or is missing.
0
- Math is wrong, work not shown.

- Written and verbal explanations are illogical or absent.
- The student does not understand questions, mathematical concepts and processes.
- The student does not meet the requirements of the task.
- Not pictured.
10 Kindergarten Lesson Fun Subtraction: Strawberry
This post contains affiliate links for your convenience. By clicking on these links, I can earn a commission at no additional cost to you.
Strawberry season! Strawberry season is the perfect time of year for little learners to practice some delicious math facts! These adorable strawberry-themed activities are a fun way to introduce subtraction to kindergarten kids? These fun 10 Kindergarten subtraction activities are a great way to learn to subtract with your kids. Choose from Google Slides or Seesaw for this fun digital event.
Compliance
Before entering first grade, students are expected to be able to add and subtract within 10 smoothly.
In addition, they should know how to add and subtract within 10 using objects or pictures to represent the problem.
Vocabulary and symbols with subtraction
Children may find it difficult to understand the concept of subtraction. You need to help kindergartners imagine the concept of how to put things away to find out what’s left (difference).
In addition to learning new academic vocabulary, it can be extremely difficult for young students to memorize the functions of various mathematical symbols.
- Plus (+) add
- sign minus / subtraction (-) Conclusion
Equal sign (=) the same as
Google slide or swing
if you prefer you to use it Google Slides or Seesaw, this cute subtraction spreadsheet package gives you access to both. These colorful, kid-friendly interactive slides allow kindergarten mathematicians to have fun practicing subtraction exercises.
Each slide sheet focuses on a visual word problem with a large strawberry on a paper plate.
Part of the strawberry is crossed out to visualize the concept of subtraction.
The slides also have large bold blocks numbered 1 to 10 in a layout similar to a tens box or number line. The gap-filling subtraction equation is printed below the picture. Children will click and drag the numbered blocks to fill in the equations. Blocks can help children use different strategies, such as counting backwards or backwards, to solve subtraction problems.
Challenge students to increase the difficulty by having them complete different parts of the equation first. This exercise will also help improve students’ understanding of the various parts of the equation.
Expanding Math
Print slides to use as math worksheets for additional subtraction activities.
Give your child small erasers or other small tokens to help him physically represent subtraction problems.
For easy work in the center or in small groups, insert worksheets into protective sleeves.
Give the children an erasable marker and have them write the numbers on the blanks to complete the subtraction equation.
For even more fun with addition and subtraction, give your little one a handful of strawberries. Help them understand the relationship between addition and subtraction while enjoying delicious math fun!
This fun subtraction package will help your kindergartner master the facts of subtraction and demonstrate addition fluency. Continuing with these activities will help your kindergartner become a first grader!
More activities you’ll love!
Mixed Addition and Subtraction Worksheets
Simple Addition and Subtraction
Addition and Subtraction Fact Family Worksheets
histograms; recording four facts of addition and subtraction in house models, dominoes, picture models and more.
Addition and Subtraction Fact Family (31 sheets)
Basic Addition and Subtraction Worksheets
The printed worksheets here include single digit addition and simple subtraction up to a difference of 9.

Simple addition and subtraction: column 1
Simple addition and subtraction subtraction: column 2
Simple addition and subtraction: horizontal 1
Simple addition and subtraction: horizontal 2
- Download all
Addition and Subtraction Drill
Enlighten your kids with this worksheet set that combines 50 addition and subtraction questions per page into a perfect combination.
Addition and subtraction drill: column 1
Addition and subtraction exercise: column 2
Addition and subtraction drill: horizontal 1
Addition and subtraction drill: horizontal 2
90 90 90 90 Download all0002 2-digit and single digits
Addition and subtraction worksheets include double and single digit numbers.
Simple Addition and Subtraction Worksheet 1
Simple Addition and Subtraction Worksheet 2
- Download All
Addition and Subtraction: Moderate
or subtract two-digit numbers arranged here in column and horizontal format.

2-digit addition and subtraction — column 1
Add and subtract two digits — column 2
Add and subtract two digits — horizontal 1
2-digit addition and subtraction — horizontal 2
- Download all6
Balancing equations
Fill in the missing fields to balance addition or subtraction problems.
Balance the equation — easy 1
Balance the equation — easy 2
Balance an equation — hard 1
Balance an equation — hard 2
- Download all
Addition and subtraction Fluency up to 100 for 2nd grade
Second grade is a very important year to develop subtraction fluency in addition and 92 100 . In Module 3 of the Math for Fun 2nd Grade Curriculum, we focus on Addition and Subtraction up to 100. Mastery of Basic Addition and Subtraction up to 20 is the basis for learning addition and subtraction up to 100. In addition, mastery of facts is up.
up to 20 years with games, practical strategies and lots of practice helps students gain confidence and skills. Students then work on more complex mathematical calculations of addition and subtraction up to 100 using a variety of strategies, models, and reasoning.
In this math block with sums up to 100, students will learn:
* Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one-step and two-step word problems
* Freely add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies
* Determine if a group of objects (up to 20) has an even or odd number of members
* Write an equation to express an even number as the sum of two equal terms
* Freely add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on digits, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction
* Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on digits and properties of operations
* Mentally add 10 to the given number 0-90 and mentally subtract 10 from the given number 10-100
* Represent integers as lengths from 0 on a numerical line chart with equally spaced points corresponding to the numbers
* Plot sums of integers and differences within 100 on a number chart
, 49 math centers, and , 93 pages NO PREPARATION / ACTION!
SAVE $$$ WITH YOUR PACKAGING!
ALL 10 UNITS INCLUDED!
Here are 10 units that will be included in Grade 2: Math Curriculum
Unit 1: Number Sense to 1,000
Block 2: Place value up to 1000
Block 3: Addition and subtraction Fluency within 100
Block 4 3-digit addition and subtraction2
Block 5: Geometry and Fractions
Block 6: Graphs and Data
Block 7: Time
Part 2 Block 8:
Money
: Measurement
Block 10: Multiplication and division
Each block
includes a scope with lenses :
Lesson plans broken into 5 easy to understand parts: 1.
Task — What students should be able to do by the end of the lesson.
2. Review- A quick warm-up that allows students to practice previous skills that will be used in the current lesson.
3. Hook- A fun introduction to get students involved.
4. Mini Lesson — Teach, simulate and discuss a new skill in today’s lesson.
5. Practice — Each practice section lists three types of exercises that go well with a particular lesson. Center(s) — New centers to be introduced in the lesson. Activity Pages- These pages require some basic materials such as scissors, glue or dice. Practice Pages — All you need is a pencil and crayons! They are great for working at your desk, doing homework or working on the go!✸ Differentiation — Each lesson includes frameworks and additional ides to meet the needs of students of all levels !
preliminary and subsequent estimates for EACH division!
Material Wrap Page !
SEE MATH CENTERS FOR BLOCK 3 IN ACTION.
..
CENTER NUMBER 1: Fact Reading Strips (add within 20)
Solve problems. Write sums with dry erase marker. Check your answers on the key.
CENTER NUMBER 2: Actual fluency bars (subtract within 20)
Solve problems. Write down the differences with a dry erase marker. Check your answers on the key.
CENTER NUMBER 3: Fact fluency strips (addition and subtraction within 20)
Solve problems. Write down the sums and differences with the dry erase marker. Check your answers on the key.
CENTER NUMBER 4: Add facts about fluency within 20
Flip the card. Solve the problem and find the correct amount on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 5: Subtraction of actual fluency within 20
Turn over the card. Solve the problem and find the matching difference on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 6: Mixed review of actual fluency for 20
Flip the card.
Solve the problem and find the corresponding amount or difference on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 7: Addition of facts (adding 3 numbers to 100)
Turn the card over. Solve the problem and find the correct amount on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 8: Addition of facts (adding 4 numbers to 100)
Turn the card over. Solve the problem and find the correct amount on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 9: Roll out and mentally solve (add up to 20)
Roll a die. Solve mentally the problems that are in this row. Color the star every time you solve problems.
CENTER NUMBER 10: Roll out and solve mentally (subtract to 20)
Roll a die. Solve in your mind the problems that are in this row. Color the star every time you solve problems.
CENTER NUMBER 11: Roll it out and solve mentally (Mixed review, up to 20)
Roll a die.
Solve in your mind the problems that are in this row. Color the star every time you solve problems.
CENTER NUMBER 12: Adding tic-tac-toe (within 100, no rearrangement)
Take turns with a friend to solve addition problems. Each player uses a different color to write answers. The first person to get three in a row wins.
CENTER NUMBER 13: Adding tic-tac-toe (within 100, with rearrangement)
Take turns with a friend to solve addition problems. Each player uses a different color to write answers. The first person to get three in a row wins.
CENTER NUMBER 14: Tic-Tac-Toe Subtraction (within 100, no regrouping)
Take turns doing subtraction problems with a friend. Each player uses a different color to write answers. The first person to get three in a row wins.
CENTER NUMBERS 15: Tic-Tac-Toe Subtraction (within 100, with rearrangement)
Take turns doing subtraction problems with a friend. Each player uses a different color to write answers.
The first person to get three in a row wins.
CENTER ROOM 16: Tic Tac Toe (Mixed)
Take turns solving math problems with a friend. Each player uses a different color to write answers. The first person to get three in a row wins.
CENTER NUMBER 17: Addition Spin & Calculate (within 100, no regrouping)
Spin both spinners. Add up the numbers. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 18: Spin and Solve Addition (within 100, with rearrangement)
Spin both spinners. Add numbers. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 19: Spin-and-solve subtraction (within 100, no regrouping)
Spin both spinners. Subtract the number of rotations B from the number of rotations A. Write the equation on your note sheet.
CENTER NUMBER 20: Spin and solve (within 100, with regrouping)
Spin both spinners. Subtract the number of rotations B from the number of rotations A. Write the equation on your note sheet.

CENTER NUMBER 21: Adding ice cream (within 100, no regrouping)
Turn the card over. Solve the addition problem. Record the equation in the protocol.
CENTER NUMBER 22: Ice cream addition (within 100, with rearrangement)
Turn the card over. Solve the addition problem. Record the equation in the protocol.
CENTER NUMBER 23: Word problems (one-step, up to 20)
Read the word problem. To solve the problem. Show off your work on the rug.
CENTER NUMBER 24: Word problems (single-stage, up to 100 with unknown onset, no regrouping)
Read the word problem. To solve the problem. Show off your work on the rug.
CENTER NUMBER 25: Word problems (one-step, up to 100 with unknown onset, with regrouping)
Read the word problem. To solve the problem. Show off your work on the rug.
CENTER NUMBER 26: Problems with words (two-stage, up to 100, no regrouping)
Read the word «problem». Solve the problem.
Show off your work on the rug.
CENTER ROOM 27: Problems with words in the number line
Read the word problem. Use the number line to solve the problem. Record the question and answer in the minutes.
CENTER ROOM 28: Spin and Cover
Spin both spinners. Add up the numbers and cover the matching number.
CENTER NUMBER 29: Roll and Lid
Roll two dice. Put them together. Solve a subtraction problem whose difference is equal to the sum of the dice.
CENTER NUMBER 30: Open lines with numbers added
Use an open number line to solve an addition problem. Record the equation in the protocol.
CENTER NUMBER 31: Number of lines with open subtraction
Use an open number line to solve a subtraction problem. Record the equation in the protocol.
CENTER NUMBER 32: Subtraction of the number line
Turn over the card. Read the issue. Decide which segments of the number line you need to help you solve the problem.
Record your answer on the log.
CENTER NUMBER 33: Add and add three two-digit numbers
Roll a die. Solve the problem in this row and close.
CENTER NUMBER 34: Fluency in Facts — No Additions
Complete each equation by completing the missing items.
CENTER NUMBER 35: Fluency in Facts — Complement to 20
Complete each equation by filling in the missing amounts.
CENTER NUMBER 36: Addition
Break the two-digit number into tens and ones. Write a new addition problem and solve.
CENTER NUMBER 37: Bubble number: shuffle (add 2 digit and 1 digit number, no rearrangement)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles. Arrange them in boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER NUMBER 38: Bubble number: shuffling (adding two two-digit numbers, no rearrangement)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles. Arrange them in boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER NUMBER 39: Bubble Number: Mixing (adding 2 digit and 1 digit number with rearrangement)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles.
Put them into boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER ROOM 40: Bubble number jumble (adding two two-digit numbers with rearrangement)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles. Arrange them in boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER NUMBER 41: Bubble number, confusion (subtraction of a single number from a two-digit number, no regrouping)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles. Arrange them in boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER NUMBER 42: Bubble number correspondence (subtracting a 2-digit number from a 2-digit number, without regrouping)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles. Arrange them in boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER NUMBER 43: Bubble number, shuffle (subtraction of a single number from a two-digit number with rearrangement)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles. Arrange them in boxes so that the equation is correct.
CENTER NUMBER 44: Bubble Confusion (subtract 2 digit number from 2 digit number with rearrangement)
Look at the numbers on the bubbles.

 Ann gave Pete 5 more apples, How many apples does Pete have now?
Ann gave Pete 5 more apples, How many apples does Pete have now?  She gave 4 dimes to Mike. How many dimes does Sandi have now?
She gave 4 dimes to Mike. How many dimes does Sandi have now?  How many children are on the team?
How many children are on the team? Sandi put in 8. How many did Bobbi put in? or Mike and Sandi put 11 dimes into a piggy bank. Mike put in 7 dimes. How many dimes did Sandi put in?
Sandi put in 8. How many did Bobbi put in? or Mike and Sandi put 11 dimes into a piggy bank. Mike put in 7 dimes. How many dimes did Sandi put in?  Sandi has 5 dimes. How many fewer dimes does Sandi have than Mike?
Sandi has 5 dimes. How many fewer dimes does Sandi have than Mike? She has 5 sweaters more than Sue. How many sweaters does Sue have?
She has 5 sweaters more than Sue. How many sweaters does Sue have?  Four of them sat down so each boy would have a partner. There are 7 boys in the dancing group. How many girls are in the dancing group?
Four of them sat down so each boy would have a partner. There are 7 boys in the dancing group. How many girls are in the dancing group?
 Textbook. 1 class At 2 hours, part 1. — M .: Education, 2017. — p. 90 – 93.
Textbook. 1 class At 2 hours, part 1. — M .: Education, 2017. — p. 90 – 93.  Two birds have flown away.
Two birds have flown away.  Number 1
Number 1 How? 1 to 5
How? 1 to 5 Number 6
Number 6 Parts of a cut
Parts of a cut Numbers 1 to 9
Numbers 1 to 9 Numbering (alphabetic, Roman)
Numbering (alphabetic, Roman) How? 11 to 20
How? 11 to 20 Numbering. Numbers and numbers
Numbering. Numbers and numbers .. Zoom in… Zoom out… Zoom out…
.. Zoom in… Zoom out… Zoom out… Types of triangles
Types of triangles Numbering
Numbering Sets of Solutions
Sets of Solutions Distributive law of multiplication with respect to addition
Distributive law of multiplication with respect to addition Minute. Second
Minute. Second Finding a part of a number
Finding a part of a number Extracting the integer part from an improper fraction
Extracting the integer part from an improper fraction Problem solving
Problem solving Roman numeration
Roman numeration Estimating and evaluating the results of calculations
Estimating and evaluating the results of calculations The concept of an ordinary fraction
The concept of an ordinary fraction Angle measurement
Angle measurement Scale. Scale types
Scale. Scale types Addition and subtraction
Addition and subtraction Decimal division
Decimal division Volume
Volume Decomposition of a natural number into prime factors
Decomposition of a natural number into prime factors Properties
Properties Coordinate plane, point coordinates
Coordinate plane, point coordinates Pi. Circumference. Area of a circle
Pi. Circumference. Area of a circle


 Video tutorials, tips and
Video tutorials, tips and 8-1 = 7, 7- 7- 7- 7- 7- 1=6 Answer: 7 hats and 6 berets
8-1 = 7, 7- 7- 7- 7- 7- 1=6 Answer: 7 hats and 6 berets 


 Underline each 2.
Underline each 2.  Emphasize each number equal to 11.
Emphasize each number equal to 11. 

 Mathematical development
Mathematical development

 Balloons
Balloons 
 To find the correct answer, you need to focus and look at the puzzle from different perspectives.
To find the correct answer, you need to focus and look at the puzzle from different perspectives. 


 This process is called education.
This process is called education.  Make it a rule to have a mystery night at least once a week. Teach your child to make puzzles.
Make it a rule to have a mystery night at least once a week. Teach your child to make puzzles.  Here you need to apply the main and basic principle — so that your child already begins to clearly understand that in this world there is always both a cause and an effect.
Here you need to apply the main and basic principle — so that your child already begins to clearly understand that in this world there is always both a cause and an effect.  How to help kids? The main thing is not to get angry with children if they do not grasp everything “on the fly”. This is for you, adults, everything is easy and simple, but for children who have just begun to master numbers and counting, everything is very difficult. Any teacher or child psychologist in Moscow will confirm that the most effective way for children to memorize new material is to play math classes.
How to help kids? The main thing is not to get angry with children if they do not grasp everything “on the fly”. This is for you, adults, everything is easy and simple, but for children who have just begun to master numbers and counting, everything is very difficult. Any teacher or child psychologist in Moscow will confirm that the most effective way for children to memorize new material is to play math classes. 
 The baby must guess what this number is.
The baby must guess what this number is.  This helps the child learn to reason, prove, explain their actions. He begins to understand what needs to be added and what should be subtracted.
This helps the child learn to reason, prove, explain their actions. He begins to understand what needs to be added and what should be subtracted.  They reflect the life of children, that is, what they usually do. This species is of particular value in the initial stages. Children develop the skills of composing tasks about themselves, the ability to talk about each other’s actions;
They reflect the life of children, that is, what they usually do. This species is of particular value in the initial stages. Children develop the skills of composing tasks about themselves, the ability to talk about each other’s actions; 

 Ask the question: “How many apples have there been?”, “How many more apples have there been?”.
Ask the question: “How many apples have there been?”, “How many more apples have there been?”. 

 The sticks will be wagons, and printouts of pictures with animals will be passengers. Children practice in ordinal counting, correlating each bar with a specific number.
The sticks will be wagons, and printouts of pictures with animals will be passengers. Children practice in ordinal counting, correlating each bar with a specific number.  For example, counting to 10 and 20 is designed for children who are learning to count objects, but still do not know numbers well and do not know how to solve mathematical expressions.
For example, counting to 10 and 20 is designed for children who are learning to count objects, but still do not know numbers well and do not know how to solve mathematical expressions. 
 Who is our last, sixth?” — «Motya».
Who is our last, sixth?” — «Motya».  The game is played at a fast pace.
The game is played at a fast pace.  Looking at the image of an object, a preschooler builds the same from cubes.
Looking at the image of an object, a preschooler builds the same from cubes. 


 In this way, the child will calculate numerical examples in the future, imagining the specified number of objects in his mind and subtracting the specified number from them in his mind.
In this way, the child will calculate numerical examples in the future, imagining the specified number of objects in his mind and subtracting the specified number from them in his mind.  Write your answers by circling the words in the numerical example.
Write your answers by circling the words in the numerical example.  As a rest and switch attention tasks can be used in the middle of the lesson.
As a rest and switch attention tasks can be used in the middle of the lesson. 

 html
html 

 In the process of coloring, the child will remember how the number looks and what it is called, and will understand its “numerical content”. In addition to the inscription of numbers, such coloring pages can also contain elements of geometry — from circles, squares, triangles, a child can add various ornaments and paint them in different colors. Moreover, there are coloring pages that can teach a child ordinal counting — these are coloring pages from the Draw by Numbers series, in which, by sequentially drawing a broken line from number to number, the kid himself can draw a rather complex picture. Coloring pages may contain various exercises. An example of such a task is a number in a large circle, the child needs to draw and color in it as many small circles as this number indicates.
In the process of coloring, the child will remember how the number looks and what it is called, and will understand its “numerical content”. In addition to the inscription of numbers, such coloring pages can also contain elements of geometry — from circles, squares, triangles, a child can add various ornaments and paint them in different colors. Moreover, there are coloring pages that can teach a child ordinal counting — these are coloring pages from the Draw by Numbers series, in which, by sequentially drawing a broken line from number to number, the kid himself can draw a rather complex picture. Coloring pages may contain various exercises. An example of such a task is a number in a large circle, the child needs to draw and color in it as many small circles as this number indicates.  Of course, the main role in such activities, at least initially, belongs to parents — they must come up with tasks and teach the child how to «play» cards.
Of course, the main role in such activities, at least initially, belongs to parents — they must come up with tasks and teach the child how to «play» cards.  Such classes are highly recommended in all pre-school programs from the age of 5. When working with any copybook, neat writing skills are developed, attentiveness and perseverance develop.
Such classes are highly recommended in all pre-school programs from the age of 5. When working with any copybook, neat writing skills are developed, attentiveness and perseverance develop.  Any mom or dad can teach their child the basics of mathematical science. The main thing is to follow a few rules so as not to turn fun activities into a dreary duty.
Any mom or dad can teach their child the basics of mathematical science. The main thing is to follow a few rules so as not to turn fun activities into a dreary duty.  This means that they can associate the number of objects with a digit.
This means that they can associate the number of objects with a digit. 


 The student should identify the key concepts and sums it contains and (sometimes) draw a picture of each sentence to better understand the problem. practice with it.
The student should identify the key concepts and sums it contains and (sometimes) draw a picture of each sentence to better understand the problem. practice with it.  Opportunities for learning these skills are everywhere—and there are simple and enjoyable activities that parents can arrange to develop these skills.
Opportunities for learning these skills are everywhere—and there are simple and enjoyable activities that parents can arrange to develop these skills.  Parents can indicate the numbers on the clock or phone.
Parents can indicate the numbers on the clock or phone.  Remember, children of mathematical language hear something important. Parents can ask questions such as «How many more plates do we need?» «
Remember, children of mathematical language hear something important. Parents can ask questions such as «How many more plates do we need?» « 
 Geometry
Geometry

 Hesitation is a sign that skill is not yet enough.
Hesitation is a sign that skill is not yet enough. 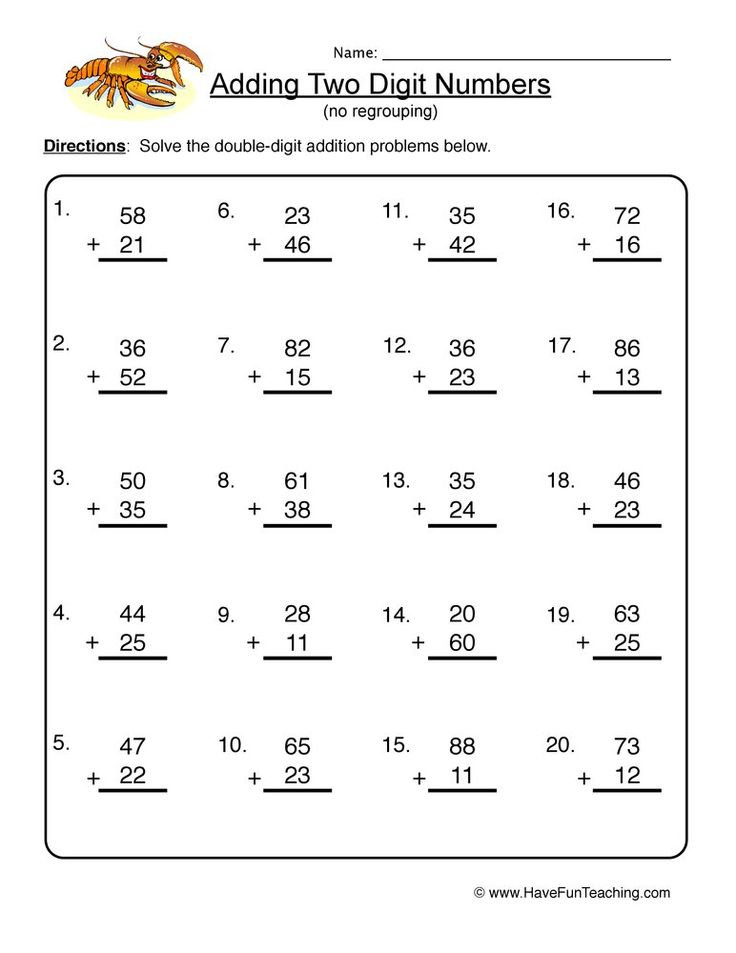 ”
”  These things are separated from each other, and from here you cannot get here.
These things are separated from each other, and from here you cannot get here.  … No single element of mathematics is suitable for everyone. People are different and people need to approach math differently.
… No single element of mathematics is suitable for everyone. People are different and people need to approach math differently.  Too often, parents and teachers think that students are not good at math, when the real problem is the lack of math practice.
Too often, parents and teachers think that students are not good at math, when the real problem is the lack of math practice.  Improving math skills, in turn, will boost a child’s self-confidence and make them feel good about math. Developing a positive attitude towards math will help them pick up new skills and concepts and further help their child improve in the subject. This is why many parents like to give their kids some extra math practice at home with free online math problems.
Improving math skills, in turn, will boost a child’s self-confidence and make them feel good about math. Developing a positive attitude towards math will help them pick up new skills and concepts and further help their child improve in the subject. This is why many parents like to give their kids some extra math practice at home with free online math problems. 
 Learn more
Learn more  How do you think you will cope with this task? Learn more
How do you think you will cope with this task? Learn more  Learn More
Learn More  Learn more
Learn more  The activity is about products and their relationship. Learn more
The activity is about products and their relationship. Learn more  Learn more
Learn more 
 Join him and you — it will be a real pirate adventure!
Join him and you — it will be a real pirate adventure!  Then you can try to complete this task for a while.
Then you can try to complete this task for a while. 
 The more often he counts objects, the faster his mathematical skills will be formed.
The more often he counts objects, the faster his mathematical skills will be formed. 

 He learns to compare them and solve problems of the studied species.
He learns to compare them and solve problems of the studied species. 

 I.Bashmakov, M.G.Nefyodova EMC “Planet of Knowledge”)
I.Bashmakov, M.G.Nefyodova EMC “Planet of Knowledge”) 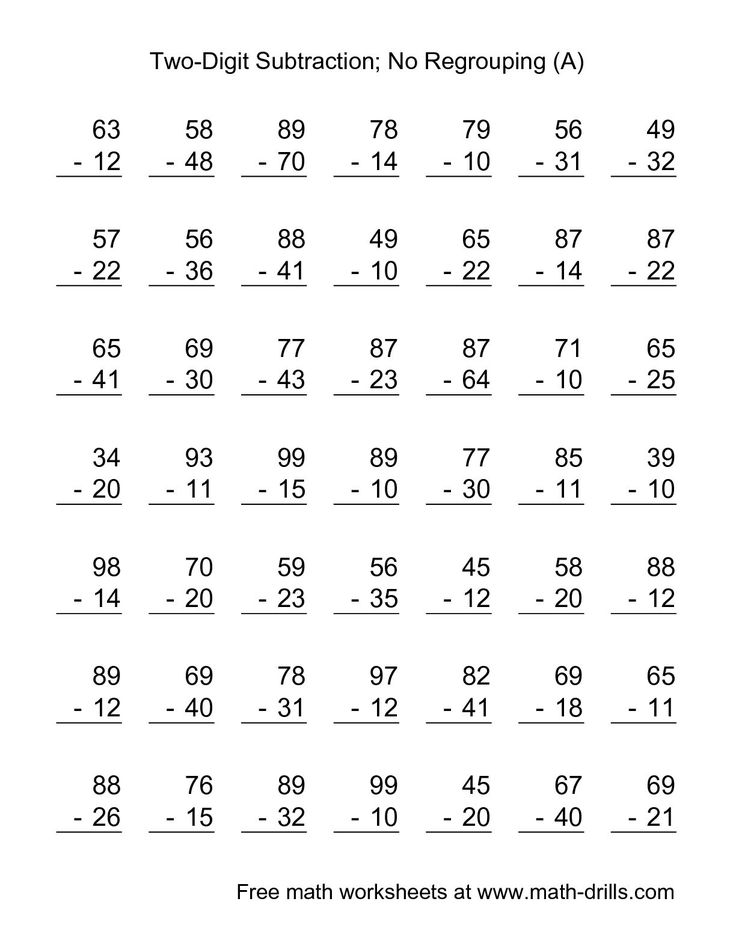 They will be to us
They will be to us

 This is a house
This is a house (Answers on the board)
(Answers on the board)  4. When Katya made friends with 4 classmates, she became 9friends. How many friends did Katya have at first? Drawing: ? 4 9 Solution: Answer: friends.
4. When Katya made friends with 4 classmates, she became 9friends. How many friends did Katya have at first? Drawing: ? 4 9 Solution: Answer: friends.  The simulator helps develop this skill and lay a solid foundation for the successful study of mathematics in the future. Grade 1 Grade 2■ Digit composition of numbers up to 10; ■ Digit composition of numbers up to 100; ■ Addition and subtraction of numbers within 10; ■ Addition and subtraction within 100; ■ Comparison of numbers within 10; ■ Comparing numbers within 100; ✔ Tasks for adding and subtracting numbers ■ Performing actions with values; ■ Tasks for actions with numbers within 100. within 20. Grade 4 Grade 3■ Addition and subtraction within 1000; ■ Numeric expressions and simple equations; ■ Multiplication and division within 1000; ■ Units of measure for mass, length, time; ■ Performing actions with quantities; ■ Tasks for determining speed, time ■ Tasks for addition, subtraction, multiplication and distance; and division; ■ Tasks to determine the perimeter and area.■ Tasks to find the fraction of a number. ISBN 978-985-565-556-6 pshop.by
The simulator helps develop this skill and lay a solid foundation for the successful study of mathematics in the future. Grade 1 Grade 2■ Digit composition of numbers up to 10; ■ Digit composition of numbers up to 100; ■ Addition and subtraction of numbers within 10; ■ Addition and subtraction within 100; ■ Comparison of numbers within 10; ■ Comparing numbers within 100; ✔ Tasks for adding and subtracting numbers ■ Performing actions with values; ■ Tasks for actions with numbers within 100. within 20. Grade 4 Grade 3■ Addition and subtraction within 1000; ■ Numeric expressions and simple equations; ■ Multiplication and division within 1000; ■ Units of measure for mass, length, time; ■ Performing actions with quantities; ■ Tasks for determining speed, time ■ Tasks for addition, subtraction, multiplication and distance; and division; ■ Tasks to determine the perimeter and area.■ Tasks to find the fraction of a number. ISBN 978-985-565-556-6 pshop.by 
 Addition is considered as the union of sets that do not have common elements. Subtraction is like removing part of a set. Addition is associated with an increase in the number of elements of a given set; subtraction — with a decrease in the number of elements of a given set.
Addition is considered as the union of sets that do not have common elements. Subtraction is like removing part of a set. Addition is associated with an increase in the number of elements of a given set; subtraction — with a decrease in the number of elements of a given set. 
 By repeatedly performing operations on sets, children understand that the operation of combining corresponds to the action of addition, and the operation of removing part of the set corresponds to the action of subtraction. Children’s attention is also drawn to the fact that when they add, it becomes more than it was; when subtracted, it becomes smaller.
By repeatedly performing operations on sets, children understand that the operation of combining corresponds to the action of addition, and the operation of removing part of the set corresponds to the action of subtraction. Children’s attention is also drawn to the fact that when they add, it becomes more than it was; when subtracted, it becomes smaller. 
 Show how to attach 2 bouquets to those 4 (the student transfers the flowers to the window: first one bouquet, then the second). Let’s write down what Vova did. How much did you add to 4 first? How much did it turn out? How can you add 2 to 4? To add 2 to 4, you must first add 1 to 4, you get 5, and then add 1 to 5, you get 6.
Show how to attach 2 bouquets to those 4 (the student transfers the flowers to the window: first one bouquet, then the second). Let’s write down what Vova did. How much did you add to 4 first? How much did it turn out? How can you add 2 to 4? To add 2 to 4, you must first add 1 to 4, you get 5, and then add 1 to 5, you get 6. 


 The children themselves can explain why only these cases are included and why the others are not included.
The children themselves can explain why only these cases are included and why the others are not included. 

 We will learn to compose problems according to pictures and solutions, explain and justify the action chosen to solve the problem. Let’s solve problems in one action to increase (decrease) the number by several units.
We will learn to compose problems according to pictures and solutions, explain and justify the action chosen to solve the problem. Let’s solve problems in one action to increase (decrease) the number by several units. 
 Addition and subtraction table with the number 2.
Addition and subtraction table with the number 2.  This table must be known by heart.
This table must be known by heart.  Remember how they are compiled and fill in the tables for addition and subtraction with the number 2.
Remember how they are compiled and fill in the tables for addition and subtraction with the number 2. 
 . How many cucumbers were on the plate?
. How many cucumbers were on the plate?  Mark with a sign which unit planted the most trees.
Mark with a sign which unit planted the most trees. 
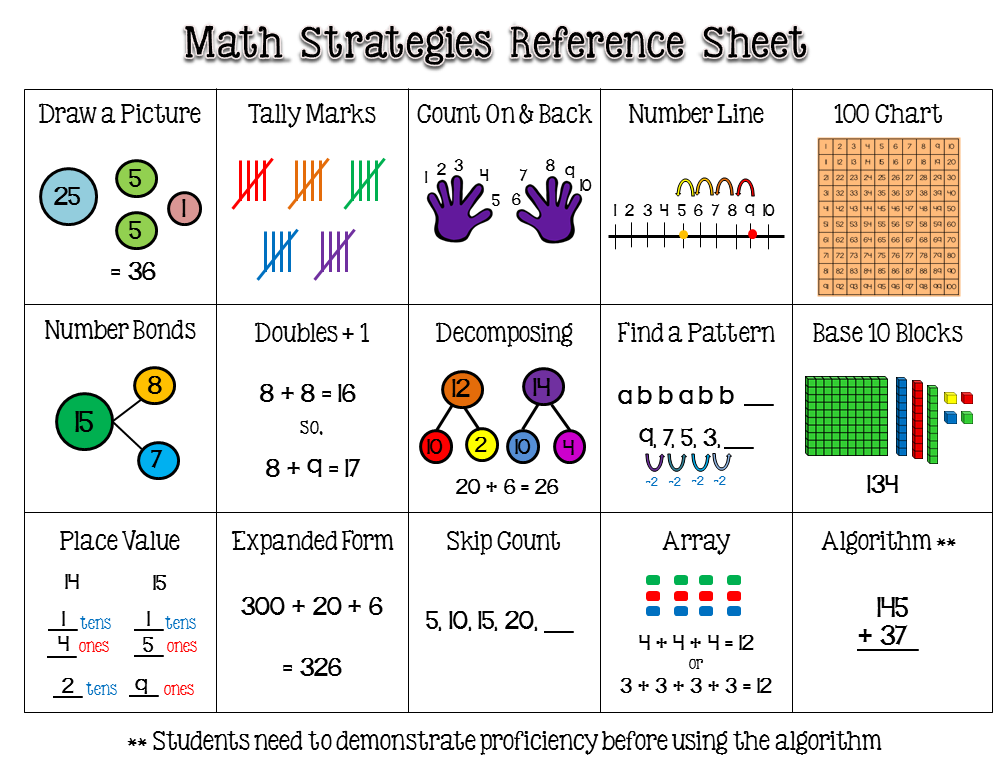 I wanted to open the door, but there was an inscription on the lock: Only the one who answers what the task consists of and solves the tasks will open.
I wanted to open the door, but there was an inscription on the lock: Only the one who answers what the task consists of and solves the tasks will open. 


 M. The purpose of the lesson: — creating conditions
M. The purpose of the lesson: — creating conditions  ”
”
 » A lesson in discovering new knowledge. Prepared by: Moiseeva E.R.
» A lesson in discovering new knowledge. Prepared by: Moiseeva E.R. 


 These include options for creating worksheets with large print and limiting the number of questions that can meet the varying needs of students. Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator (adding and/or subtracting zeros, ones and/or doubles) Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator (Cuisenaire Rod-like) Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator Addition and subtraction with 3 numbers (e.g. gram 5) + 6 + 3 = 14, 12 — 3 + 7 = 16) Regroup ten subtraction (includes base decimal block visuals) Regroup subtraction (with place value blocks) Custom addition worksheet generator Addition and subtraction tables Custom subtraction worksheet generator
These include options for creating worksheets with large print and limiting the number of questions that can meet the varying needs of students. Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator (adding and/or subtracting zeros, ones and/or doubles) Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator (Cuisenaire Rod-like) Addition/Subtraction Worksheet Generator Addition and subtraction with 3 numbers (e.g. gram 5) + 6 + 3 = 14, 12 — 3 + 7 = 16) Regroup ten subtraction (includes base decimal block visuals) Regroup subtraction (with place value blocks) Custom addition worksheet generator Addition and subtraction tables Custom subtraction worksheet generator  Examples: 3 + 4 = 7, 4 + 3 = 7, 7-3 = 4, 7-4 = 3
Examples: 3 + 4 = 7, 4 + 3 = 7, 7-3 = 4, 7-4 = 3 
 The player with the highest margin wins the round. All lows and responses are 10 or less.
The player with the highest margin wins the round. All lows and responses are 10 or less. 


 Complete the concatenation of the numbers that add to 10.
Complete the concatenation of the numbers that add to 10. 
 They must also show an understanding that the two columns are related. That is, when an object is removed from a set and placed in another set on the same row, one number decreases and another increases.
They must also show an understanding that the two columns are related. That is, when an object is removed from a set and placed in another set on the same row, one number decreases and another increases. 

 In addition, they should know how to add and subtract within 10 using objects or pictures to represent the problem.
In addition, they should know how to add and subtract within 10 using objects or pictures to represent the problem.  Part of the strawberry is crossed out to visualize the concept of subtraction.
Part of the strawberry is crossed out to visualize the concept of subtraction.  Give the children an erasable marker and have them write the numbers on the blanks to complete the subtraction equation.
Give the children an erasable marker and have them write the numbers on the blanks to complete the subtraction equation. 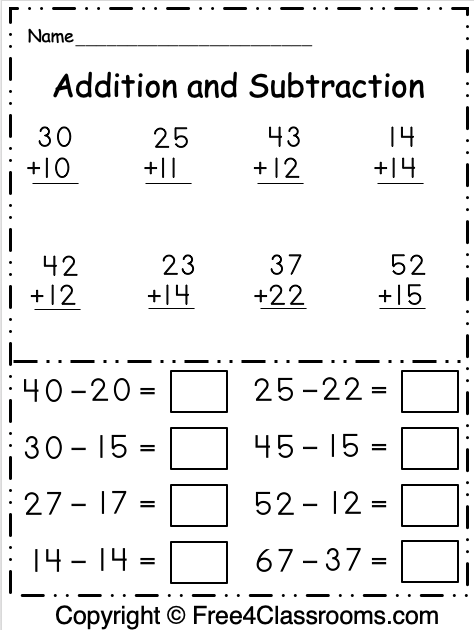

 up to 20 years with games, practical strategies and lots of practice helps students gain confidence and skills. Students then work on more complex mathematical calculations of addition and subtraction up to 100 using a variety of strategies, models, and reasoning.
up to 20 years with games, practical strategies and lots of practice helps students gain confidence and skills. Students then work on more complex mathematical calculations of addition and subtraction up to 100 using a variety of strategies, models, and reasoning.  Task — What students should be able to do by the end of the lesson.
Task — What students should be able to do by the end of the lesson. ..
..
 Solve the problem and find the corresponding amount or difference on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.
Solve the problem and find the corresponding amount or difference on the board. Write the equation on your note sheet.  Solve in your mind the problems that are in this row. Color the star every time you solve problems.
Solve in your mind the problems that are in this row. Color the star every time you solve problems.  The first person to get three in a row wins.
The first person to get three in a row wins. 
 Show off your work on the rug.
Show off your work on the rug.  Record your answer on the log.
Record your answer on the log.  Put them into boxes so that the equation is correct.
Put them into boxes so that the equation is correct. 